5 HSA Tax Forms
Understanding HSA Tax Forms: A Comprehensive Guide

When it comes to Health Savings Accounts (HSAs), tax forms play a crucial role in ensuring compliance with the IRS regulations. There are several HSA tax forms that individuals and employers need to be aware of, and understanding these forms is essential for accurate tax reporting and avoiding potential penalties. In this article, we will delve into the details of the five key HSA tax forms, their purposes, and the information they require.
Form 8889: Health Savings Account (HSA) Contribution and Distribution

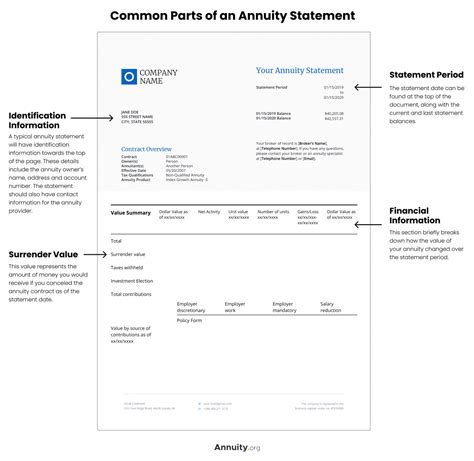
Form 8889 is one of the most critical HSA tax forms, as it reports contributions to and distributions from an HSA. This form is used to calculate the deductible amount of HSA contributions, as well as to report any distributions from the account. The form requires detailed information about the account holder, including their name, address, and social security number. It also requires information about the HSA contributions, such as the amount contributed and the date of contribution. Additionally, the form requires reporting of any distributions from the HSA, including the amount distributed and the date of distribution.
Form 1099-SA: Distributions from an HSA, Archer MSA, or Medicare Advantage MSA

Form 1099-SA is used to report distributions from an HSA, Archer Medical Savings Account (MSA), or Medicare Advantage MSA. This form is typically provided by the HSA custodian or trustee to the account holder and the IRS. The form reports the total amount distributed from the account during the tax year, as well as any amount that was used for qualified medical expenses. The account holder is required to report this information on their tax return, using Form 8889 to calculate the taxable amount of the distribution.
Form 5498-SA: HSA, Archer MSA, or Medicare Advantage MSA Information

Form 5498-SA is used to report contributions to an HSA, Archer MSA, or Medicare Advantage MSA. This form is typically provided by the HSA custodian or trustee to the account holder and the IRS. The form reports the total amount contributed to the account during the tax year, as well as any amount that was carried over from the previous year. The account holder is required to report this information on their tax return, using Form 8889 to calculate the deductible amount of the contribution.
Form W-2: Wage and Tax Statement

Form W-2 is used to report wages and taxes withheld from an employee’s paycheck. For employees who contribute to an HSA through a cafeteria plan or salary reduction arrangement, the employer is required to report the amount of HSA contributions on the employee’s W-2 form. The employer must also report any employer contributions to the HSA on the W-2 form. This information is used to calculate the employee’s taxable income and to determine the amount of HSA contributions that are deductible.
Form 5329: Additional Taxes on Qualified Plans (Including IRAs) and Other Tax-Favored Accounts

Form 5329 is used to report additional taxes on qualified plans, including HSAs. This form is used to calculate the excise tax on excess contributions to an HSA, as well as the tax on prohibited transactions. The form requires detailed information about the account holder, including their name, address, and social security number. It also requires information about the HSA, including the amount of excess contributions and the date of the prohibited transaction.
| Form Number | Form Name | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 8889 | Health Savings Account (HSA) Contribution and Distribution | Reports contributions to and distributions from an HSA |
| 1099-SA | Distributions from an HSA, Archer MSA, or Medicare Advantage MSA | Reports distributions from an HSA, Archer MSA, or Medicare Advantage MSA |
| 5498-SA | HSA, Archer MSA, or Medicare Advantage MSA Information | Reports contributions to an HSA, Archer MSA, or Medicare Advantage MSA |
| W-2 | Wage and Tax Statement | Reports wages and taxes withheld from an employee's paycheck, including HSA contributions |
| 5329 | Additional Taxes on Qualified Plans (Including IRAs) and Other Tax-Favored Accounts | Reports additional taxes on qualified plans, including HSAs |

📝 Note: It is essential to carefully review and complete these forms to avoid any errors or omissions that may result in penalties or delays in processing.
In summary, understanding the different HSA tax forms is crucial for individuals and employers who contribute to or administer HSAs. By familiarizing themselves with these forms, they can ensure compliance with IRS regulations and avoid potential penalties. It is also essential to seek professional advice if there are any questions or concerns about completing these forms.
What is the purpose of Form 8889?
+
Form 8889 is used to report contributions to and distributions from an HSA, and to calculate the deductible amount of HSA contributions.
What is the difference between Form 1099-SA and Form 5498-SA?

+
Form 1099-SA reports distributions from an HSA, while Form 5498-SA reports contributions to an HSA.
Do I need to file Form W-2 if I contribute to an HSA through a cafeteria plan?

+
No, your employer will report your HSA contributions on your W-2 form.