5 Unemployment Paper Tips

Understanding the Impact of Unemployment

Unemployment is a complex and multifaceted issue that affects individuals, communities, and economies as a whole. It is characterized by a state where individuals are able and willing to work but are unable to find employment. The impact of unemployment can be far-reaching, influencing not only the economic stability of a region but also the mental and physical well-being of those affected. In this context, understanding the causes, consequences, and potential solutions to unemployment is crucial for policymakers, researchers, and the general public.
Causes of Unemployment

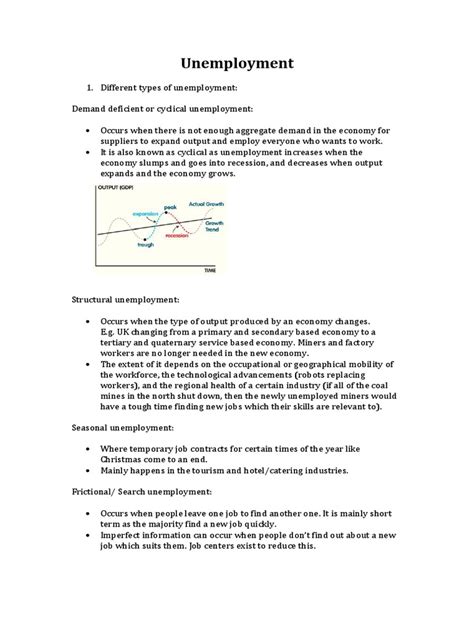
The causes of unemployment can be broadly categorized into several types, including frictional unemployment, structural unemployment, cyclical unemployment, and seasonal unemployment. - Frictional unemployment occurs due to the time it takes for workers to find new jobs, often resulting from a mismatch between the skills workers possess and the skills required by available jobs. - Structural unemployment arises from changes in the structure of the economy, such as technological advancements or shifts in industry, which can leave certain workers without the necessary skills to adapt. - Cyclical unemployment is directly related to the fluctuations in the economy, typically increasing during recessions and decreasing during economic expansions. - Seasonal unemployment is a result of the seasonal nature of certain industries, where employment opportunities are abundant during specific periods and scarce in others.
Consequences of Unemployment

The consequences of unemployment are multifaceted and can have profound effects on individuals and society. Some of the key consequences include: - Economic instability: Unemployment leads to reduced consumer spending, which can further exacerbate economic downturns. - Social impacts: Prolonged unemployment can lead to increased rates of poverty, crime, and social unrest. - Psychological effects: Individuals experiencing unemployment may face depression, anxiety, and a loss of self-esteem. - Skills depreciation: The longer individuals are unemployed, the more their skills can depreciate, making it harder to return to work.
Addressing Unemployment

To address unemployment, governments and organizations can implement a variety of strategies, including: - Education and Training Programs: Providing individuals with the skills needed to adapt to changing job markets. - Stimulus Packages: Injecting funds into the economy to boost job creation and economic growth. - Job Creation Initiatives: Implementing policies that encourage businesses to hire, such as tax incentives for new employees. - Support for Entrepreneurs: Encouraging entrepreneurship by providing resources and funding for start-ups.
Empowering the Workforce

Empowering the workforce is crucial in the fight against unemployment. This can be achieved through: - Continuous Learning: Encouraging workers to continually update their skills to remain competitive. - Diversification of Skills: Promoting the acquisition of a wide range of skills to increase adaptability in the job market. - Networking: Building professional networks to access job opportunities and advice. - Entrepreneurial Spirit: Fostering an environment where individuals feel encouraged to start their own businesses.
| Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Upskilling | Acquiring new skills to enhance employability. |
| Reskilling | Learning new skills to transition into different roles. |
| Lifelong Learning | Embracing a mindset of continuous learning and professional development. |

📝 Note: Implementing these strategies requires a collaborative effort from governments, educational institutions, and the private sector to ensure that the workforce is equipped with the skills necessary to thrive in a rapidly changing job market.
In wrapping up the discussion on unemployment, it’s clear that addressing this issue requires a multifaceted approach that includes understanding its causes, mitigating its consequences, and implementing effective strategies to empower the workforce. By fostering an environment that supports education, innovation, and job creation, we can work towards reducing unemployment rates and building a more resilient and adaptable workforce for the future. The journey to achieving full employment is ongoing, and its success hinges on the collective efforts of individuals, organizations, and governments to address the challenges posed by unemployment and to capitalize on the opportunities presented by a dynamic and evolving job market.
What are the main types of unemployment?
+
The main types of unemployment include frictional, structural, cyclical, and seasonal unemployment, each resulting from different factors such as job searching, economic structure, business cycles, and seasonal industries.
How does education impact unemployment?

+
Education plays a crucial role in reducing unemployment by providing individuals with the necessary skills to secure and maintain employment. It enhances employability, increases adaptability in the job market, and supports lifelong learning and professional development.
What can governments do to address unemployment?

+
Governments can address unemployment through various strategies, including implementing education and training programs, introducing stimulus packages to boost economic growth, creating job opportunities through incentives, and supporting entrepreneurship and small businesses.