7 Year Rule

Introduction to the 7 Year Rule

The 7 Year Rule is a financial concept that has been widely discussed and debated among financial experts and individuals alike. It suggests that credit reporting agencies can only report negative information on an individual’s credit report for a period of 7 years from the date of the initial incident. This rule has significant implications for individuals who are trying to rebuild their credit after experiencing financial difficulties. In this blog post, we will delve into the details of the 7 Year Rule, its implications, and provide guidance on how to navigate the credit reporting system.
Understanding the 7 Year Rule

The 7 Year Rule is based on the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA), which regulates the credit reporting industry. According to the FCRA, credit reporting agencies are only allowed to report negative information on an individual’s credit report for a limited period. This includes late payments, accounts sent to collections, and bankruptcies. The 7-year period begins from the date of the initial incident, and after this period, the negative information must be removed from the credit report. For example, if an individual missed a payment in January 2018, the credit reporting agency can only report this late payment until January 2025.
Types of Negative Information

There are several types of negative information that can be reported on an individual’s credit report, including: * Late payments: Payments that are 30 days or more late * Accounts sent to collections: Accounts that have been sent to a collections agency * Bankruptcies: Chapter 7 and Chapter 13 bankruptcies * Foreclosures: Foreclosures on a primary residence or investment property * Tax liens: Unpaid tax debts
Implications of the 7 Year Rule

The 7 Year Rule has significant implications for individuals who are trying to rebuild their credit. By limiting the amount of time that negative information can be reported, the 7 Year Rule provides individuals with an opportunity to start fresh and rebuild their credit. However, it’s essential to note that the 7 Year Rule only applies to negative information, and positive information can remain on a credit report indefinitely. This means that individuals who have a history of on-time payments and responsible credit behavior can continue to benefit from this positive information even after the 7-year period has expired.
How to Rebuild Credit

Rebuilding credit after experiencing financial difficulties can be a challenging and time-consuming process. However, by following these steps, individuals can improve their credit score and rebuild their credit: * Make on-time payments: Payment history accounts for 35% of an individual’s credit score, so making on-time payments is crucial * Keep credit utilization low: Keeping credit utilization below 30% can help to improve credit scores * Monitor credit reports: Regularly monitoring credit reports can help to identify errors and negative information that may be affecting credit scores * Avoid new credit inquiries: Applying for too many credit cards or loans can negatively affect credit scores
📝 Note: It's essential to monitor credit reports regularly to ensure that negative information is removed after the 7-year period has expired.
Conclusion

In conclusion, the 7 Year Rule is an essential concept in the world of credit reporting. By understanding how the 7 Year Rule works and how to rebuild credit, individuals can take control of their financial health and improve their credit scores. Remember, rebuilding credit takes time and effort, but by following the steps outlined above and staying informed about the credit reporting system, individuals can achieve their financial goals.
What is the 7 Year Rule?

+
The 7 Year Rule is a financial concept that suggests that credit reporting agencies can only report negative information on an individual’s credit report for a period of 7 years from the date of the initial incident.
How does the 7 Year Rule affect credit scores?
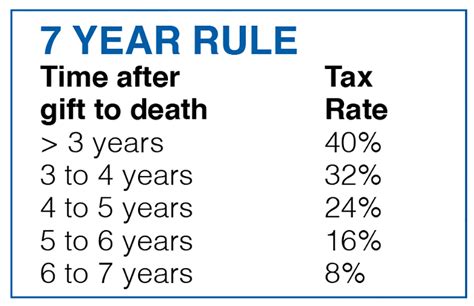
+
The 7 Year Rule can have a significant impact on credit scores. By limiting the amount of time that negative information can be reported, the 7 Year Rule provides individuals with an opportunity to start fresh and rebuild their credit.
Can I rebuild my credit after experiencing financial difficulties?

+
Yes, it is possible to rebuild credit after experiencing financial difficulties. By making on-time payments, keeping credit utilization low, monitoring credit reports, and avoiding new credit inquiries, individuals can improve their credit scores and rebuild their credit.



