Paperwork
Decoding Mortgage Paperwork
Introduction to Mortgage Paperwork

When navigating the complex world of real estate, understanding mortgage paperwork is crucial for a smooth and successful transaction. The plethora of documents involved can be overwhelming, especially for first-time homebuyers. Mortgage paperwork encompasses a wide range of documents, each serving a specific purpose in the home buying process. From the initial application to the final closing, every document plays a vital role in securing a mortgage and ensuring that the transaction is legally binding and transparent.
Pre-Approval and Pre-Qualification

The journey begins with pre-qualification and pre-approval. These initial steps are often confused with one another, but they serve distinct purposes. Pre-qualification is an informal estimate of how much a lender might be willing to lend based on a brief overview of the borrower’s financial situation. On the other hand, pre-approval involves a more thorough review of the borrower’s credit report and financial documents, resulting in a more accurate estimate of the loan amount. This step is crucial as it not only gives the borrower an idea of their budget but also strengthens their position when making an offer on a property.
Understanding Key Documents

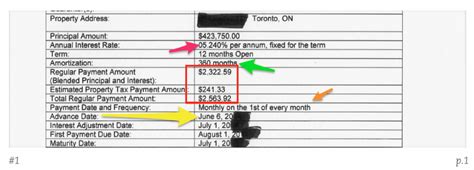
Several key documents are involved in the mortgage process, each with its own significance: - Loan Estimate (LE): Provided within three business days of applying for a mortgage, this document outlines the terms of the loan, including the interest rate, monthly payments, and closing costs. - Closing Disclosure (CD): Given at least three business days before closing, the CD provides a detailed breakdown of the transaction, including all costs and terms of the loan. - Promissory Note: This is the borrower’s promise to repay the loan, including the amount borrowed, interest rate, repayment terms, and the consequences of default. - Mortgage or Deed of Trust: This document secures the loan by giving the lender a claim against the property if the borrower fails to repay the loan. - Title Report and Insurance: These documents ensure that the seller has the right to sell the property and protects the buyer and lender from any defects in the title.
The Application and Processing Stage

The application and processing stage involves submitting a formal application and providing extensive financial documentation. This includes:
- Identification documents
- Income verification (pay stubs, W-2 forms, tax returns)
- Asset verification (bank statements, investment accounts)
- Credit reports
- Employment verification
Appraisal and Inspection

An appraisal is conducted to determine the value of the property, ensuring that it serves as sufficient collateral for the loan. This process is crucial for the lender, as it protects them against lending more than the property is worth. Additionally, borrowers often opt for a home inspection to identify any potential issues with the property, which can be used as a bargaining chip or to negotiate repairs.
Closing the Deal

The final step in the mortgage process is closing, where the buyer signs the loan documents, transfers the ownership of the property, and the lender disburses the funds. It’s essential for buyers to carefully review all documents before signing, ensuring they understand their obligations and the terms of the loan.
📝 Note: It's advisable for borrowers to seek legal advice if they are unsure about any aspect of the mortgage paperwork.
Post-Closing Procedures

After closing, the lender will record the mortgage or deed of trust with the local government, making it a public record. The borrower will then begin making mortgage payments, which typically include principal, interest, taxes, and insurance (PITI). Understanding the breakdown of these payments and how they apply to the loan is vital for managing the borrower’s financial obligations.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Principal | The amount borrowed |
| Interest | The cost of borrowing, calculated as a percentage of the principal |
| Taxes | Property taxes, which vary by location |
| Insurance | Homeowners insurance, which protects against loss or damage |

Conclusion Summary

Navigating the complex landscape of mortgage paperwork requires patience, diligence, and a thorough understanding of the process. From pre-approval to post-closing procedures, each step is designed to ensure a transparent and legally binding transaction. By grasping the significance of each document and stage, borrowers can better manage their expectations and obligations, ultimately securing a mortgage that aligns with their financial capabilities and goals.
What is the difference between pre-qualification and pre-approval?

+
Pre-qualification is an informal estimate of how much a lender might be willing to lend, while pre-approval involves a more thorough review of the borrower’s credit report and financial documents, resulting in a more accurate estimate of the loan amount.
Why is credit score important in the mortgage application process?

+
Credit score reflects the borrower’s history of managing debt and is used by lenders to assess the borrower’s creditworthiness and ability to repay the loan.
What is the purpose of an appraisal in the mortgage process?
+
The appraisal determines the value of the property, ensuring that it serves as sufficient collateral for the loan and protecting the lender against lending more than the property is worth.