5 Tips on FMLA Restrictions

Introduction to FMLA Restrictions
The Family and Medical Leave Act (FMLA) is a federal law that provides eligible employees with up to 12 weeks of unpaid leave in a 12-month period for certain family and medical reasons. While the FMLA offers protections for employees, there are also restrictions and limitations that employers and employees must be aware of. In this article, we will explore five tips on FMLA restrictions that can help employers navigate the complexities of the law and ensure compliance.
Understanding Eligibility Requirements
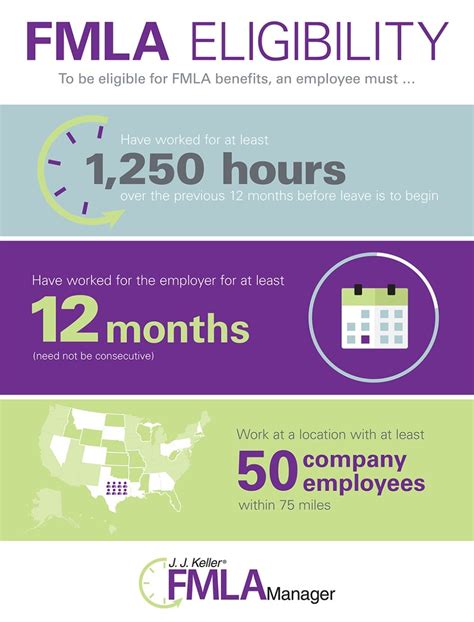
One of the most important FMLA restrictions is the eligibility requirement. To be eligible for FMLA leave, an employee must have worked for the employer for at least 12 months, have completed at least 1,250 hours of service in the 12 months preceding the start of leave, and work at a location where the employer has at least 50 employees within a 75-mile radius. Employers must understand these eligibility requirements to determine which employees are entitled to FMLA leave. It is essential to note that these requirements can be complex, and employers should consult with HR professionals or attorneys to ensure compliance.
Leave Entitlement and Limitations

Another crucial aspect of FMLA restrictions is the leave entitlement and limitations. Eligible employees are entitled to up to 12 weeks of unpaid leave in a 12-month period for certain family and medical reasons, such as the birth or adoption of a child, a serious health condition, or to care for a family member with a serious health condition. However, there are limitations on the use of FMLA leave, such as the requirement that employees provide 30 days’ notice for foreseeable leave and that employers can require employees to provide certification from a healthcare provider to support their leave request. The following are some key limitations: * Employees can take up to 12 weeks of leave in a 12-month period * Employers can require employees to provide certification from a healthcare provider * Employees must provide 30 days’ notice for foreseeable leave * Employers can deny leave if the employee fails to provide required documentation
Coverage and Exceptions
FMLA restrictions also include coverage and exceptions. The FMLA applies to all public agencies, public and private elementary and secondary schools, and private sector employers with 50 or more employees. However, there are exceptions for certain employees, such as those who work for small businesses or are considered “key employees.” It is essential for employers to understand which employees are covered under the FMLA and which are not. The following table highlights some key exceptions:
| Employee Type | FMLA Coverage |
|---|---|
| Public agency employees | Covered |
| Private sector employees with 50+ employees | Covered |
| Small business employees (less than 50 employees) | Not covered |
| Key employees | Not covered |

Notification and Certification Requirements

Employers must also be aware of the notification and certification requirements under the FMLA. Employees must provide 30 days’ notice for foreseeable leave, and employers can require employees to provide certification from a healthcare provider to support their leave request. It is essential for employers to have a clear understanding of these requirements to ensure compliance with the FMLA. Some key notification and certification requirements include: * Employees must provide 30 days’ notice for foreseeable leave * Employers can require employees to provide certification from a healthcare provider * Employees must provide documentation to support their leave request
Consequences of Non-Compliance

Finally, it is essential for employers to understand the consequences of non-compliance with the FMLA. Failure to comply with the FMLA can result in serious consequences, including lawsuits, fines, and damage to an employer’s reputation. Employers must take the FMLA seriously and ensure that they are in compliance with all requirements. Some key consequences of non-compliance include: * Lawsuits and fines * Damage to an employer’s reputation * Loss of employee trust and morale * Increased risk of employee turnover
💡 Note: Employers should consult with HR professionals or attorneys to ensure compliance with the FMLA and avoid potential consequences.
In summary, understanding FMLA restrictions is crucial for employers to ensure compliance with the law. By knowing the eligibility requirements, leave entitlement and limitations, coverage and exceptions, notification and certification requirements, and consequences of non-compliance, employers can navigate the complexities of the FMLA and provide eligible employees with the protections they are entitled to. This knowledge will help employers to create a positive and supportive work environment, reduce the risk of lawsuits and fines, and maintain a good reputation.
What is the purpose of the FMLA?

+
The purpose of the FMLA is to provide eligible employees with up to 12 weeks of unpaid leave in a 12-month period for certain family and medical reasons, while also protecting their job and benefits.
Who is eligible for FMLA leave?

+
Eligible employees must have worked for the employer for at least 12 months, have completed at least 1,250 hours of service in the 12 months preceding the start of leave, and work at a location where the employer has at least 50 employees within a 75-mile radius.
What are the consequences of non-compliance with the FMLA?

+
The consequences of non-compliance with the FMLA can include lawsuits, fines, damage to an employer’s reputation, loss of employee trust and morale, and increased risk of employee turnover.
Can employers require employees to provide certification from a healthcare provider?

+
Yes, employers can require employees to provide certification from a healthcare provider to support their leave request.
How many weeks of leave are eligible employees entitled to under the FMLA?

+
Eligible employees are entitled to up to 12 weeks of unpaid leave in a 12-month period for certain family and medical reasons.