Notarization Requirements

Introduction to Notarization Requirements
The process of notarization is a critical aspect of verifying the authenticity of documents and preventing fraud. Notarization involves a notary public, an impartial third-party witness, verifying the identity of individuals signing documents and ensuring they do so voluntarily. This process is essential for various legal, financial, and administrative transactions. In this article, we will delve into the notarization requirements, exploring the role of a notary public, the types of notarizations, and the steps involved in the notarization process.
Role of a Notary Public

A notary public is a state-commissioned official who serves as an impartial witness to the signing of important documents. Their primary role is to: - Verify the identity of the signers. - Ensure the signers are signing the documents voluntarily. - Witness the signing of the documents. - Validate the authenticity of the documents through their notary stamp or seal.
Types of Notarizations
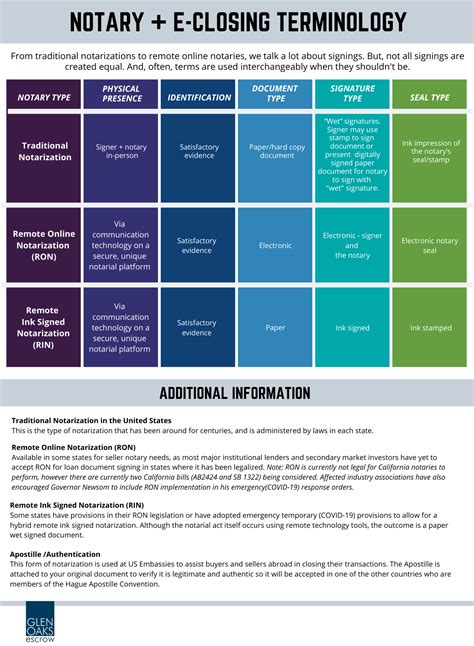
There are several types of notarizations, each serving a specific purpose: - Acknowledgment: The most common type, where the notary verifies the identity of the signer and ensures they are signing voluntarily. - Jurat: Requires the signer to swear or affirm the contents of the document are true, often used for affidavits. - Copy Certification: The notary certifies that a copy of a document is true and accurate. - Oath or Affirmation: The notary administers an oath or affirmation to the signer.
Steps in the Notarization Process

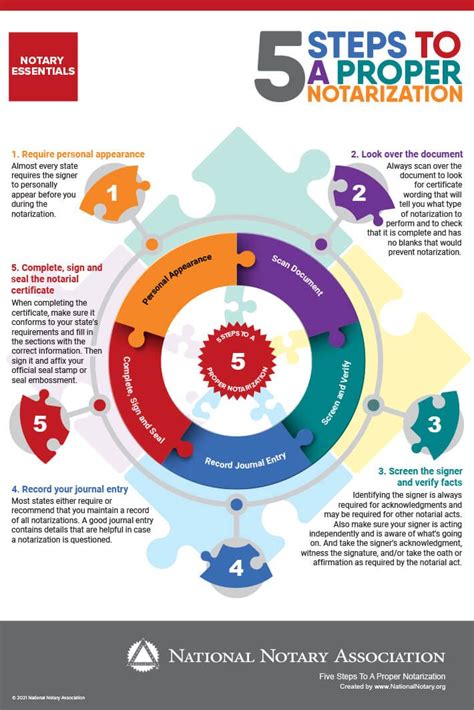
The notarization process is straightforward and involves the following steps: 1. Prepare Your Document: Ensure the document is complete and ready for signing. Some documents may require specific wording or formats, so it’s crucial to review the requirements. 2. Find a Notary: Locate a notary public. Notaries can be found at banks, post offices, libraries, and shipping stores, or you can hire a mobile notary. 3. Meet with the Notary: Bring the document and a valid form of identification (such as a driver’s license or passport) to the meeting with the notary. 4. Sign the Document: In the presence of the notary, sign the document. The notary will then verify your identity and ensure you are signing voluntarily. 5. Notary Verification: The notary will then complete their part of the document, which includes their signature, stamp, or seal, confirming they have witnessed the signing.
📝 Note: It's essential to ensure the notary's commission has not expired and that they are licensed to perform notarizations in your state or country.
Documents Requiring Notarization

Several types of documents require notarization to be considered valid: - Real Estate Documents: Deeds, mortgages, and property transfers. - Last Will and Testament: To ensure the authenticity of the will and the intent of the deceased. - Powers of Attorney: Documents granting someone the authority to act on another’s behalf. - Affidavits: Written statements that are sworn to be true, often used in legal proceedings. - International Documents: For use abroad, such as apostilles and authentications.
Benefits of Notarization

Notarization offers several benefits, including: - Prevention of Fraud: By verifying the identity of signers and ensuring documents are signed voluntarily. - Authentication: Provides a level of assurance regarding the authenticity of documents. - Compliance with Laws: Many jurisdictions require notarization for certain documents to be legally binding. - International Recognition: Notarized documents are more easily recognized and accepted internationally.
Challenges and Future of Notarization

The notarization process, while effective, faces challenges such as: - Accessibility: Finding a notary can be inconvenient for some individuals. - Cost: Notarization services can come at a cost, which may be a barrier for some. - Digitalization: The move towards digital documents and remote notarizations is changing the landscape of notarization, offering more convenience and accessibility but also raising concerns about security and authenticity.
In response to these challenges, remote notarization and electronic notarization are becoming more prevalent, allowing for the notarization process to occur online. This shift aims to increase accessibility while maintaining the security and authenticity of the notarization process.
As we move forward, it’s clear that notarization will continue to play a vital role in verifying the authenticity of documents and preventing fraud. Understanding the notarization requirements and the evolving nature of the notarization process is crucial for both individuals and businesses navigating legal, financial, and administrative transactions.
The notarization process, with its emphasis on verification and authentication, serves as a cornerstone of trust in document signing. Whether through traditional in-person notarization or the emerging technologies of remote and electronic notarization, the core principles of ensuring the integrity and legality of documents remain paramount.
In essence, notarization requirements are designed to protect individuals and entities by ensuring that documents are genuine and that the signing parties are who they claim to be. This protection is fundamental in maintaining the integrity of legal and financial systems worldwide.
What is the primary role of a notary public?

+
The primary role of a notary public is to serve as an impartial witness to the signing of important documents, verifying the identity of signers and ensuring they sign voluntarily.
What types of documents require notarization?

+
Documents such as real estate deeds, last will and testaments, powers of attorney, affidavits, and certain international documents require notarization to be considered valid.
Can notarization be done remotely?

+
Yes, remote notarization and electronic notarization are becoming more prevalent, allowing for the notarization process to occur online, increasing accessibility while maintaining security and authenticity.