Read Medical Results Paperwork Easily

Understanding Medical Jargon

When it comes to reading medical results paperwork, it can be overwhelming due to the complex medical terminology used. Deciphering these terms is crucial to comprehend the diagnosis, treatment, and other essential details. To start, familiarize yourself with common medical abbreviations and acronyms. For instance, BP stands for blood pressure, HR for heart rate, and WBC for white blood cell count. Knowing these abbreviations will help you navigate through the paperwork more efficiently.
Breaking Down the Components

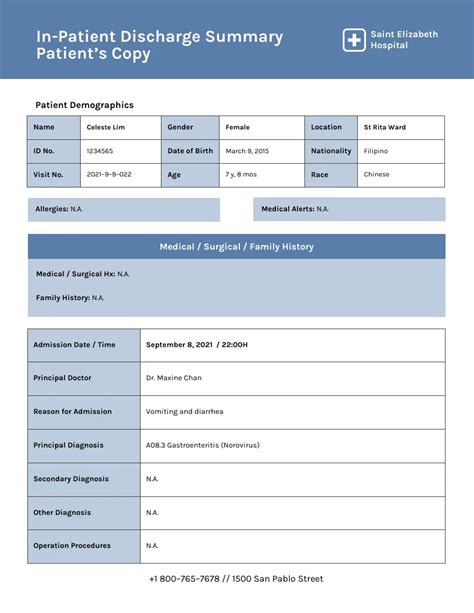
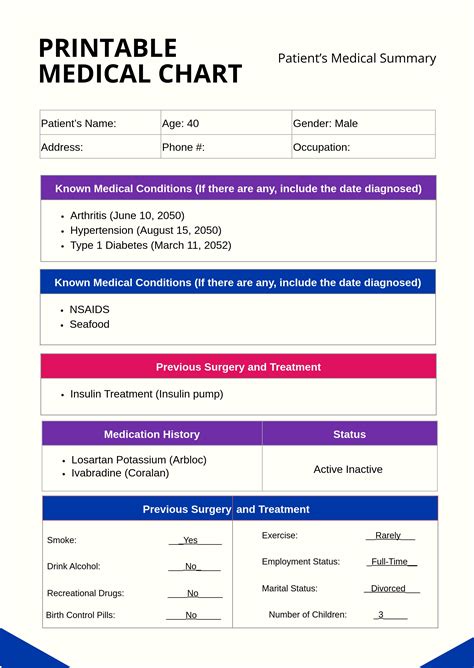
Medical results paperwork typically consists of several sections, each containing vital information. The key components include: * Patient Information: This section contains personal details such as name, date of birth, and contact information. * Medical History: A summary of the patient’s medical history, including previous illnesses, surgeries, and allergies. * Test Results: This section presents the results of various medical tests, such as blood work, imaging studies, or biopsies. * Diagnosis: The healthcare provider’s diagnosis based on the test results and medical history. * Treatment Plan: Outlines the recommended course of treatment, including medications, therapies, or lifestyle changes.
Interpreting Test Results

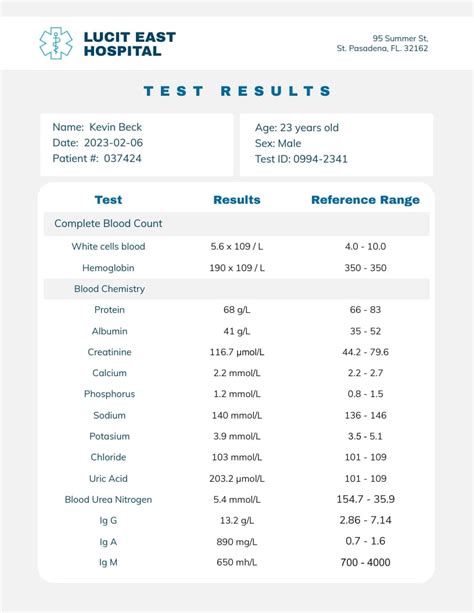
Interpreting test results can be challenging, especially for those without a medical background. It’s essential to understand the reference ranges for each test, as these indicate the normal values for a particular parameter. For example, a complete blood count (CBC) test measures various components of the blood, including red and white blood cell counts, hemoglobin, and platelets. The reference ranges for these parameters vary depending on age, sex, and other factors. If a result falls outside the reference range, it may indicate an underlying condition that requires further investigation.
Common Medical Tests

Some common medical tests include: * Complete Blood Count (CBC): Measures various components of the blood, including red and white blood cell counts, hemoglobin, and platelets. * Basic Metabolic Panel (BMP): Evaluates kidney function, electrolyte levels, and blood sugar control. * Lipid Profile: Assesses cholesterol and triglyceride levels to evaluate cardiovascular risk. * Liver Function Tests (LFTs): Measures liver enzymes and proteins to assess liver health. * Imaging Studies: Includes X-rays, computed tomography (CT) scans, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans, and ultrasounds to visualize internal structures and diagnose conditions.
| Test | Reference Range | Indication |
|---|---|---|
| CBC | Varies depending on age and sex | Evaluates blood cell counts and detects anemia, infection, or bleeding disorders |
| BMP | Varies depending on age and sex | Assesses kidney function, electrolyte levels, and blood sugar control |
| Lipid Profile | Cholesterol: < 200 mg/dL, Triglycerides: < 150 mg/dL | Evaluates cardiovascular risk and detects lipid disorders |

💡 Note: It's essential to consult with a healthcare provider to understand the results and their implications, as reference ranges may vary depending on individual factors and laboratory standards.
Tips for Reading Medical Results Paperwork
To read medical results paperwork effectively, follow these tips: * Start with the summary: Many medical reports include a summary or overview of the results. This section provides a concise description of the findings and diagnosis. * Focus on abnormal results: Identify results that fall outside the reference range, as these may indicate an underlying condition. * Look for trends: Analyze the results over time to detect any changes or trends that may indicate a developing condition. * Ask questions: If you’re unsure about any aspect of the results, don’t hesitate to ask your healthcare provider for clarification.
Staying Organized

Keeping track of medical results paperwork can be overwhelming, especially if you have multiple tests or appointments. To stay organized, consider the following strategies: * Keep a medical journal: Record your test results, medications, and appointments in a dedicated journal or digital tool. * Use a file system: Store your medical records in a secure and easily accessible location, such as a file cabinet or digital storage service. * Set reminders: Schedule reminders for upcoming appointments, tests, or medication refills to ensure you stay on track.
As we conclude this discussion on reading medical results paperwork, it’s clear that understanding medical terminology, interpreting test results, and staying organized are crucial to navigating the complex world of medical documentation. By following these tips and strategies, you’ll be better equipped to manage your health and make informed decisions about your care.
What is the purpose of a complete blood count (CBC) test?
+
A CBC test measures various components of the blood, including red and white blood cell counts, hemoglobin, and platelets, to evaluate overall health and detect potential conditions such as anemia, infection, or bleeding disorders.
How do I understand the reference ranges for medical tests?

+
Reference ranges indicate the normal values for a particular parameter, and these ranges may vary depending on age, sex, and other factors. It’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider to understand the results and their implications, as reference ranges may vary depending on individual factors and laboratory standards.
What is the importance of keeping a medical journal?
+
Keeping a medical journal helps you stay organized and track your test results, medications, and appointments. This information is valuable for making informed decisions about your care and communicating with your healthcare provider.