Paperwork
Dangerous Goods PaperworkRetention Period

Introduction to Dangerous Goods Paperwork

When dealing with dangerous goods, also known as hazardous materials, it is crucial to understand the importance of proper documentation and paperwork. This includes understanding the retention period for such documents, which can vary depending on the type of goods, the mode of transport, and the regulations of the countries involved. In this article, we will delve into the world of dangerous goods paperwork, focusing on the retention period and its significance.
Understanding Dangerous Goods

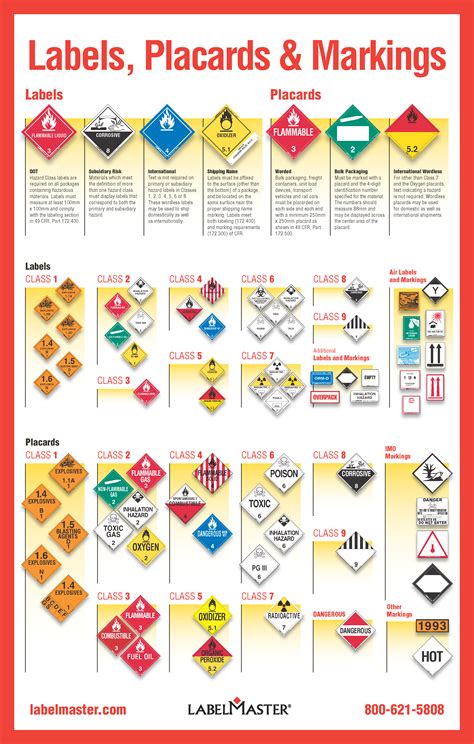
Dangerous goods are substances or materials that pose a risk to people, animals, and the environment due to their chemical or physical properties. Examples include explosives, gases, flammable liquids, toxic substances, and corrosives. The transportation of these goods is strictly regulated to ensure safety and prevent accidents. Key regulations include those set by the International Air Transport Association (IATA), the International Maritime Organization (IMO), and the European Agreement concerning the International Carriage of Dangerous Goods by Road (ADR).
Importance of Paperwork in Dangerous Goods Transport
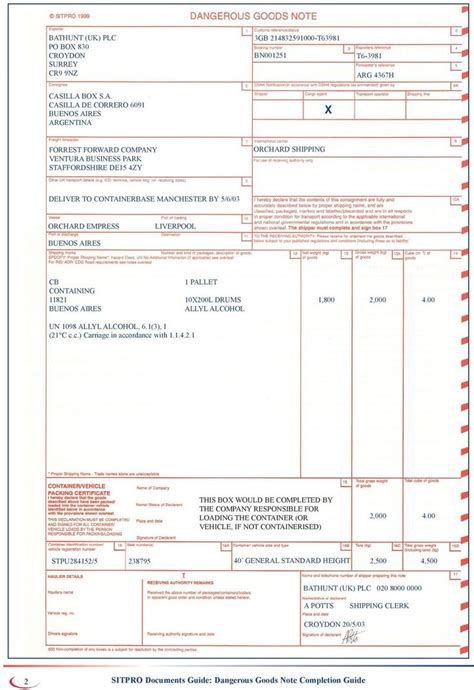
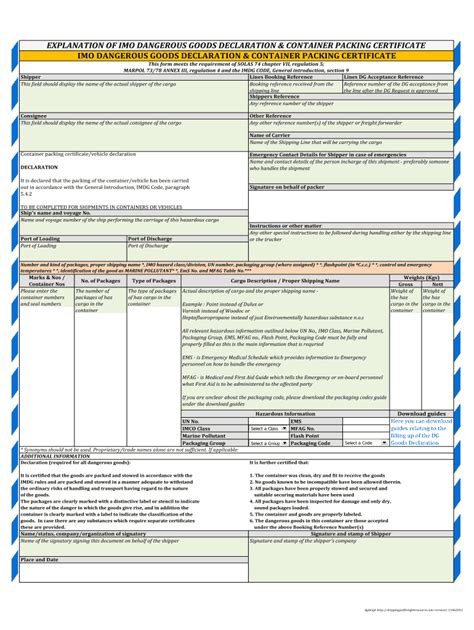
Proper paperwork is essential for the safe and legal transport of dangerous goods. This includes shipping documents, safety data sheets (SDS), and labels. The paperwork must accurately describe the goods, including their UN number, proper shipping name, class, and packaging group. It also needs to provide emergency contact information and instructions for handling and storage. The retention period for these documents varies, but they must be kept for a certain period to comply with regulations and in case of audits or incidents.
Retention Period for Dangerous Goods Paperwork

The retention period for dangerous goods paperwork can vary: - For air transport, IATA regulations suggest that records related to the transport of dangerous goods should be kept for at least 3 years from the date of transport. - For road transport, regulations such as ADR require that documents be retained for 3 years from the date of transport. - For sea transport, IMO regulations under the International Maritime Dangerous Goods (IMDG) Code require retention for 3 years from the date of transport.
Key Documents and Their Significance
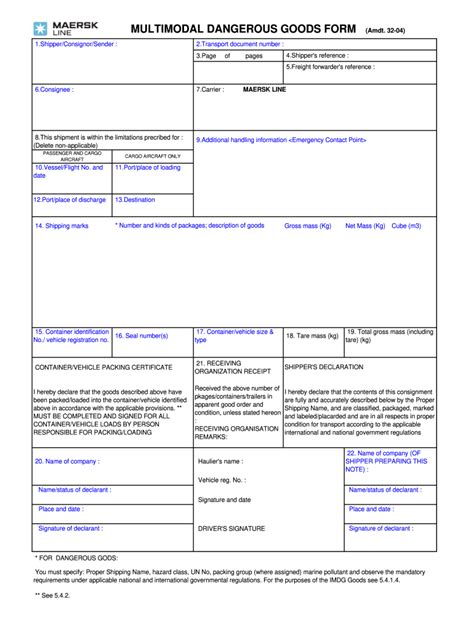
Several documents are crucial in the transport of dangerous goods: - Shippers Declaration for Dangerous Goods: This document is prepared by the shipper and includes detailed information about the dangerous goods being transported. - Safety Data Sheets (SDS): These provide information on the safe handling, use, storage, and disposal of dangerous goods. - Certificates of Approval for Packaging: These are required for packaging that has been specifically approved for use with dangerous goods.
Compliance and Audits
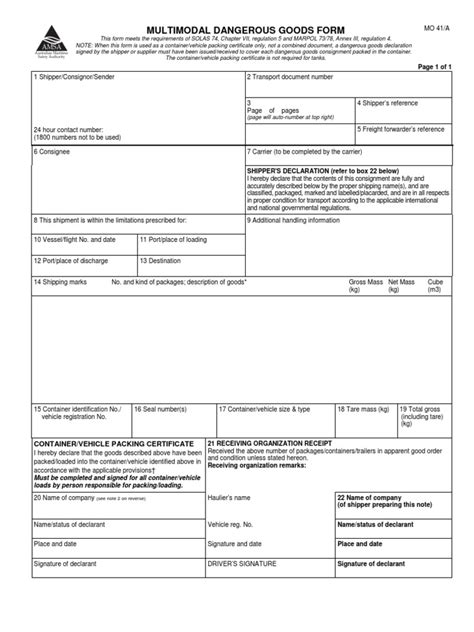
Compliance with regulations regarding the retention of dangerous goods paperwork is critical. Regular audits may be conducted by regulatory bodies to ensure that companies are adhering to these regulations. Failure to comply can result in penalties, fines, and damage to a company’s reputation. Therefore, it is essential for companies involved in the transport of dangerous goods to have a robust system in place for managing and retaining the necessary paperwork.
Best Practices for Managing Paperwork

To manage paperwork effectively, companies should: - Implement a digital document management system to ensure easy access and storage of documents. - Train staff on the importance of accurate and complete paperwork. - Regularly review and update paperwork to ensure compliance with the latest regulations. - Ensure security and backup of documents to prevent loss.
📝 Note: Companies must stay updated with the latest regulations and amendments to ensure compliance and avoid any legal or safety issues.
Future of Dangerous Goods Paperwork

The future of managing dangerous goods paperwork looks towards digitalization and automation. Electronic data interchange (EDI) and blockchain technology are being explored for their potential to enhance security, transparency, and efficiency in the documentation process. This shift is expected to reduce errors, improve compliance, and make the transport of dangerous goods safer.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the retention period for dangerous goods paperwork is a critical aspect of ensuring compliance with regulations and maintaining safety during transport. Understanding the specific requirements for different modes of transport and the types of goods being transported is essential. By implementing best practices for managing paperwork and staying abreast of regulatory changes, companies can minimize risks and contribute to a safer and more compliant industry.
What is the primary purpose of retaining dangerous goods paperwork?
+
The primary purpose is to ensure compliance with regulations and to provide a record of transport in case of audits or incidents, thereby enhancing safety and accountability.
How long should records related to the transport of dangerous goods by air be kept?

+
According to IATA regulations, records should be kept for at least 3 years from the date of transport.
What are the consequences of not complying with dangerous goods paperwork regulations?

+
Consequences can include penalties, fines, and damage to a company’s reputation, emphasizing the importance of compliance.