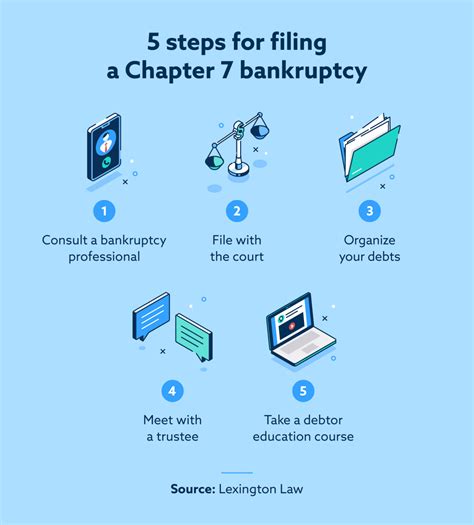
5 Steps Bankruptcy Filing

Understanding the Bankruptcy Process

The decision to file for bankruptcy is not an easy one, but for many individuals and businesses, it can be a necessary step towards financial recovery. The process of filing for bankruptcy can seem daunting, with numerous steps and considerations to take into account. However, by breaking down the process into manageable parts, individuals can better understand what to expect and how to navigate the system. In this article, we will explore the 5 key steps involved in filing for bankruptcy, providing a comprehensive guide for those considering this option.
Step 1: Determine Eligibility and Choose the Right Chapter

The first step in the bankruptcy process is to determine eligibility and choose the right chapter under which to file. The most common chapters for individuals are Chapter 7 and Chapter 13, while businesses may also consider Chapter 11. Chapter 7, also known as liquidation bankruptcy, involves the sale of non-exempt assets to pay off creditors, while Chapter 13 involves the creation of a repayment plan to pay off debts over time. To determine eligibility, individuals must assess their income, expenses, debts, and assets, and consider factors such as the means test for Chapter 7 or the debt limits for Chapter 13.
Step 2: Gather Required Documents and Information

Once eligibility has been determined, the next step is to gather all required documents and information. This includes: * A list of all creditors, including addresses and account numbers * A detailed list of all assets, including property, vehicles, and personal belongings * Income statements and pay stubs * Tax returns for the past two years * A list of all debts, including credit card debt, loans, and mortgages * Information about any pending lawsuits or collections activities It is essential to be thorough and accurate when gathering this information, as it will be used to complete the bankruptcy petition and schedules.
Step 3: Complete the Bankruptcy Petition and Schedules

With all necessary documents and information in hand, the next step is to complete the bankruptcy petition and schedules. The petition is the formal document that initiates the bankruptcy process, and it must be filed with the court. The schedules provide detailed information about the individual’s or business’s financial situation, including assets, liabilities, income, and expenses. It is crucial to ensure that all information is accurate and complete, as errors or omissions can lead to delays or even dismissal of the case. It is highly recommended to seek the assistance of a bankruptcy attorney to ensure that the petition and schedules are completed correctly.
Step 4: File the Petition and Schedules with the Court

Once the petition and schedules are complete, the next step is to file them with the court. This involves submitting the documents to the bankruptcy court and paying the required filing fee. The filing fee for Chapter 7 bankruptcy is currently 335, while the fee for Chapter 13 is 310. After filing, the court will assign a case number and a trustee will be appointed to oversee the case. The trustee’s role is to review the petition and schedules, conduct the meeting of creditors, and ensure that the bankruptcy process is completed in accordance with the law.
Step 5: Attend the Meeting of Creditors and Complete the Bankruptcy Process
The final step in the bankruptcy process is to attend the meeting of creditors, also known as the 341 meeting. This meeting provides an opportunity for creditors to ask questions and object to the bankruptcy discharge, if necessary. The individual or business filing for bankruptcy must attend this meeting and answer questions under oath. After the meeting, the court will review the case and determine whether to grant the discharge. If the discharge is granted, the individual or business will be released from personal liability for most debts, and the bankruptcy process will be complete.
💡 Note: It is essential to understand that bankruptcy should only be considered as a last resort, after exploring all other options for debt relief. Additionally, bankruptcy can have long-term consequences on credit scores and financial stability, so it is crucial to carefully consider the decision and seek professional advice before proceeding.
As we reflect on the 5 steps involved in filing for bankruptcy, it is clear that the process can be complex and overwhelming. However, by breaking it down into manageable parts and seeking the assistance of a qualified bankruptcy attorney, individuals and businesses can navigate the system and achieve a fresh start. The key to a successful bankruptcy filing is to be thorough, accurate, and informed, and to approach the process with a clear understanding of the benefits and consequences.
What are the main differences between Chapter 7 and Chapter 13 bankruptcy?

+
Chapter 7 involves the sale of non-exempt assets to pay off creditors, while Chapter 13 involves the creation of a repayment plan to pay off debts over time. Chapter 7 is typically faster, but may result in the loss of assets, while Chapter 13 allows individuals to keep their assets, but requires a longer repayment period.
How long does the bankruptcy process typically take?

+
The length of the bankruptcy process varies depending on the chapter and the complexity of the case. Chapter 7 cases are typically resolved within 4-6 months, while Chapter 13 cases can take 3-5 years to complete.
Will filing for bankruptcy affect my credit score?

+
Yes, filing for bankruptcy can have a significant impact on credit scores. However, the effect is typically temporary, and credit scores can be rebuilt over time by establishing a positive payment history and keeping credit utilization low.