5 FMLA Billing Tips

Understanding the Basics of FMLA Billing

The Family and Medical Leave Act (FMLA) is a federal law that provides eligible employees with up to 12 weeks of unpaid leave in a 12-month period for certain family and medical reasons. One of the key aspects of managing FMLA is the billing process, which can be complex and time-consuming. In this article, we will provide 5 essential FMLA billing tips to help employers navigate this process efficiently.
Tip 1: Determine Eligibility and Entitlement
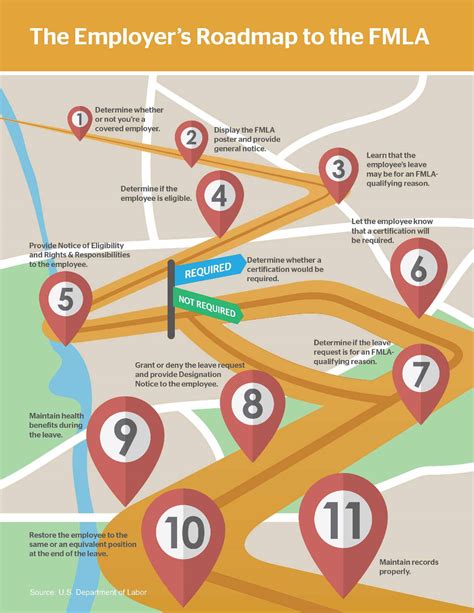
Before initiating the billing process, it is crucial to determine whether an employee is eligible for FMLA leave and the amount of leave they are entitled to. Eligibility criteria include working for a covered employer, completing at least 1,250 hours of service in the 12 months preceding the start of leave, and working at a location where at least 50 employees are employed within 75 miles. Employers must also ensure that they have accurate records of employee work hours and leave usage to avoid errors in billing.
Tip 2: Choose the Right Leave Year

The FMLA leave year is the 12-month period used to calculate an employee’s leave entitlement. There are four possible methods for determining the leave year: the calendar year, a fixed 12-month period (e.g., January 1 to December 31), the anniversary date (the date the employee’s first FMLA leave began), or a rolling 12-month period (measured backward from the date an employee uses any FMLA leave). Employers must select a leave year method and apply it consistently to all employees.
Tip 3: Manage Intermittent Leave and Reduced Schedule Leave

Intermittent leave and reduced schedule leave are two types of FMLA leave that can be particularly challenging to manage. Intermittent leave involves taking leave in blocks of time, such as a few hours or days, rather than all at once. Reduced schedule leave involves reducing an employee’s work schedule, such as working part-time instead of full-time. Employers must have a system in place to track and record intermittent and reduced schedule leave to ensure accurate billing.
Tip 4: Communicate with Employees and Healthcare Providers
Effective communication is essential for managing FMLA billing. Employers must notify employees of their eligibility for FMLA leave, the amount of leave available, and any requirements for providing medical certification. Employers may also need to communicate with healthcare providers to verify the employee’s medical condition and the need for leave. Clear communication helps prevent errors and ensures that employees receive the leave they are entitled to.
Tip 5: Keep Accurate Records and Monitor Leave Usage

Maintaining accurate records is critical for managing FMLA billing. Employers must keep track of employee leave usage, including the dates and hours of leave taken, and ensure that employees do not exceed their entitled amount of leave. Employers must also monitor leave usage to prevent abuse and ensure that employees are using leave for legitimate purposes. By keeping accurate records and monitoring leave usage, employers can prevent errors and ensure compliance with FMLA regulations.
💡 Note: Employers should regularly review and update their FMLA policies and procedures to ensure compliance with changing regulations and to prevent errors in billing.
In summary, managing FMLA billing requires a thorough understanding of eligibility and entitlement, choosing the right leave year, managing intermittent and reduced schedule leave, communicating with employees and healthcare providers, and keeping accurate records. By following these 5 essential tips, employers can navigate the complex FMLA billing process efficiently and ensure compliance with federal regulations.
What is the purpose of the Family and Medical Leave Act (FMLA)?

+
The purpose of the FMLA is to provide eligible employees with up to 12 weeks of unpaid leave in a 12-month period for certain family and medical reasons, such as the birth or adoption of a child, a serious health condition, or the need to care for a family member with a serious health condition.
Who is eligible for FMLA leave?

+
To be eligible for FMLA leave, an employee must have worked for a covered employer for at least 12 months, completed at least 1,250 hours of service in the 12 months preceding the start of leave, and work at a location where at least 50 employees are employed within 75 miles.
What is the difference between intermittent leave and reduced schedule leave?

+
Intermittent leave involves taking leave in blocks of time, such as a few hours or days, rather than all at once. Reduced schedule leave involves reducing an employee’s work schedule, such as working part-time instead of full-time. Both types of leave can be used for the same purposes, such as to care for a family member with a serious health condition or to recover from a serious health condition.



