After Death Paperwork Retention Period

Introduction to After Death Paperwork

When a loved one passes away, it can be a difficult and emotional time for family and friends. In addition to coping with grief, there are also various administrative tasks that need to be taken care of, including dealing with the deceased person’s paperwork and estate. One of the important aspects of this process is understanding the retention period for after death paperwork. In this article, we will explore the different types of paperwork that need to be retained, the recommended retention periods, and the reasons why it’s essential to keep these documents.
Types of After Death Paperwork

There are several types of paperwork that need to be retained after a person’s death, including: * Will and testament: The deceased person’s last will and testament, which outlines their wishes for the distribution of their estate. * Probate documents: Documents related to the probate process, such as the petition for probate, inventory of assets, and notices to creditors. * Tax returns: The deceased person’s tax returns for the year of their death, as well as any prior years that may be relevant. * Bank and financial statements: Statements from the deceased person’s bank and financial accounts, which can help identify assets and liabilities. * Insurance policies: Life insurance policies, as well as any other insurance policies that may be relevant to the estate. * Real estate documents: Deeds, titles, and other documents related to the deceased person’s real estate holdings.
Retention Periods for After Death Paperwork
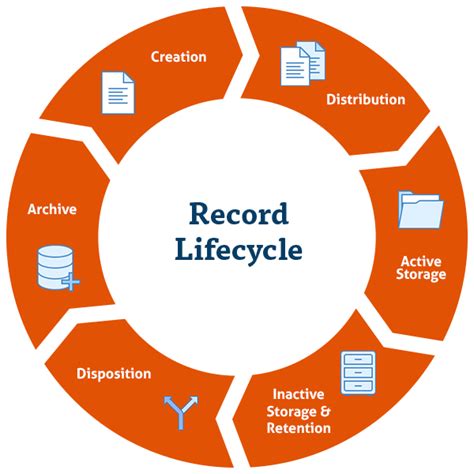
The retention period for after death paperwork varies depending on the type of document and the relevant laws and regulations. Here are some general guidelines: * Will and testament: The original will should be retained indefinitely, as it is a critical document that outlines the deceased person’s wishes for their estate. * Probate documents: Probate documents should be retained for at least 7-10 years after the probate process is complete, in case of any disputes or audits. * Tax returns: Tax returns should be retained for at least 3-7 years after the tax year in question, in case of any audits or disputes with the tax authorities. * Bank and financial statements: Bank and financial statements should be retained for at least 1-3 years after the account is closed, in case of any disputes or errors. * Insurance policies: Insurance policies should be retained for at least 3-5 years after the policy is paid out or cancelled, in case of any disputes or audits. * Real estate documents: Real estate documents should be retained for at least 10-20 years after the property is sold or transferred, in case of any disputes or audits.
Reasons for Retaining After Death Paperwork

Retaining after death paperwork is essential for several reasons, including: * Avoiding disputes: Retaining paperwork can help avoid disputes between beneficiaries, heirs, and other parties involved in the estate. * Ensuring compliance with laws and regulations: Retaining paperwork can help ensure compliance with relevant laws and regulations, such as tax laws and probate laws. * Identifying assets and liabilities: Retaining paperwork can help identify assets and liabilities, which is essential for distributing the estate and paying off debts. * Providing evidence: Retaining paperwork can provide evidence in case of any disputes or audits, which can help resolve issues quickly and efficiently.
Best Practices for Retaining After Death Paperwork

Here are some best practices for retaining after death paperwork: * Store documents securely: Store documents in a secure location, such as a safe or a locked cabinet, to protect them from damage or loss. * Make digital copies: Make digital copies of important documents, such as the will and tax returns, to ensure they are easily accessible and can be shared with relevant parties. * Organize documents: Organize documents in a logical and consistent manner, using folders and labels to make them easy to find and access. * Review and update documents regularly: Review and update documents regularly to ensure they are accurate and up-to-date.
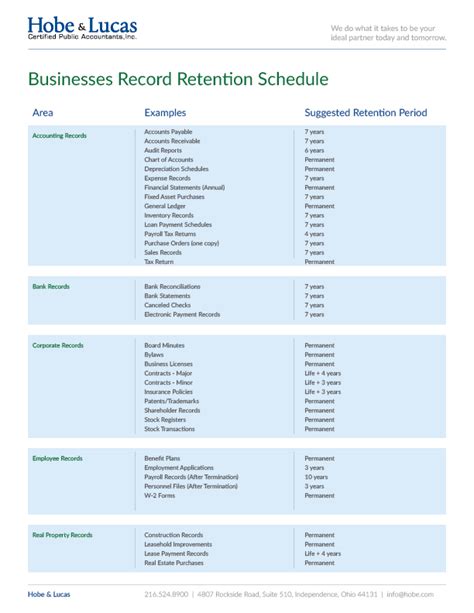
| Document Type | Retention Period |
|---|---|
| Will and testament | Indefinitely |
| Probate documents | 7-10 years |
| Tax returns | 3-7 years |
| Bank and financial statements | 1-3 years |
| Insurance policies | 3-5 years |
| Real estate documents | 10-20 years |
📝 Note: The retention periods listed above are general guidelines and may vary depending on the specific laws and regulations in your jurisdiction.
In summary, retaining after death paperwork is an essential part of the estate administration process. By understanding the different types of paperwork that need to be retained, the recommended retention periods, and the reasons why it’s essential to keep these documents, you can ensure that the estate is distributed according to the deceased person’s wishes and that all relevant parties are protected. It’s also important to follow best practices for retaining after death paperwork, such as storing documents securely, making digital copies, organizing documents, and reviewing and updating them regularly.
What is the purpose of retaining after death paperwork?
+
The purpose of retaining after death paperwork is to ensure that the estate is distributed according to the deceased person’s wishes, to avoid disputes between beneficiaries and heirs, and to comply with relevant laws and regulations.
How long should I retain after death paperwork?

+
The retention period for after death paperwork varies depending on the type of document and the relevant laws and regulations. Generally, it’s recommended to retain documents for at least 3-7 years after the tax year in question, and up to 10-20 years for real estate documents.
What are some best practices for retaining after death paperwork?
+
Some best practices for retaining after death paperwork include storing documents securely, making digital copies, organizing documents, and reviewing and updating them regularly.



