Paperwork
Selective Service Registration Paperwork
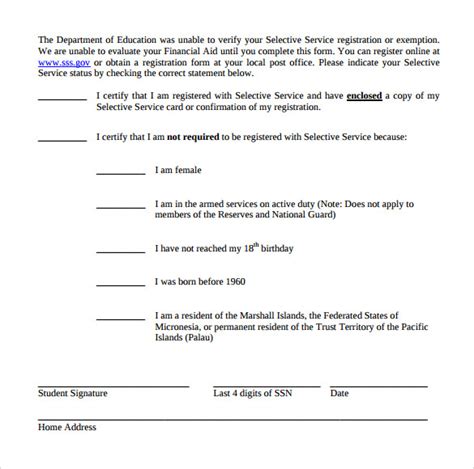
Introduction to Selective Service Registration
The Selective Service System is a government agency that maintains information on those potentially subject to military conscription. In the United States, almost all male U.S. citizens between the ages of 18 and 25 are required to register with the Selective Service System. This registration makes them eligible for a potential military draft, should the country need to reinstate one. The process is straightforward and can be completed online, by mail, or through other methods.
Why Register with the Selective Service?
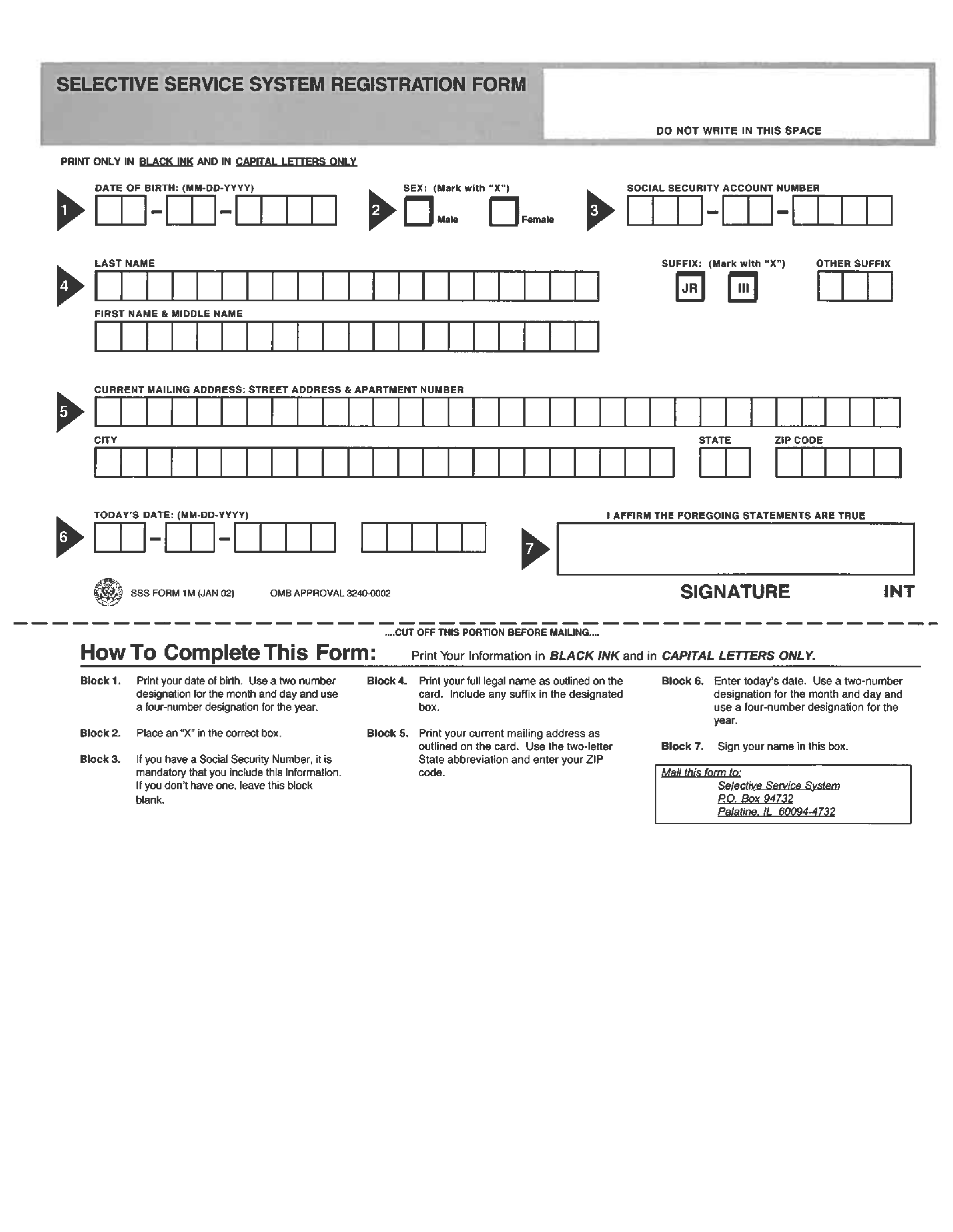
Registering with the Selective Service is mandatory for most male U.S. citizens and male immigrants (documented or undocumented) between the ages of 18 and 25. Failure to register can have serious consequences, including being ineligible for federal student loans and civil service jobs, and potentially facing fines or imprisonment. However, the primary reason for registration is to create a pool of individuals who could be called upon to serve in the military if a national emergency requires more troops than the volunteer military can provide.
Who Must Register?

The requirement to register applies to: - U.S. male citizens - Male immigrants (both documented and undocumented) living in the United States - Male U.S. nationals All these individuals must register within 30 days of their 18th birthday.
Exemptions and Exceptions
Some individuals are not required to register, including: - Female U.S. citizens (as the draft has historically only applied to men, though this could change) - Males who are currently in the military or have previously served - Males with disabilities that would prevent them from serving - Certain individuals with conscientious objections - Non-citizens living outside the United States
How to Register

Registration can be completed in several ways: - Online: Through the Selective Service System’s official website, which is the quickest method. - Mail: By filling out and mailing a registration form. - Post Office: Some post offices have the forms available. - High School: Many high schools help their male students register.
Benefits of Registration
Besides the legal requirement, registering with the Selective Service has several benefits, including: - Eligibility for Federal Student Loans - Eligibility for Federal Jobs - Job Training and Employment - U.S. Citizenship for Immigrants
📝 Note: It's essential to understand the process and importance of registration to avoid any legal or financial repercussions.
Consequences of Not Registering
Failure to register can lead to severe consequences, including: - Ineligibility for Federal Student Loans - Ineligibility for Federal Jobs - Denial of U.S. Citizenship for immigrants - Fines and Potential Imprisonment
Keeping Registration Information Up-to-Date

After registering, it’s crucial to keep the Selective Service informed of any changes in status, such as: - Change of address - Change in marital status - Change in family status This ensures that the information on file is accurate and up-to-date.
Conclusion and Final Thoughts
In summary, registering with the Selective Service is a critical step for male U.S. citizens and male immigrants between the ages of 18 and 25. It’s not just a legal requirement but also a step that can affect future opportunities, from education and employment to citizenship. By understanding the process and ensuring timely registration, individuals can avoid potential legal and financial issues. The Selective Service System plays a vital role in the country’s defense strategy, and registration is a civic duty for those who are eligible.
What is the purpose of the Selective Service System?

+
The purpose of the Selective Service System is to maintain information on those potentially subject to military conscription, should the country need to reinstate a draft.
Who needs to register with the Selective Service?
+
Almost all male U.S. citizens and male immigrants between the ages of 18 and 25 are required to register.
What are the consequences of not registering with the Selective Service?

+
Failure to register can lead to ineligibility for federal student loans and civil service jobs, denial of U.S. citizenship for immigrants, and potential fines or imprisonment.