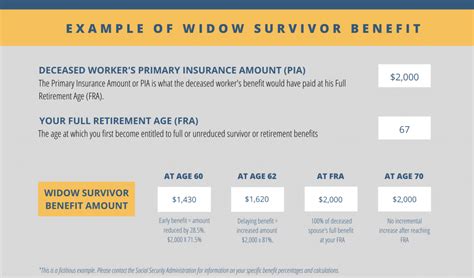
5 Ways To Vote

Introduction to Voting Methods

Voting is a fundamental right in many countries, allowing citizens to participate in the decision-making process of their government. There are several ways to vote, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. In this article, we will explore five common methods of voting, discussing their characteristics, benefits, and drawbacks. Understanding these methods is essential for citizens to make informed decisions and for governments to ensure the integrity and fairness of the electoral process.
1. In-Person Voting

In-person voting is the traditional method where voters physically go to a polling station to cast their ballots. This method is widely used and offers a sense of community and immediacy, as voters can see the polling process firsthand. Security and transparency are significant advantages of in-person voting, as the process is openly conducted, and ballots are counted manually or through secure machines. However, it can be inconvenient for voters who live far from polling stations or have mobility issues.
2. Mail-In Voting

Mail-in voting, also known as absentee voting, allows voters to cast their ballots by mail. This method has gained popularity due to its convenience and ability to increase voter turnout by allowing people to vote from anywhere. It is particularly beneficial for individuals who are unable to vote in person due to health issues, travel, or other commitments. However, mail-in voting also raises concerns about voter fraud and the potential for ballots to be lost or tampered with during transit.
3. Electronic Voting

Electronic voting uses electronic systems to record and count votes. This can include touch-screen voting machines, electronic voting booths, or even internet-based voting systems. The primary advantage of electronic voting is its speed and efficiency in counting votes, which can significantly reduce the time it takes to announce election results. Additionally, electronic systems can reduce errors associated with manual counting. Nonetheless, concerns about cybersecurity and the potential for votes to be altered or deleted have raised questions about the reliability of these systems.
4. Proxy Voting
Proxy voting is a method where a voter appoints another person to vote on their behalf. This is commonly used in corporate settings but can also be applied in political elections under specific circumstances. The main benefit of proxy voting is that it allows voters who cannot be present to still have their say. However, it also introduces risks related to the trustworthiness of the proxy and the potential for undue influence or coercion.
5. Ranked-Choice Voting

Ranked-choice voting (RCV) is a system where voters rank candidates in order of preference. This method is designed to more accurately reflect the will of the voters, as it allows for a more nuanced expression of preference than traditional plurality voting systems. The key advantage of RCV is that it reduces the spoiler effect and encourages civility among candidates, as they seek to be the second choice of voters who support other candidates. However, RCV can be complex and may require additional rounds of counting to determine a winner, which can delay the announcement of results.
🗳️ Note: Understanding the voting method used in your jurisdiction is crucial for making your vote count. It's also important to follow local voting regulations and deadlines to ensure your participation in the electoral process.
To summarize, each voting method has its strengths and weaknesses, and the choice of method can significantly impact the voting experience and outcome. Informed decision-making, security, convenience, and transparency are key considerations when evaluating voting methods. As societies evolve, so too must their electoral processes, incorporating technology and innovative methods to increase participation and ensure the integrity of elections. By considering these factors, voters and policymakers can work together to create a more inclusive and effective democratic process.