Estimated Quarterly Tax Paperwork Needed
Understanding Estimated Quarterly Tax Paperwork

When it comes to managing taxes for individuals with varying income sources, such as freelancers, independent contractors, or small business owners, understanding the requirements for estimated quarterly tax paperwork is crucial. The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) mandates that these individuals make estimated tax payments each quarter to avoid penalties and interest on their tax liabilities. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of estimated quarterly taxes, exploring the necessary paperwork, due dates, and tips for compliance.
Who Needs to File Estimated Quarterly Tax Paperwork?

Not everyone is required to file estimated quarterly tax paperwork. Generally, individuals who expect to owe $1,000 or more in taxes for the year and receive income that is not subject to withholding (such as self-employment income, interest, dividends, rents, alimony, etc.) must make estimated tax payments. This includes: - Freelancers and Independent Contractors: Individuals who work on a freelance or contract basis and receive payments reported on Form 1099-MISC. - Small Business Owners: Sole proprietors, partners, and S corporation shareholders who receive income from their businesses. - Investors: Individuals who receive significant income from investments, such as interest, dividends, and capital gains.
Necessary Paperwork for Estimated Quarterly Tax Payments
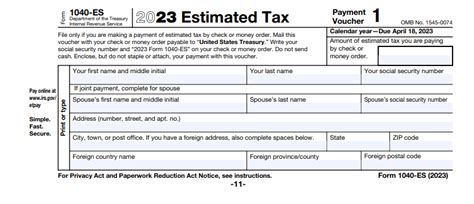
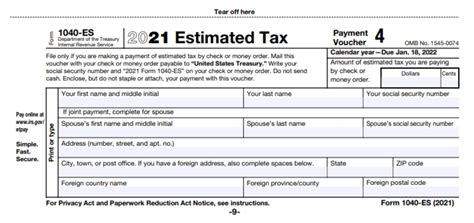
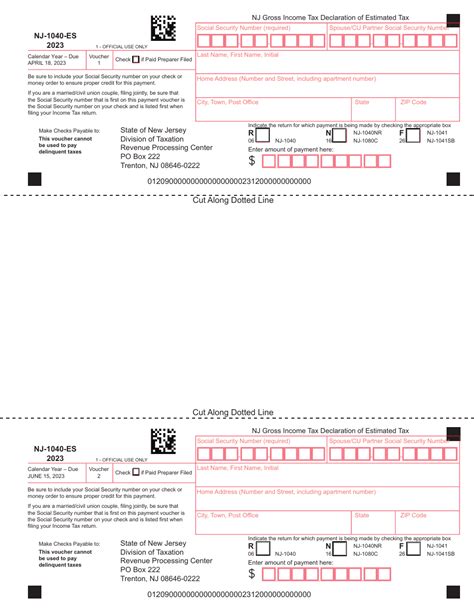
To make estimated tax payments, you will need to file Form 1040-ES, which is used to figure and pay your estimated taxes. Here are the key components of the paperwork needed: - Form 1040-ES: This form is used to make estimated tax payments and is due on a quarterly basis. - Estimated Tax Payment Voucher: Each payment due date has a corresponding voucher (Form 1040-ES) that you must submit with your payment. - Annual Tax Return (Form 1040): At the end of the tax year, you will need to file your annual tax return, reporting all income and deductions, including those related to your estimated tax payments.
Due Dates for Estimated Quarterly Tax Payments

Estimated tax payments are due on a quarterly basis, with the following due dates: - April 15th for January 1 - March 31 - June 15th for April 1 - May 31 - September 15th for June 1 - August 31 - January 15th of the following year for September 1 - December 31
Calculating Estimated Tax Payments

To calculate your estimated tax payments, you can use one of two methods: 1. Safe Harbor Rule: Pay either 90% of your current year’s tax liability or 100% of your prior year’s tax liability (110% if your adjusted gross income is over $150,000). 2. Annualized Estimated Tax Method: Make estimated tax payments based on your income and expenses for each quarter.
📝 Note: It is essential to accurately calculate your estimated tax payments to avoid penalties and interest. You may want to consult a tax professional to ensure you are meeting your tax obligations.
Electronic Federal Tax Payment System (EFTPS)
The IRS offers an online system, the Electronic Federal Tax Payment System (EFTPS), which allows you to make estimated tax payments electronically. This system is convenient, secure, and provides a record of your payments.
Penalties and Interest for Underpayment
If you fail to make estimated tax payments or underpay your taxes, you may be subject to penalties and interest. The IRS will charge a penalty for each quarter that you underpay your taxes, which can add up quickly.
Tips for Compliance

To ensure compliance with estimated quarterly tax requirements: - Keep Accurate Records: Maintain detailed records of your income, expenses, and estimated tax payments. - Consult a Tax Professional: If you are unsure about your tax obligations or need help calculating your estimated tax payments, consider consulting a tax professional. - Make Timely Payments: Submit your estimated tax payments on or before the due dates to avoid penalties and interest.
As we summarize the key points of estimated quarterly tax paperwork, it is clear that understanding the requirements and deadlines is vital for individuals with varying income sources. By following the guidelines outlined in this guide, you can ensure compliance with the IRS and avoid penalties and interest on your tax liabilities. Remember to keep accurate records, consult a tax professional if needed, and make timely payments to stay on top of your tax obligations.
What is the purpose of estimated quarterly tax payments?
+
Estimated quarterly tax payments are required for individuals who receive income that is not subject to withholding, such as freelancers, independent contractors, and small business owners, to avoid penalties and interest on their tax liabilities.
How do I calculate my estimated tax payments?

+
You can use either the Safe Harbor Rule or the Annualized Estimated Tax Method to calculate your estimated tax payments. It is recommended to consult a tax professional to ensure accuracy.
What are the due dates for estimated quarterly tax payments?
+
The due dates for estimated quarterly tax payments are April 15th, June 15th, September 15th, and January 15th of the following year.



