5 MSDS Tips

Introduction to MSDS

When working with hazardous materials, it is essential to have access to critical information that can help prevent accidents and ensure a safe working environment. A Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) is a document that provides detailed information about a particular substance, including its properties, handling procedures, and emergency response measures. In this article, we will discuss five essential tips for working with MSDS, highlighting the importance of understanding and following the guidelines outlined in these documents.
Tip 1: Understanding MSDS Content
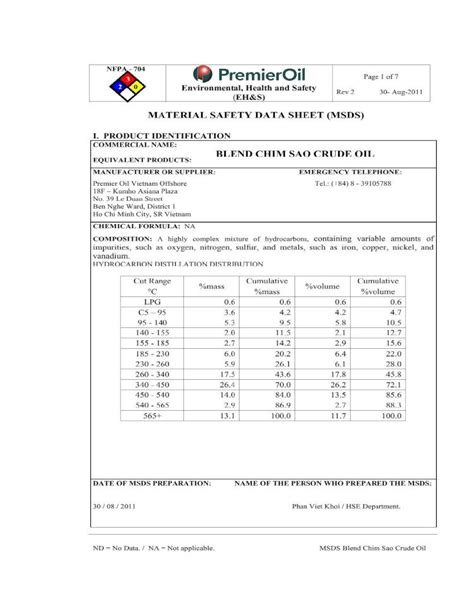
An MSDS typically includes information on the following: * Chemical identification: The name, synonyms, and chemical formula of the substance. * Hazards identification: Information on the potential health, fire, and environmental hazards associated with the substance. * Composition: The chemical composition of the substance, including the percentage of each component. * First aid measures: Procedures for treating exposure to the substance, including skin and eye contact, inhalation, and ingestion. * Fire-fighting measures: Information on how to extinguish fires involving the substance, including the type of extinguishing agent to use. * Accidental release measures: Procedures for responding to spills or leaks, including containment and cleanup methods. * Handling and storage: Guidelines for safe handling and storage of the substance, including recommended storage conditions and compatibility with other materials. * Exposure controls: Information on personal protective equipment (PPE) and engineering controls that can be used to minimize exposure to the substance. Understanding the content of an MSDS is crucial for ensuring a safe working environment and preventing accidents.
Tip 2: Accessing MSDS

It is essential to have easy access to MSDS for all hazardous materials used in the workplace. This can be achieved by: * Maintaining a library of MSDS for all hazardous substances used in the workplace. * Providing electronic access to MSDS through a company intranet or online database. * Ensuring that all employees have access to MSDS for the substances they work with. * Reviewing and updating MSDS regularly to ensure that the information is current and accurate. By providing easy access to MSDS, employers can ensure that employees have the information they need to work safely with hazardous materials.
Tip 3: Training Employees

Employers must provide training to employees on the safe handling and use of hazardous materials, including: * Initial training: Providing employees with training on the hazards associated with the substances they will be working with, as well as the procedures for safe handling and use. * Refresher training: Providing regular refresher training to ensure that employees remain aware of the hazards and safe handling procedures. * Specialized training: Providing specialized training for employees who work with particularly hazardous substances or who are responsible for responding to emergencies. By providing comprehensive training, employers can ensure that employees are equipped to work safely with hazardous materials.
Tip 4: Maintaining MSDS Records

Employers must maintain accurate and up-to-date records of MSDS, including: * MSDS documents: Maintaining a complete and accurate copy of the MSDS for each hazardous substance used in the workplace. * Employee training records: Maintaining records of employee training, including the date and content of training sessions. * Incident reports: Maintaining records of incidents involving hazardous substances, including the cause of the incident and any injuries or damage that occurred. By maintaining accurate and up-to-date records, employers can demonstrate compliance with regulatory requirements and ensure that they have the information they need to prevent future incidents.
Tip 5: Reviewing and Updating MSDS

MSDS must be reviewed and updated regularly to ensure that the information is current and accurate. This includes: * Reviewing MSDS for new substances: Reviewing the MSDS for new substances before they are introduced into the workplace. * Updating MSDS for existing substances: Updating the MSDS for existing substances whenever new information becomes available. * Revising procedures: Revising procedures for handling and using hazardous substances whenever the MSDS is updated. By regularly reviewing and updating MSDS, employers can ensure that employees have access to the most current and accurate information, which is essential for preventing accidents and ensuring a safe working environment.
💡 Note: Employers must ensure that they comply with all relevant regulations and standards when working with MSDS, including OSHA's Hazard Communication Standard (HCS) and the Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labeling of Chemicals (GHS).
In summary, working with MSDS requires a thorough understanding of the content, access, training, record-keeping, and review and update procedures. By following these five tips, employers can ensure a safe working environment and prevent accidents involving hazardous materials. The key to successful MSDS management is to stay informed, provide comprehensive training, and maintain accurate and up-to-date records. By doing so, employers can minimize the risks associated with hazardous materials and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements.
What is the purpose of an MSDS?
+
The purpose of an MSDS is to provide detailed information about a particular substance, including its properties, handling procedures, and emergency response measures, to help prevent accidents and ensure a safe working environment.
How often should MSDS be reviewed and updated?
+
MSDS should be reviewed and updated regularly, whenever new information becomes available, to ensure that the information is current and accurate.
What information is typically included in an MSDS?
+
An MSDS typically includes information on the chemical identification, hazards identification, composition, first aid measures, fire-fighting measures, accidental release measures, handling and storage, and exposure controls.



