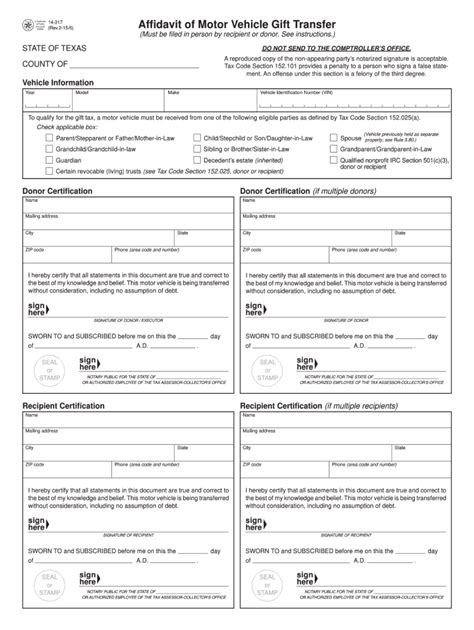
Notary Self Notarization Rules

Introduction to Notary Self-Notarization Rules
The role of a notary public is crucial in verifying the authenticity of documents and ensuring that signers are who they claim to be. One of the key aspects of notarization is the principle of impartiality, which dictates that a notary cannot notarize a document in which they have a personal interest. However, there are instances where a notary might need to sign a document, such as in the case of a business or personal transaction. This is where the concept of self-notarization comes into play. Self-notarization refers to the process where a notary public notarizes their own signature on a document.
Understanding the Rules of Self-Notarization

The rules regarding self-notarization vary significantly from one jurisdiction to another. In some states or countries, self-notarization is prohibited due to concerns about impartiality and the potential for fraud. The rationale behind this prohibition is to prevent notaries from using their position for personal gain or to circumvent legal requirements. On the other hand, some jurisdictions allow self-notarization under specific circumstances, provided that the notary complies with all applicable laws and regulations.
For instance, a notary might be permitted to self-notarize a document if it is for a personal transaction that does not involve a conflict of interest. However, the notary must still adhere to the fundamental principles of notarization, including verifying their own identity and ensuring that they are signing the document voluntarily.
Key Considerations for Notaries

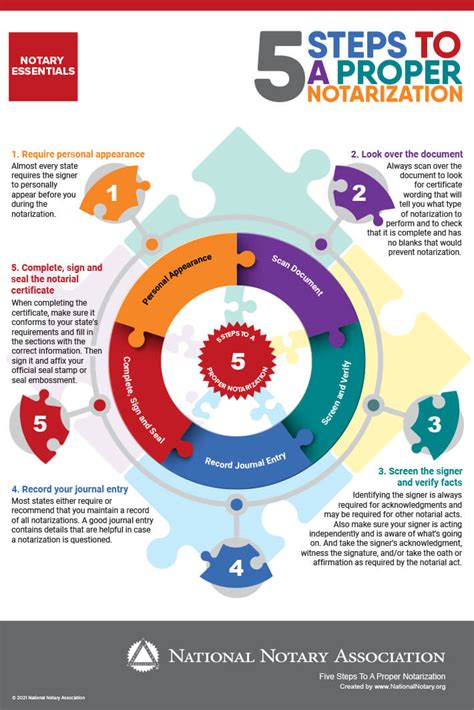
Notaries considering self-notarization must be aware of the following key considerations: - Jurisdictional Laws: Familiarize yourself with the laws of your jurisdiction regarding self-notarization. Some states have specific statutes or regulations that permit or prohibit self-notarization. - Conflict of Interest: Ensure that self-notarizing a document does not create a conflict of interest. If the document benefits you directly or involves a personal interest, it may be considered a conflict. - Impartiality: Maintain impartiality. The core of notarization is verifying the authenticity of signatures without bias. Self-notarization must not compromise this principle. - Documentation: Keep detailed records of any self-notarization. This includes the type of document notarized, the date, and any other relevant details.
Best Practices for Self-Notarization

When self-notarization is permitted, following best practices is essential to maintain the integrity of the notarization process: - Transparency: Be transparent about your role in the transaction. If you are both the notary and a signer, this should be clearly indicated on the document. - Compliance with Laws: Always comply with the laws and regulations of your jurisdiction. This includes any specific requirements for self-notarization, such as using a particular type of stamp or wording. - Education: Stay updated on the latest laws, regulations, and best practices regarding notarization and self-notarization. This might involve attending seminars or workshops focused on notary practices.
Potential Risks and Consequences

There are potential risks and consequences associated with self-notarization, particularly if it is not done correctly or in accordance with the law. These can include: - Legal Repercussions: If a notary self-notarizes a document improperly, it could lead to legal issues, including the document being deemed invalid or the notary facing legal action. - Professional Consequences: Engaging in improper self-notarization can damage a notary’s professional reputation and potentially lead to the revocation of their notary commission. - Ethical Concerns: Self-notarization raises ethical concerns, particularly regarding impartiality and conflict of interest. Notaries must navigate these issues carefully to maintain the trust and integrity of the notarization process.
📝 Note: Notaries should consult with legal professionals or their state's notary public commission to understand the specific laws and best practices regarding self-notarization in their jurisdiction.
Conclusion and Final Thoughts
In conclusion, the rules and practices surrounding self-notarization are complex and vary widely depending on the jurisdiction. Notaries must be well-informed about the laws and regulations in their area and always act with integrity and impartiality. Whether self-notarization is permitted or prohibited, the fundamental principles of notarization must be upheld to ensure the authenticity and validity of documents. By understanding and adhering to these principles and any applicable laws, notaries can fulfill their critical role in verifying identities and documents while maintaining the highest standards of professionalism.
What is self-notarization?

+
Self-notarization refers to the process where a notary public notarizes their own signature on a document.
Is self-notarization allowed everywhere?
+
No, the rules regarding self-notarization vary significantly from one jurisdiction to another. Some states or countries prohibit self-notarization due to concerns about impartiality and the potential for fraud.
What are the key considerations for notaries regarding self-notarization?

+
Notaries must consider jurisdictional laws, conflict of interest, impartiality, and documentation. They must also follow best practices to maintain the integrity of the notarization process.