5 Ways To Scan

Introduction to Scanning

Scanning is a fundamental process in various industries, including healthcare, technology, and security. It involves the use of specialized devices to capture and analyze data from physical objects or environments. There are several ways to scan, each with its unique applications and benefits. In this article, we will explore five common methods of scanning, their principles, and uses.
1. Optical Scanning
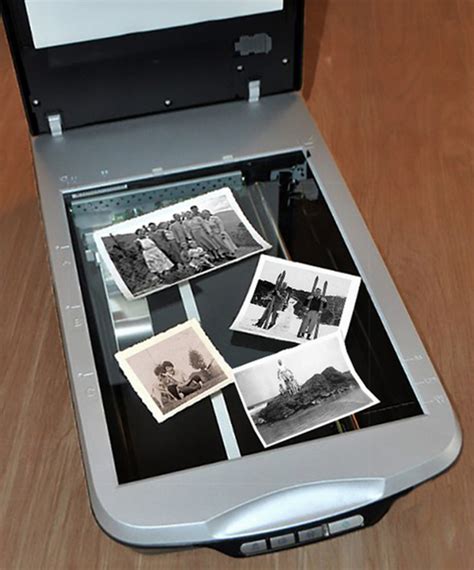

Optical scanning, also known as optical character recognition (OCR), is a technique used to convert printed or handwritten text into digital format. This method involves the use of optical scanners, which employ light to detect and capture images of text or objects. Optical scanning is widely used in document scanning, barcode reading, and image processing. Its applications include: * Document digitization * Barcode scanning * Image processing * Text recognition
2. Thermal Scanning

Thermal scanning, also known as thermography, is a technique used to detect and measure temperature differences in objects or environments. This method involves the use of thermal cameras, which capture images based on heat radiation. Thermal scanning is commonly used in: * Predictive maintenance * Building inspection * Medical imaging * Security surveillance
3. 3D Scanning

3D scanning is a technique used to capture the shape and appearance of physical objects or environments. This method involves the use of 3D scanners, which employ laser, structured light, or other technologies to create detailed models. 3D scanning is widely used in: * Product design * Architecture * Engineering * Video game development
4. Biometric Scanning

Biometric scanning is a technique used to capture and analyze physical or behavioral characteristics of individuals, such as fingerprints, facial features, or iris patterns. This method involves the use of biometric scanners, which employ specialized sensors and algorithms to verify identities. Biometric scanning is commonly used in: * Security and access control * Border control * Law enforcement * Identity verification
5. Wireless Scanning
Wireless scanning, also known as wireless network scanning, is a technique used to detect and analyze wireless networks and devices. This method involves the use of wireless scanners, which employ radio frequency (RF) signals to capture and analyze network data. Wireless scanning is widely used in: * Network security * Wireless troubleshooting * Device discovery * Spectrum analysis
📝 Note: When using scanning techniques, it is essential to consider factors such as data accuracy, security, and privacy to ensure reliable and efficient results.
To illustrate the differences between these scanning methods, consider the following table:
| Scanning Method | Description | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Optical Scanning | Converts printed or handwritten text into digital format | Document scanning, barcode reading, image processing |
| Thermal Scanning | Detects and measures temperature differences | Predictive maintenance, building inspection, medical imaging |
| 3D Scanning | Captures the shape and appearance of physical objects or environments | Product design, architecture, engineering, video game development |
| Biometric Scanning | Captures and analyzes physical or behavioral characteristics | Security and access control, border control, law enforcement, identity verification |
| Wireless Scanning | Detects and analyzes wireless networks and devices | Network security, wireless troubleshooting, device discovery, spectrum analysis |

In summary, scanning techniques play a vital role in various industries, enabling efficient data capture, analysis, and processing. By understanding the principles and applications of different scanning methods, individuals and organizations can harness the power of scanning to improve their operations, security, and decision-making.
What is the primary purpose of optical scanning?

+
The primary purpose of optical scanning is to convert printed or handwritten text into digital format, enabling efficient data capture and processing.
What are the common applications of thermal scanning?
+
Thermal scanning is commonly used in predictive maintenance, building inspection, medical imaging, and security surveillance to detect and measure temperature differences.
How does 3D scanning work?
+
3D scanning works by capturing the shape and appearance of physical objects or environments using laser, structured light, or other technologies, creating detailed models for various applications.



