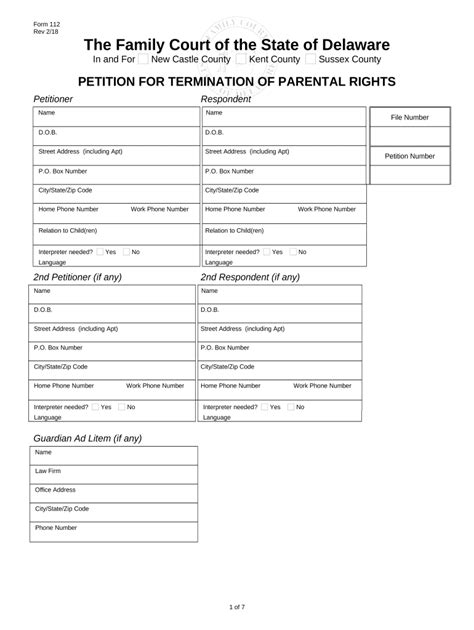
5 Ways Terminate Rights

Understanding Termination of Rights

When discussing the concept of terminating rights, it’s essential to approach the topic with a clear understanding of what rights are being referred to and the context in which they are being terminated. Rights can encompass a wide range of entitlements, from contractual rights in business agreements to intellectual property rights, and even human rights. The termination of rights can significantly impact individuals, businesses, and societies, making it a complex and sensitive subject. In this discussion, we will delve into five ways rights can be terminated, focusing on contractual and legal rights as primary examples.
1. Expiration

One of the most common ways rights are terminated is through expiration. Many rights, especially those granted through contracts or agreements, have a specified duration. Once this duration ends, the rights granted under the contract expire, and the parties involved are no longer bound by the terms of the agreement. For instance, a lease agreement grants the tenant the right to occupy a property for a specified period. Upon expiration of the lease, the tenant’s right to occupy the property terminates, unless the lease is renewed or a new agreement is made.
2. Breach of Contract

A breach of contract can lead to the termination of rights. When one party fails to fulfill their obligations as outlined in the contract, the other party may choose to terminate the agreement, thereby terminating the rights and obligations of both parties under the contract. For example, if a business fails to deliver goods as agreed upon, the buyer may terminate the contract due to breach, ending their rights and obligations, as well as those of the seller, under that specific agreement.
3. Mutual Agreement

Rights can also be terminated through mutual agreement between the parties involved. This method involves both parties agreeing to end the contract or agreement, thereby terminating the rights and obligations that come with it. Mutual agreements to terminate are common in employment contracts, business partnerships, and licensing agreements, among others. The terms of the termination, including any compensation or next steps, are usually negotiated and agreed upon by both parties.
4. Notice of Termination

In some cases, rights can be terminated by serving a notice of termination. This is often stipulated in the contract and outlines the procedure for terminating the agreement, including the notice period that must be given. For instance, in employment law, an employer may be required to give an employee a certain amount of notice before terminating their contract. Similarly, in rental agreements, a landlord may need to provide tenants with a notice period before terminating the lease.
5. Legal Action

Finally, rights can be terminated through legal action. This can occur when a court or legal authority rules that a contract or agreement is invalid or should be terminated due to illegal activities, fraud, or other legal grounds. For example, a court may terminate a business contract if it finds that the contract was entered into under false pretenses or that it violates public policy. Legal termination of rights can have significant consequences and is typically a last resort after other methods of resolution have been explored.
📝 Note: The specific laws and regulations regarding the termination of rights can vary significantly depending on the jurisdiction and the type of rights involved. It's crucial to consult with legal professionals to understand the specific circumstances and legal implications of terminating rights in any given situation.
In summary, the termination of rights can occur through various means, including expiration, breach of contract, mutual agreement, notice of termination, and legal action. Each method has its own set of implications and requirements, and understanding these is crucial for navigating contractual and legal agreements effectively.
What are the common reasons for terminating a contract?

+
Common reasons for terminating a contract include expiration, breach of contract, mutual agreement, and notice of termination. Each situation is unique and may involve different legal and contractual considerations.
Can rights be terminated without legal action?
+
Yes, rights can be terminated without legal action through methods such as mutual agreement, expiration, or serving a notice of termination as stipulated in the contract. However, legal action may be necessary in cases where there is a dispute or when the termination involves complex legal issues.
What happens to the obligations of the parties after the termination of rights?

+
After the termination of rights, the obligations of the parties under the contract typically cease to exist. However, parties may still have obligations related to the termination, such as returning property or paying compensation, as agreed upon in the contract or as required by law.



