5 Forms for 1099 Employees

Introduction to 1099 Employees and Tax Forms
As a 1099 employee, also known as an independent contractor, it’s essential to understand the various tax forms required for reporting income and expenses. Unlike traditional W-2 employees, 1099 workers are responsible for their own taxes, which can be a bit more complex. In this article, we’ll delve into the five primary forms that 1099 employees need to be familiar with, ensuring they stay on top of their tax obligations.
Form 1099-MISC: Miscellaneous Income

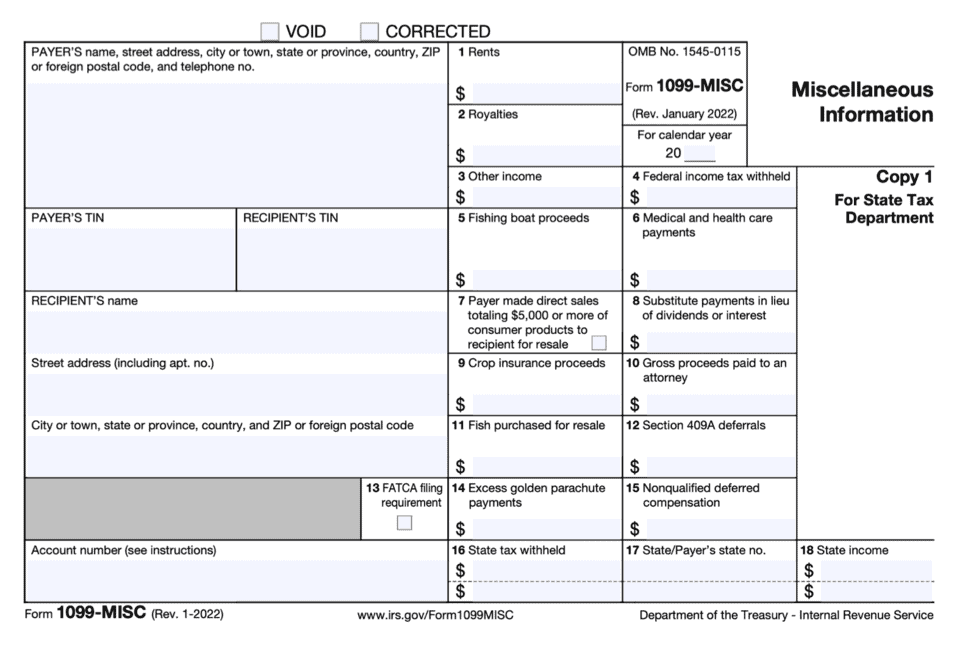
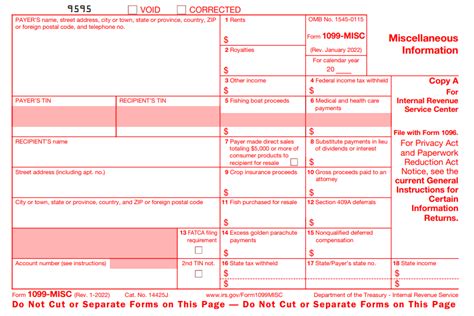
The Form 1099-MISC is a crucial document for 1099 employees, as it reports miscellaneous income earned from various sources, such as freelance work, consulting, or contract labor. This form is typically provided by the payer (client or employer) and includes details like: * Payer’s information: Name, address, and taxpayer identification number * Recipient’s information: Name, address, and taxpayer identification number * Income details: Type of income, amount paid, and any taxes withheld 1099 employees should receive a Form 1099-MISC from each payer who paid them $600 or more in a calendar year.
Form W-9: Request for Taxpayer Identification Number and Certification
Before starting work with a new client or payer, 1099 employees are often required to complete a Form W-9. This form provides the payer with the necessary information to generate a Form 1099-MISC, including: * Taxpayer identification number: Social Security number or Employer Identification Number (EIN) * Certification: Confirmation that the provided information is accurate and that the taxpayer is not subject to backup withholding It’s essential for 1099 employees to have a completed Form W-9 on file with each payer to avoid any potential issues with tax reporting.
Form 1040: U.S. Individual Income Tax Return
As a 1099 employee, Form 1040 is used to report personal income, including income from self-employment. This form requires detailed information about: * Income: Total income from all sources, including 1099 income * Deductions: Business expenses, itemized deductions, and standard deductions * Credits: Eligible tax credits, such as the Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC) 1099 employees will need to complete Schedule C (Form 1040) to report business income and expenses.
Schedule C (Form 1040): Profit or Loss from Business

Schedule C is a supporting schedule for Form 1040, used to calculate the profit or loss from a business. This schedule requires 1099 employees to report: * Business income: Total income from the business, including 1099 income * Business expenses: Detailed list of expenses related to the business, such as equipment, supplies, and travel expenses * Net profit or loss: Calculation of the business’s net profit or loss Accurate completion of Schedule C is crucial for 1099 employees to ensure they’re reporting their business income and expenses correctly.
Form 8829: Expenses for Business Use of Your Home

For 1099 employees who use a dedicated space in their home for business purposes, Form 8829 is used to calculate the home office deduction. This form requires: * Business use percentage: Calculation of the percentage of the home used for business purposes * Expenses: Detailed list of expenses related to the home office, such as rent, utilities, and insurance * Deduction: Calculation of the home office deduction By completing Form 8829, 1099 employees can claim a deduction for the business use of their home, which can help reduce their taxable income.
📝 Note: It's essential for 1099 employees to maintain accurate records and consult with a tax professional to ensure they're meeting all tax obligations and taking advantage of eligible deductions.
In summary, 1099 employees need to be familiar with these five forms to navigate their tax obligations: Form 1099-MISC, Form W-9, Form 1040, Schedule C (Form 1040), and Form 8829. By understanding the purpose and requirements of each form, 1099 employees can ensure they’re reporting their income and expenses correctly, avoiding any potential issues with the IRS.
What is the deadline for filing Form 1040?
+
The deadline for filing Form 1040 is typically April 15th of each year, unless the 15th falls on a weekend or holiday, in which case the deadline is the next business day.
Do I need to complete Form 8829 if I don’t have a dedicated home office?
+
No, Form 8829 is only required for 1099 employees who use a dedicated space in their home for business purposes and want to claim the home office deduction.
Can I e-file my tax return as a 1099 employee?

+
Yes, as a 1099 employee, you can e-file your tax return using tax preparation software or through the IRS website. E-filing can help reduce errors and speed up the refund process.