5 Covid Facts

Introduction to Covid-19
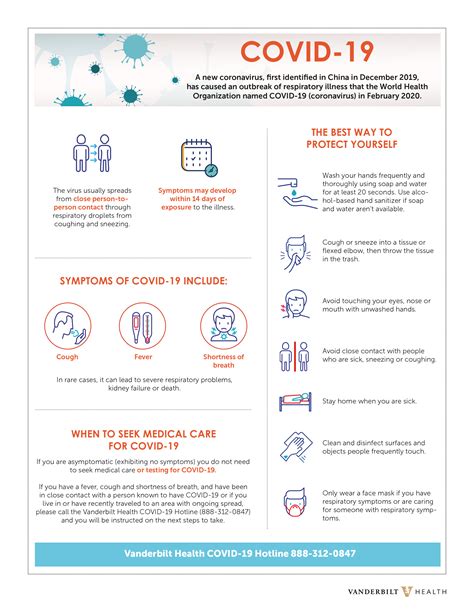
The Covid-19 pandemic has been a global health crisis that has affected millions of people worldwide. It is essential to understand the facts about Covid-19 to take necessary precautions and stay safe. In this article, we will discuss five critical facts about Covid-19 that everyone should know.
Fact 1: Transmission of Covid-19

Covid-19 is primarily spread through respiratory droplets that are released when an infected person talks, coughs, or sneezes. These droplets can land in the mouths or noses of people nearby or be inhaled into the lungs. It is crucial to maintain a distance of at least 6 feet from others to reduce the risk of transmission. Additionally, wearing a mask can help prevent the spread of Covid-19 by blocking these respiratory droplets.
Fact 2: Symptoms of Covid-19

The symptoms of Covid-19 can range from mild to severe and may include: * Fever * Cough * Shortness of breath or difficulty breathing * Fatigue * Headache * Sore throat * Runny nose * Body aches * Diarrhea * Nausea or vomiting It is essential to seek medical attention immediately if you experience any of these symptoms, especially if you have a fever, cough, or difficulty breathing.
Fact 3: High-Risk Groups

Some groups of people are at a higher risk of developing severe illness from Covid-19, including: * Older adults (65 years and older) * Young children (under the age of 5) * People with underlying medical conditions, such as: + Heart disease + Diabetes + Lung disease + Kidney disease + Liver disease * People with weakened immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS or undergoing chemotherapy It is crucial for these high-risk groups to take extra precautions to prevent the spread of Covid-19, such as wearing a mask, maintaining social distancing, and staying up to date on vaccinations.
Fact 4: Prevention and Treatment

There are several ways to prevent the spread of Covid-19, including: * Getting vaccinated * Wearing a mask * Maintaining social distancing * Avoiding close contact with others * Staying home when sick * Practicing good hygiene, such as washing hands frequently and avoiding touching the face Treatment for Covid-19 typically involves managing symptoms and supporting the body’s immune system. In severe cases, hospitalization may be necessary to provide oxygen therapy, mechanical ventilation, or other life-supporting treatments.
Fact 5: Vaccination and Immunity
Vaccination is a critical tool in preventing the spread of Covid-19. The Covid-19 vaccine has been shown to be highly effective in preventing severe illness and hospitalization. It is essential to stay up to date on vaccinations and follow the recommended schedule to ensure optimal protection. Additionally, it is crucial to understand that immunity to Covid-19 can wane over time, and booster shots may be necessary to maintain protection.
💡 Note: It is essential to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice on Covid-19 prevention and treatment.
As we continue to navigate the Covid-19 pandemic, it is crucial to stay informed and take necessary precautions to protect ourselves and our loved ones. By understanding the facts about Covid-19, we can work together to prevent the spread of the virus and stay safe.
In the end, staying informed and taking proactive steps to prevent the spread of Covid-19 is key to protecting public health. By following the facts and guidelines outlined in this article, we can all play a role in mitigating the impact of the pandemic and keeping our communities safe.
What are the common symptoms of Covid-19?

+
The common symptoms of Covid-19 include fever, cough, shortness of breath or difficulty breathing, fatigue, headache, sore throat, runny nose, body aches, diarrhea, nausea or vomiting.
How is Covid-19 transmitted?
+
Covid-19 is primarily spread through respiratory droplets that are released when an infected person talks, coughs, or sneezes. These droplets can land in the mouths or noses of people nearby or be inhaled into the lungs.
Who is at high risk of developing severe illness from Covid-19?

+
High-risk groups include older adults (65 years and older), young children (under the age of 5), people with underlying medical conditions, and people with weakened immune systems.