5 TipsFMLA

Understanding the Family and Medical Leave Act (FMLA): 5 Key Tips

The Family and Medical Leave Act (FMLA) is a federal law that provides eligible employees with up to 12 weeks of unpaid leave in a 12-month period for certain family and medical reasons. It is essential for both employers and employees to understand the provisions and rules of the FMLA to ensure compliance and to navigate the leave process smoothly. In this article, we will explore 5 critical tips related to the FMLA, covering eligibility, qualifying reasons, notice requirements, and more.
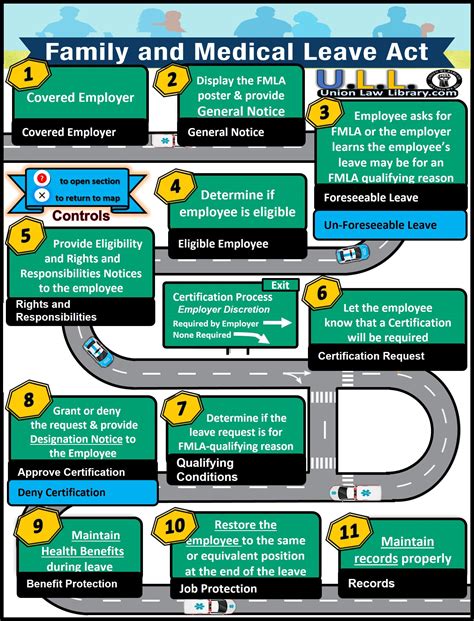
Tip 1: Determine Eligibility

To be eligible for FMLA leave, an employee must meet specific criteria. The employee must have worked for the employer for at least 12 months, although these months do not have to be consecutive. Additionally, the employee must have completed at least 1,250 hours of service in the 12 months preceding the start of the leave. It is also important to note that the employer must have at least 50 employees within a 75-mile radius for the FMLA to apply. Understanding these eligibility requirements is crucial for both employers in managing their workforce and for employees in planning their leave.
Tip 2: Identify Qualifying Reasons

The FMLA allows leave for several qualifying reasons, including: - The birth of a child and to care for the newborn child within one year of birth. - The placement with the employee of a child for adoption or foster care and to care for the newly placed child within one year of placement. - To care for the employee’s spouse, child, or parent with a serious health condition. - A serious health condition that makes the employee unable to perform the essential functions of their job. - Qualifying exigency related to the covered active duty or call to covered active duty of a family member in the Armed Forces. - To care for a covered service member with a serious injury or illness if the eligible employee is the spouse, child, parent, or next of kin of the covered service member.
Tip 3: Understand Notice Requirements

When an employee becomes aware of the need for FMLA leave, they must provide their employer with 30 days’ advance notice when the leave is foreseeable. If the leave is not foreseeable, the employee must notify the employer as soon as practicable, which typically means within one or two business days of learning of the need for leave. Employers are also required to provide notice to employees about their eligibility and rights under the FMLA.
Tip 4: Manage Leave and Benefits

During the FMLA leave, the employer must maintain the employee’s health coverage under any group health plan on the same terms as if the employee had continued to work. Employees are also entitled to return to their job or an equivalent job with equivalent pay, benefits, and other terms and conditions of employment. It is essential for employers to have a clear policy and procedure in place for managing FMLA leave, including how benefits will be handled and how the employee’s job will be protected.
Tip 5: Document Everything

Accurate and detailed documentation is crucial in managing FMLA leave. Employers should document all notices given to and received from the employee, including the initial notice of the need for leave, any medical certifications, and notices of leave approval or denial. Employees should also keep a record of their communication with their employer regarding their leave. Proper documentation helps in preventing disputes and ensuring compliance with the FMLA.
📝 Note: Employers should consult with legal counsel to ensure their FMLA policies and procedures are compliant with federal regulations and to address any specific questions or concerns regarding employee leave.
In essence, navigating the FMLA requires a clear understanding of eligibility, qualifying reasons, notice requirements, leave management, and the importance of documentation. By following these 5 tips, both employers and employees can better navigate the complexities of the FMLA, ensuring that leaves are taken smoothly and that all parties comply with the law.
What is the maximum amount of leave an employee can take under the FMLA?

+
The maximum amount of leave an employee can take under the FMLA is 12 weeks in a 12-month period for most qualifying reasons, and up to 26 weeks in a 12-month period for military caregiver leave.
Can an employer deny an employee’s request for FMLA leave?

+
An employer can deny an employee’s request for FMLA leave if the employee is not eligible or if the reason for the leave does not qualify under the FMLA. The employer must provide the employee with a clear reason for the denial in writing.
Is the FMLA leave paid or unpaid?
+
The FMLA provides for unpaid leave. However, employees may choose to use accrued paid leave (such as vacation or sick leave) during their FMLA leave, and some employers may offer paid family leave as a benefit.



