Late 941 Filing Penalties

Introduction to Late 941 Filing Penalties
The Employer’s Quarterly Federal Tax Return, also known as Form 941, is a crucial document that employers must file with the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) on a quarterly basis. This form is used to report employment taxes, including income tax withheld and Social Security and Medicare taxes. Employers who fail to file Form 941 on time may be subject to late filing penalties, which can be substantial. In this blog post, we will delve into the world of late 941 filing penalties, exploring the reasons for these penalties, how they are calculated, and most importantly, how to avoid them.
Understanding the Importance of Timely Filing

The IRS requires employers to file Form 941 by the last day of the month following the end of each quarter. The due dates for Form 941 are: - April 30th for the first quarter (January 1 - March 31) - July 31st for the second quarter (April 1 - June 30) - October 31st for the third quarter (July 1 - September 30) - January 31st of the following year for the fourth quarter (October 1 - December 31) Employers who fail to meet these deadlines may face penalties, which can add up quickly.
Calculating Late Filing Penalties
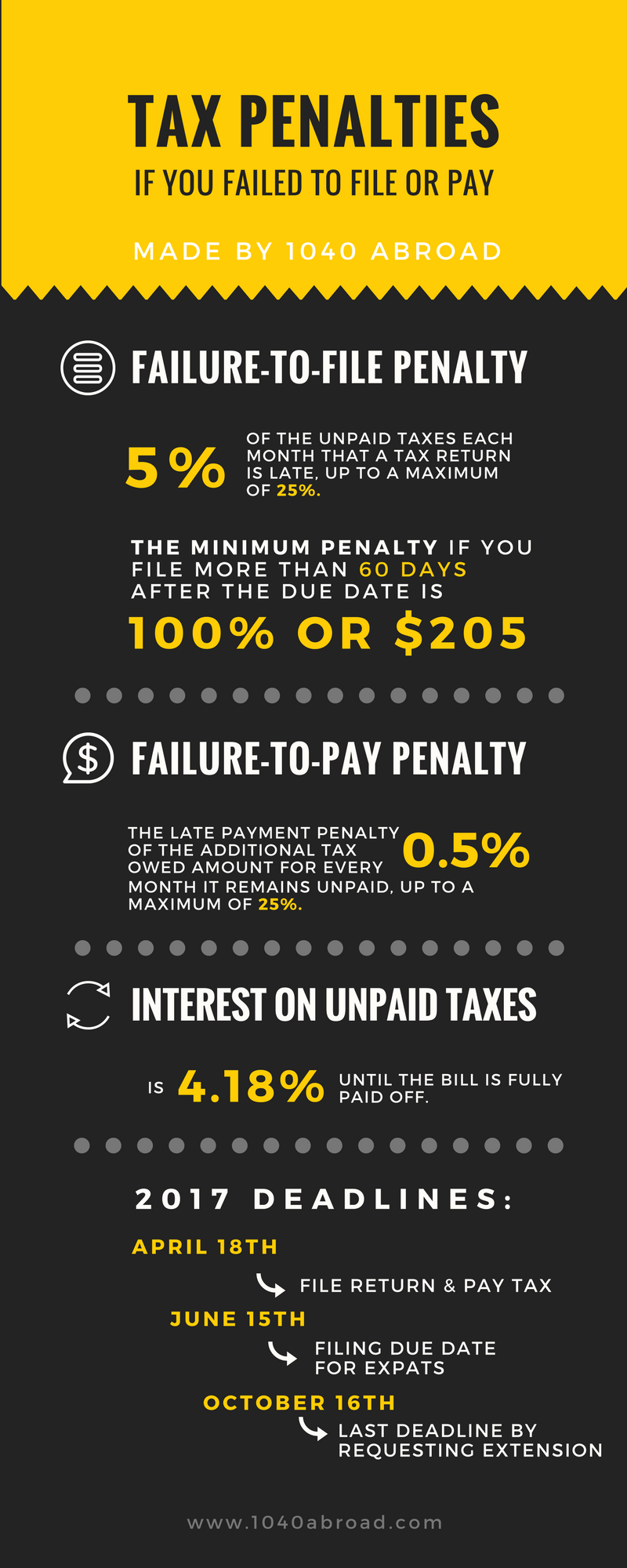
The late filing penalty for Form 941 is calculated based on the unpaid tax amount. The penalty is 5% of the unpaid tax for each month or part of a month the return is late, up to a maximum of 25%. For example, if an employer owes 1,000 in employment taxes and files Form 941 2 months late, the late filing penalty would be 100 (5% of 1,000 for the first month) + 100 (5% of 1,000 for the second month) = 200. Additionally, the IRS may also impose interest on the unpaid tax amount, which can further increase the total amount owed.
Avoiding Late Filing Penalties
To avoid late filing penalties, employers should prioritize timely filing of Form 941. Here are some tips to help employers stay on track: * Mark the due dates on your calendar to ensure you never miss a deadline * File electronically to reduce errors and speed up the filing process * Keep accurate records of employment taxes to ensure you are reporting the correct amounts * Consult with a tax professional if you are unsure about any aspect of the filing process
📝 Note: Employers who are experiencing financial difficulties and are unable to file Form 941 on time may be eligible for a penalty waiver. To request a penalty waiver, employers must submit Form 843, Claim for Refund and Request for Abatement, to the IRS.
Consequences of Repeated Late Filings

Employers who repeatedly file Form 941 late may face more severe consequences, including: * Increased penalty rates: The IRS may increase the penalty rate for repeated late filers * Loss of trust fund recovery penalty relief: Employers who are found to have willfully failed to pay employment taxes may be subject to the trust fund recovery penalty, which can be up to 100% of the unpaid tax amount * Damage to credit score: Repeated late filings can negatively impact an employer’s credit score, making it more difficult to obtain loans or credit in the future
Best Practices for Employment Tax Compliance

To ensure compliance with employment tax regulations and avoid late filing penalties, employers should follow these best practices: * Stay up-to-date with tax law changes: Regularly review IRS publications and consult with a tax professional to ensure you are aware of any changes to employment tax laws and regulations * Implement a robust record-keeping system: Accurate and detailed records are essential for ensuring compliance with employment tax regulations * Conduct regular audits: Regularly review your employment tax filings to ensure accuracy and compliance
| Quarter | Due Date |
|---|---|
| First Quarter (January 1 - March 31) | April 30th |
| Second Quarter (April 1 - June 30) | July 31st |
| Third Quarter (July 1 - September 30) | October 31st |
| Fourth Quarter (October 1 - December 31) | January 31st of the following year |

In summary, late 941 filing penalties can be substantial, but they can be avoided by prioritizing timely filing and following best practices for employment tax compliance. Employers should stay up-to-date with tax law changes, implement a robust record-keeping system, and conduct regular audits to ensure accuracy and compliance. By taking these steps, employers can minimize the risk of late filing penalties and ensure a smooth and efficient employment tax filing process.
What is the deadline for filing Form 941?

+
The deadline for filing Form 941 is the last day of the month following the end of each quarter. The due dates are April 30th for the first quarter, July 31st for the second quarter, October 31st for the third quarter, and January 31st of the following year for the fourth quarter.
How are late filing penalties calculated?

+
The late filing penalty for Form 941 is calculated based on the unpaid tax amount. The penalty is 5% of the unpaid tax for each month or part of a month the return is late, up to a maximum of 25%.
Can I request a penalty waiver if I am experiencing financial difficulties?

+
Yes, employers who are experiencing financial difficulties and are unable to file Form 941 on time may be eligible for a penalty waiver. To request a penalty waiver, employers must submit Form 843, Claim for Refund and Request for Abatement, to the IRS.