Paperwork
Canada Tax Paperwork Retention Period

Introduction to Canada Tax Paperwork Retention Period
When it comes to managing tax-related documents, understanding the Canada tax paperwork retention period is crucial for both individuals and businesses. The Canada Revenue Agency (CRA) requires taxpayers to maintain accurate and detailed records to support their tax claims, in case of an audit or reassessment. In this blog post, we will delve into the importance of retaining tax paperwork, the recommended retention periods, and the types of documents that should be kept.
Importance of Retaining Tax Paperwork

Retaining tax paperwork is essential for several reasons: * It helps to support tax claims and ensure that you receive the correct amount of refunds or credits. * It provides a paper trail in case of an audit or reassessment, reducing the risk of penalties and interest. * It enables you to track your financial history, making it easier to identify trends and make informed decisions about your finances. * It helps to comply with CRA requirements, avoiding potential fines and penalties for non-compliance.
Recommended Retention Periods

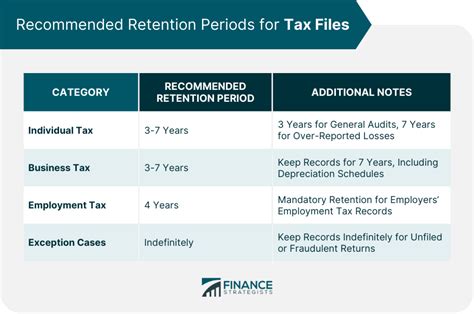
The CRA recommends that taxpayers retain their tax-related documents for a minimum of six years from the end of the tax year to which they relate. This includes: * Personal tax returns: Keep copies of your tax returns, including supporting documents, for at least six years. * Business tax returns: Retain business tax returns, financial statements, and supporting documents for at least six years. * GST/HST returns: Keep records of GST/HST returns, including invoices and receipts, for at least six years. * Payroll records: Retain payroll records, including employee information and payment details, for at least six years.
Types of Documents to Retain
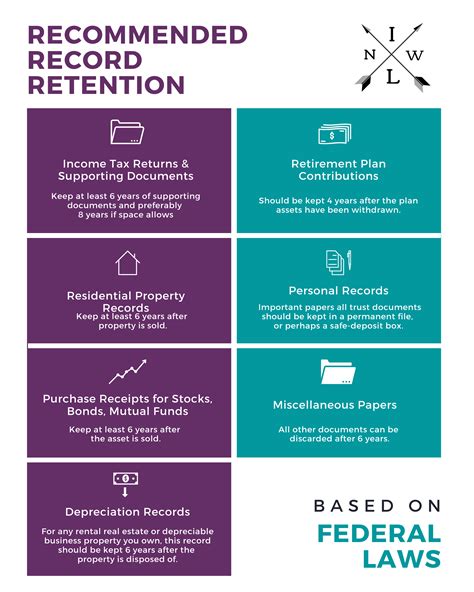
The following types of documents should be retained: * Income statements: Keep records of income from employment, self-employment, investments, and other sources. * Expense receipts: Retain receipts for business expenses, charitable donations, and medical expenses. * Invoices and contracts: Keep copies of invoices, contracts, and agreements related to your business or personal finances. * Bank statements: Retain bank statements, including cancelled cheques and deposit slips. * Investment records: Keep records of investments, including purchase and sale agreements, and dividend payments.
Electronic Record-Keeping

In today’s digital age, many taxpayers opt for electronic record-keeping. This can include: * Scanning documents: Scan paper documents and save them electronically. * Using accounting software: Utilize accounting software to manage financial records and generate reports. * Cloud storage: Store electronic records in a secure cloud storage service, such as Dropbox or Google Drive.
📝 Note: When using electronic record-keeping, ensure that your systems are secure and that you have a backup plan in place in case of data loss or system failure.
Disposing of Tax Paperwork

When disposing of tax paperwork, it is essential to do so securely to protect your personal and financial information. Consider: * Shredding documents: Shred paper documents before disposing of them. * Deleting electronic files: Permanently delete electronic files, using a secure deletion method. * Using a secure disposal service: Utilize a secure disposal service, such as a shredding company, to dispose of sensitive documents.
Conclusion and Final Thoughts
In conclusion, retaining tax paperwork is a critical aspect of managing your finances and ensuring compliance with CRA requirements. By understanding the recommended retention periods and types of documents to retain, you can ensure that you are well-prepared in case of an audit or reassessment. Remember to dispose of tax paperwork securely, and consider using electronic record-keeping to streamline your financial management.
What is the minimum retention period for personal tax returns?

+
The minimum retention period for personal tax returns is six years from the end of the tax year to which they relate.
Can I dispose of tax paperwork after the retention period has ended?

+
Yes, you can dispose of tax paperwork after the retention period has ended, but ensure that you do so securely to protect your personal and financial information.
Is electronic record-keeping acceptable for tax purposes?
+
Yes, electronic record-keeping is acceptable for tax purposes, as long as your systems are secure and you have a backup plan in place in case of data loss or system failure.