Paperwork
7 Healthcare Costs
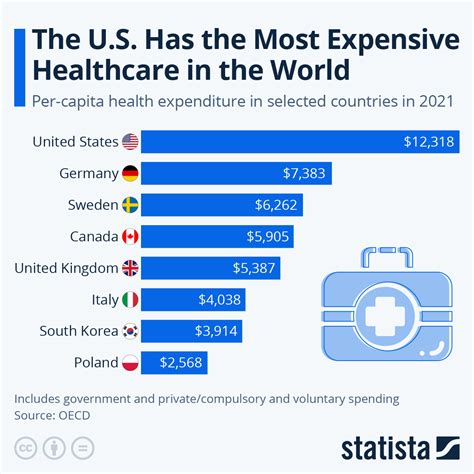
Introduction to Healthcare Costs
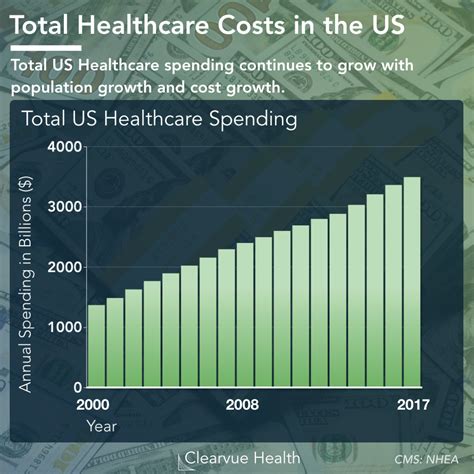
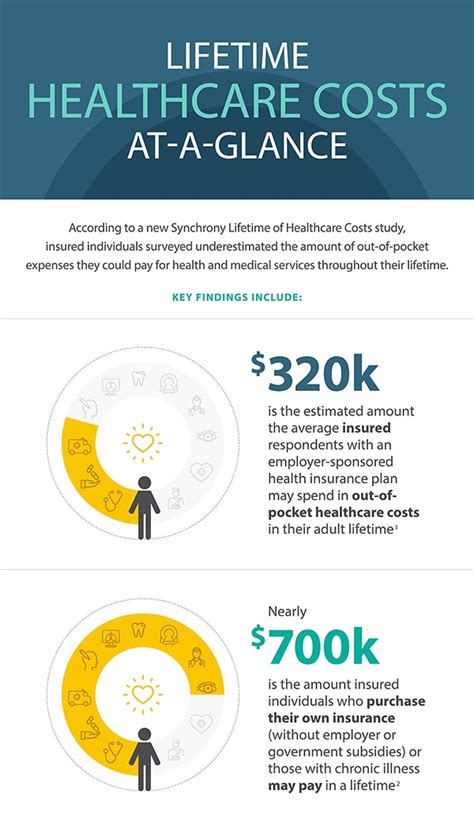
The cost of healthcare is a significant concern for individuals, families, and governments worldwide. Rising healthcare costs can lead to financial burdens, reduced access to necessary medical care, and decreased overall well-being. In this blog post, we will delve into the world of healthcare costs, exploring the factors that contribute to these expenses, the impact on individuals and society, and potential solutions to mitigate these costs.
Factors Contributing to Healthcare Costs
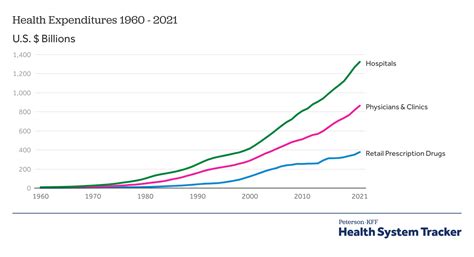
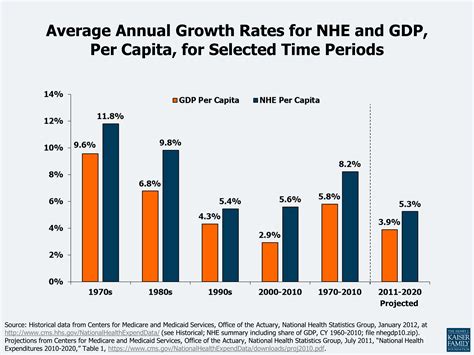
Several factors contribute to the increasing healthcare costs. Some of the key factors include: * Aging population: As people live longer, they require more medical care, leading to increased costs. * Advances in medical technology: New treatments, medications, and equipment can be expensive, driving up costs. * Chronic diseases: Conditions like diabetes, heart disease, and obesity require ongoing care, leading to higher costs. * Administrative costs: The cost of administering healthcare systems, including paperwork, billing, and insurance claims, can be substantial.
The Impact of Healthcare Costs
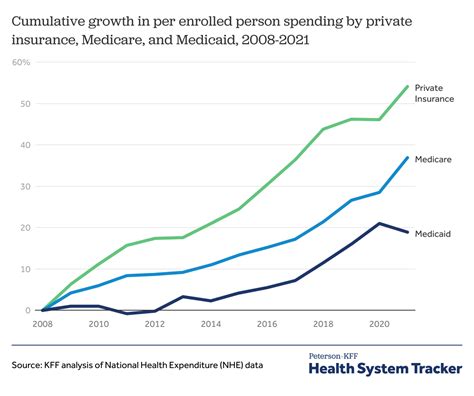
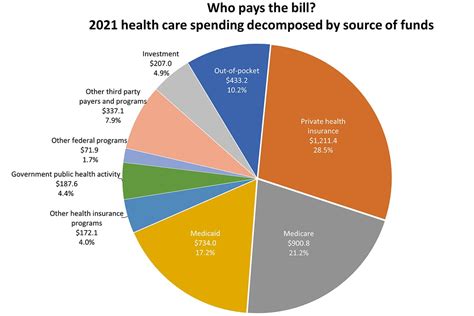
The impact of healthcare costs can be far-reaching, affecting not only individuals but also families, communities, and the broader economy. Some of the consequences of high healthcare costs include: * Financial burdens: Medical expenses can lead to debt, bankruptcy, and reduced financial security. * Reduced access to care: High costs can prevent people from seeking necessary medical care, leading to poorer health outcomes. * Increased stress and anxiety: The financial burden of healthcare costs can cause significant stress and anxiety.
Strategies to Reduce Healthcare Costs

To mitigate the rising healthcare costs, several strategies can be employed. These include: * Preventive care: Encouraging preventive measures, such as regular check-ups, screenings, and vaccinations, can help reduce the need for costly medical interventions. * Healthy lifestyle choices: Promoting healthy habits, such as a balanced diet, regular exercise, and not smoking, can help prevent chronic diseases. * Cost-effective treatments: Identifying and implementing cost-effective treatments can help reduce healthcare costs. * Improved healthcare infrastructure: Investing in efficient healthcare systems, including electronic health records and streamlined administrative processes, can help reduce costs.
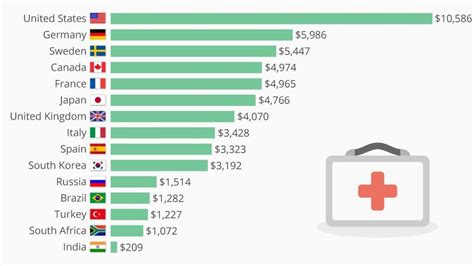
Healthcare Cost Comparison
A comparison of healthcare costs across different countries can provide insight into the factors contributing to these expenses. The following table highlights the average healthcare costs per person in several countries:
| Country | Average Healthcare Cost per Person |
|---|---|
| United States | 11,072</td> </tr> <tr> <td>Canada</td> <td>5,412 |
| United Kingdom | 4,333</td> </tr> <tr> <td>Australia</td> <td>4,193 |
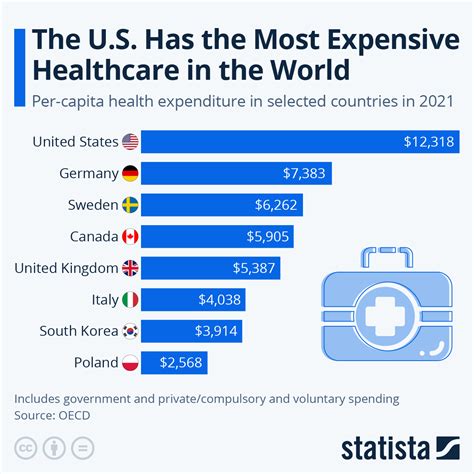
💡 Note: The costs listed are approximate and based on available data from 2020.
Conclusion and Future Directions
In conclusion, the cost of healthcare is a complex issue, influenced by various factors, including demographic changes, advances in medical technology, and administrative costs. To address these costs, it is essential to implement strategies that promote preventive care, healthy lifestyle choices, and cost-effective treatments. By working together, individuals, healthcare providers, and governments can help reduce the financial burden of healthcare costs and improve overall well-being.
What are the main factors contributing to healthcare costs?
+
The main factors contributing to healthcare costs include an aging population, advances in medical technology, chronic diseases, and administrative costs.
How can individuals reduce their healthcare costs?
+
Individuals can reduce their healthcare costs by adopting healthy lifestyle choices, such as a balanced diet, regular exercise, and not smoking, and by taking advantage of preventive care services.
What role can governments play in reducing healthcare costs?
+
Governments can play a crucial role in reducing healthcare costs by implementing policies that promote cost-effective treatments, improving healthcare infrastructure, and increasing access to preventive care services.



