Guardianship Paperwork Order

Understanding the Guardianship Process

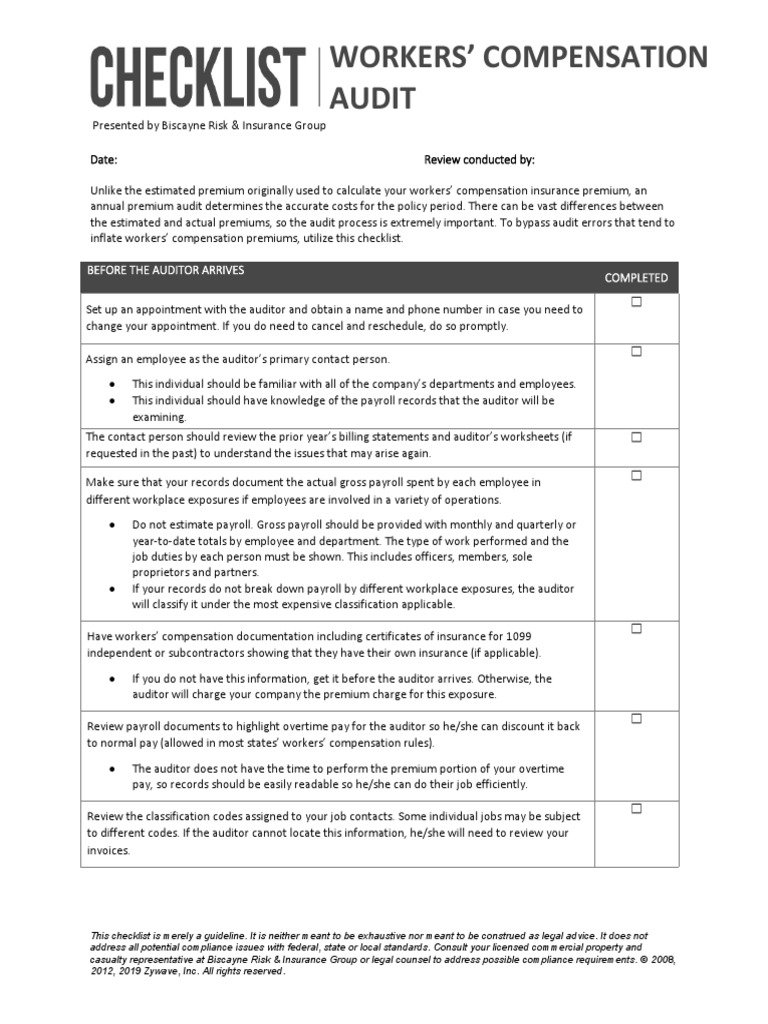
The process of establishing guardianship for a minor or an incapacitated adult involves several steps and requires the completion of specific guardianship paperwork. This process is designed to protect the well-being and interests of the individual under guardianship, ensuring they receive the care and support they need. The first step in this process is to determine the type of guardianship that is required, as this will influence the specific paperwork and legal procedures that must be followed.
Types of Guardianship
There are several types of guardianship, each serving different needs and circumstances. These include: - Full Guardianship: This type grants the guardian complete control over the ward’s financial, legal, and personal affairs. - Limited Guardianship: The court grants the guardian control over specific aspects of the ward’s life, while the ward retains some rights and autonomy. - Temporary Guardianship: This is a short-term arrangement, often put in place during an emergency or until a permanent guardian can be appointed. - Co-Guardianship: Two or more individuals are appointed to act as guardians, sharing the responsibilities and decision-making authority.
Guardianship Paperwork Requirements

The guardianship paperwork order typically involves the following documents and steps:
- Petition for Guardianship: The initial document filed with the court to request the appointment of a guardian. It outlines the reasons for the guardianship, the proposed guardian’s qualifications, and the best interests of the potential ward.
- Notice of Hearing: After the petition is filed, a hearing is scheduled, and all relevant parties must be notified. This includes the potential ward (if capable of understanding), their family members, and sometimes other interested parties.
- Guardianship Inventory: If the guardianship is granted, the guardian must prepare an inventory of the ward’s assets. This document is crucial for managing the ward’s financial affairs and is typically filed with the court within a specified timeframe after the guardianship is established.
- Annual Accountings: The guardian is usually required to submit annual reports to the court, detailing the management of the ward’s financial and personal affairs. This ensures the guardian is acting in the best interest of the ward.
The Role of the Court in Guardianship

The court plays a central role in the guardianship process, from the initial petition to the ongoing oversight of the guardianship arrangement. The court’s primary concern is the well-being and protection of the ward, and it will review the guardianship paperwork and circumstances to ensure this goal is met. This includes: - Reviewing the petition and supporting documents to determine if guardianship is necessary and in the best interest of the potential ward. - Conducting hearings to gather more information and assess the qualifications of the proposed guardian. - Monitoring the guardian’s actions through required reports and investigations, if necessary, to prevent abuse or neglect.
Challenges and Considerations

Establishing and maintaining a guardianship can be complex and emotionally challenging for all parties involved. It’s essential to consider the following: - Emotional Impact: The process can be stressful for the ward and their family members, especially if there are disagreements about the need for guardianship or the choice of guardian. - Legal Fees: The cost of legal representation and court fees can be significant, and these expenses are typically paid from the ward’s estate. - Ongoing Commitment: Guardianship is a long-term commitment that requires the guardian to be actively involved in the ward’s life, making decisions, and managing their affairs.
📝 Note: It's crucial to seek legal advice from an attorney experienced in guardianship law to navigate the process effectively and ensure compliance with all legal requirements.
Preparing for the Guardianship Process

To prepare for the guardianship process, individuals should: - Gather Necessary Documents: This includes birth certificates, identification, financial records, and any relevant medical or psychological evaluations. - Understand the Legal Process: Familiarize yourself with the steps involved in establishing guardianship, including the paperwork, hearings, and court decisions. - Choose the Right Guardian: If you are planning for your own potential incapacity, consider who would be the best guardian for you, based on their ability to manage your affairs and make decisions in your best interest.
| Document | Description |
|---|---|
| Petition for Guardianship | The initial request to the court for guardianship. |
| Notice of Hearing | Notification of the scheduled court hearing to all relevant parties. |
| Guardianship Inventory | A detailed list of the ward's assets, filed with the court after guardianship is granted. |
| Annual Accountings | Reports submitted by the guardian to the court, detailing the management of the ward's affairs. |

In summary, the process of establishing guardianship involves complex legal procedures, significant paperwork, and ongoing commitments. Understanding the types of guardianship, the role of the court, and the challenges involved can help navigate this process. By being prepared and seeking the right legal advice, individuals can ensure that the best interests of the ward are protected and that the guardianship arrangement serves its intended purpose of providing care and support.
What is the primary role of a guardian?

+
The primary role of a guardian is to act in the best interest of the ward, making decisions regarding their personal, financial, and legal affairs.
How long does the guardianship process typically take?

+
The length of the guardianship process can vary significantly depending on the complexity of the case, the court’s schedule, and the availability of all necessary parties and documents. It can range from a few weeks to several months.
Can a guardianship be terminated or modified?

+
Yes, a guardianship can be terminated or modified. This typically requires a court petition and hearing, where the court will assess whether the change is in the best interest of the ward. Reasons for termination or modification can include the ward’s recovery of capacity, a change in the guardian’s circumstances, or a determination that the guardianship is no longer necessary.