Arkansas Medical Consent Law

Understanding Arkansas Medical Consent Law

The Arkansas medical consent law is designed to protect the rights of patients and ensure that they receive the best possible care. Informed consent is a crucial aspect of this law, requiring healthcare providers to obtain explicit permission from patients before performing any medical procedure or treatment. This law applies to all healthcare providers in Arkansas, including doctors, nurses, and hospitals.
Key Provisions of the Law

The Arkansas medical consent law outlines the following key provisions: * Informed consent: Patients must be fully informed about their medical condition, treatment options, and potential risks and benefits before giving their consent. * Capacity to consent: Patients must have the mental capacity to understand the information provided and make informed decisions about their care. * Voluntary consent: Patients must give their consent voluntarily, without coercion or undue influence. * Documentation: Healthcare providers must document the patient’s consent in their medical record.
Types of Consent
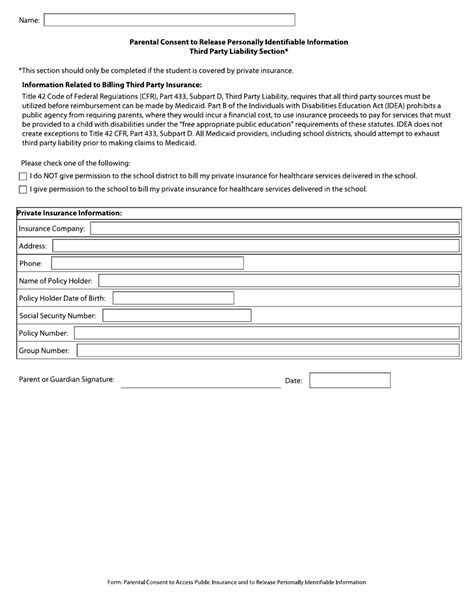
There are several types of consent recognized under the Arkansas medical consent law, including: * Express consent: Patients give explicit permission for a specific treatment or procedure. * Implied consent: Patients imply their consent through their actions or behavior, such as showing up for a scheduled appointment. * Informed refusal: Patients have the right to refuse treatment or care, and their decision must be respected.
Exceptions to the Law

There are certain exceptions to the Arkansas medical consent law, including: * Emergency situations: Healthcare providers may provide treatment without consent in emergency situations where the patient’s life is at risk. * Incompetent patients: Healthcare providers may make decisions on behalf of patients who are deemed incompetent or unable to make informed decisions. * Minor patients: Parents or guardians may give consent on behalf of minor patients.
Penalties for Non-Compliance

Healthcare providers who fail to obtain informed consent or violate the Arkansas medical consent law may face penalties, including: * Civil liability: Patients may sue healthcare providers for damages resulting from unauthorized treatment. * Professional discipline: Healthcare providers may face disciplinary action, including loss of licensure or certification. * Criminal charges: In severe cases, healthcare providers may face criminal charges for violating the law.
📝 Note: Healthcare providers must stay up-to-date with the latest developments in Arkansas medical consent law to ensure compliance and avoid penalties.
Best Practices for Healthcare Providers

To ensure compliance with the Arkansas medical consent law, healthcare providers should follow these best practices: * Clearly communicate with patients: Provide patients with accurate and understandable information about their medical condition and treatment options. * Document consent: Ensure that patients’ consent is properly documented in their medical record. * Respect patient autonomy: Respect patients’ decisions and right to refuse treatment or care. * Stay up-to-date with the law: Regularly review and update policies and procedures to ensure compliance with the latest developments in Arkansas medical consent law.
| Healthcare Provider | Consent Requirement |
|---|---|
| Doctors | Must obtain informed consent before performing any medical procedure or treatment |
| Nurses | Must obtain informed consent before administering any medication or treatment |
| Hospitals | Must have policies and procedures in place to ensure informed consent is obtained from patients |

As the Arkansas medical consent law continues to evolve, it is essential for healthcare providers to stay informed and adapt their practices to ensure compliance and provide the best possible care for their patients. By understanding the key provisions, types of consent, exceptions, and penalties for non-compliance, healthcare providers can navigate the complexities of the law and prioritize patient-centered care.
In summary, the Arkansas medical consent law is designed to protect patients’ rights and ensure that they receive informed and respectful care. By following best practices and staying up-to-date with the latest developments in the law, healthcare providers can provide high-quality care while minimizing the risk of non-compliance and penalties. Ultimately, the goal of the law is to promote patient autonomy, dignity, and well-being, and healthcare providers must prioritize these values in their daily practice.
What is informed consent in Arkansas medical consent law?

+
Informed consent requires healthcare providers to obtain explicit permission from patients before performing any medical procedure or treatment, after providing them with accurate and understandable information about their medical condition and treatment options.
What are the exceptions to the Arkansas medical consent law?

+
Exceptions to the law include emergency situations, incompetent patients, and minor patients. In these situations, healthcare providers may provide treatment without consent or make decisions on behalf of the patient.
What are the penalties for non-compliance with the Arkansas medical consent law?
+
Penalties for non-compliance may include civil liability, professional discipline, and criminal charges. Healthcare providers who fail to obtain informed consent or violate the law may face severe consequences, including loss of licensure or certification.



