Who Can Notarize Paperwork

Understanding Notarization and Who Can Perform It

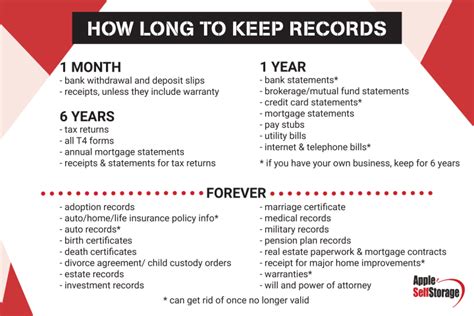
Notarization is a process that verifies the authenticity of a document, ensuring that the signatory is who they claim to be and that they are signing the document voluntarily. This process is crucial for preventing fraud and protecting the rights of individuals and organizations. But who exactly can notarize paperwork? The answer varies by country and even by state or province within a country, but there are common roles and qualifications associated with notaries.
Roles of a Notary Public

A notary public is the most common official authorized to notarize documents. Notaries are appointed by the government to serve as impartial witnesses to the signing of important documents. Their primary role is to: - Verify the identity of the person signing the document. - Ensure the signatory is signing voluntarily and is not under duress. - Witness the signing of the document. - Place their official seal or stamp on the document to confirm its authenticity.
Qualifications and Appointment

The qualifications to become a notary public vary, but they generally include: - Being at least 18 years old. - Being a resident of the state or country where the notary public will be practicing. - Passing a background check. - Completing a notary education course (in some jurisdictions). - Passing a notary exam (in some jurisdictions). - Obtaining a notary bond (in some jurisdictions). - Applying for a notary commission through the appropriate government agency.
Other Officials Who Can Notarize

While notaries public are the primary officials for notarizing documents, other officials may also have this authority: - Judges and Magistrates: In some jurisdictions, judges and magistrates can perform notarizations, especially for certain types of documents. - Clerks of Court: Court clerks may be authorized to notarize documents related to court proceedings. - Bank Officials: Some bank officials, particularly those in managerial positions, may be notaries public and can notarize documents for bank customers. - Shippers and Postal Workers: For certain documents related to shipping and postal services, specific officials within these industries may have notarization powers. - Consular Officers: For documents related to international transactions or for citizens living abroad, consular officers at embassies and consulates may notarize documents.
Notarization Process

The notarization process typically involves the following steps: 1. Identification: The signatory must provide identification to prove their identity. 2. Document Presentation: The document to be notarized is presented to the notary. 3. Verification of Identity and Voluntary Signature: The notary verifies the identity of the signatory and ensures they are signing voluntarily. 4. Signing and Witnessing: The signatory signs the document in the presence of the notary. 5. Notarization: The notary places their seal or stamp on the document and completes any required notary wording.
Types of Notarizations

There are several types of notarizations, including: - Acknowledgments: The most common type, where the signatory acknowledges signing the document. - Jurats: The notary administers an oath or affirmation to the signatory, who then signs the document. - Certified Copies: The notary certifies that a copy of a document is true and accurate.
Modern Trends in Notarization

With advancements in technology, remote notarization (also known as online notarization or e-notarization) is becoming more common. This allows documents to be notarized electronically, with the notary and signatory interacting through audio-visual technology. This trend is increasing access to notarization services, especially in rural or underserved areas.
📝 Note: Laws regarding remote notarization vary significantly by jurisdiction, and not all states or countries have legalized this practice.
Conclusion

In summary, while the role of notarizing documents is primarily performed by notaries public, other officials may also have the authority to do so, depending on the jurisdiction and the type of document. Understanding who can notarize paperwork and the process involved is essential for individuals and organizations to ensure the authenticity and legality of their documents. Whether through traditional in-person notarization or the increasingly available remote notarization, verifying the identity and voluntary signature of a document’s signatory remains a critical step in preventing fraud and protecting rights.
What is the primary role of a notary public?
+
The primary role of a notary public is to verify the identity of the signatory, ensure they are signing voluntarily, witness the signing, and place their official seal or stamp on the document to confirm its authenticity.
Who else can notarize documents besides notaries public?

+
Other officials who can notarize documents include judges, magistrates, clerks of court, certain bank officials, shippers, postal workers, and consular officers, though their authority may be limited to specific types of documents or situations.
What is remote notarization, and is it widely available?

+
Remote notarization, or online notarization, allows documents to be notarized electronically through audio-visual technology. While it is becoming more common, its availability varies significantly by jurisdiction, with laws and regulations differing widely.