HSA Paperwork Requirements

Understanding HSA Paperwork Requirements
The Health Savings Account (HSA) is a valuable tool for individuals with high-deductible health plans (HDHPs) to save for medical expenses on a tax-free basis. However, to ensure compliance with IRS regulations and to maximize the benefits of an HSA, it’s crucial to understand the associated paperwork requirements. In this article, we will delve into the details of HSA paperwork, including eligibility, contributions, distributions, and reporting requirements.
Eligibility and Enrollment

To be eligible for an HSA, an individual must be covered under a high-deductible health plan (HDHP) and not be covered under any other health plan that is not a high-deductible plan. Additionally, the individual cannot be enrolled in Medicare, and they cannot be claimed as a dependent on someone else’s tax return. The first step in the HSA paperwork process is to obtain an HDHP and then enroll in an HSA through the health insurance provider or an HSA custodian.
Contribution Requirements

Contributions to an HSA can be made by the individual or their employer. The contribution limits are set annually by the IRS and are based on the type of HDHP coverage (individual or family). It’s essential to keep track of contributions made throughout the year, as excess contributions can result in penalties. Individuals are responsible for ensuring they do not exceed the annual contribution limits.
Distribution Requirements

Distributions from an HSA can be used to pay for qualified medical expenses. To avoid penalties and taxes, it’s crucial to keep receipts and records of all medical expenses paid with HSA funds. Qualified medical expenses include doctor visits, prescriptions, hospital stays, and other health care services. HSA holders should also be aware of the rules regarding reimbursement for expenses incurred in previous years.
Reporting Requirements

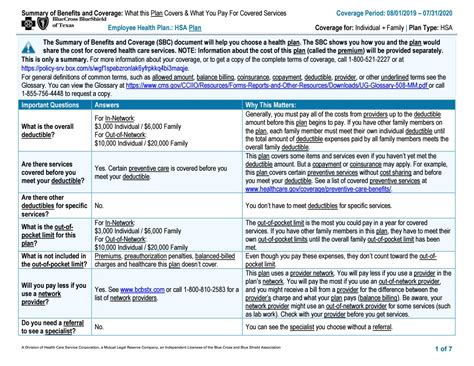
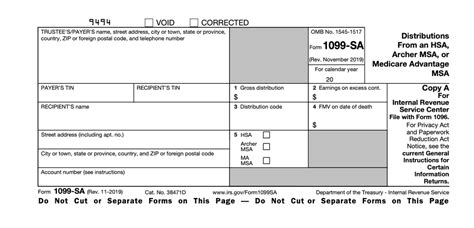
Each year, HSA custodians must provide account holders with a Form 1099-SA by January 31st, detailing all distributions made from the HSA during the previous tax year. Additionally, individuals must file Form 8889 with their tax return to report HSA contributions and distributions. Accurate reporting is critical to avoid any tax implications or penalties associated with HSA misuse.
Record Keeping
Maintaining detailed records of HSA contributions, distributions, and qualified medical expenses is vital. These records should include: - Contribution receipts - Distribution records - Medical expense receipts - Documentation of qualified medical expenses
📝 Note: Keeping organized and detailed records can help in case of an audit and ensure compliance with IRS regulations.
Annual Limits and Requirements
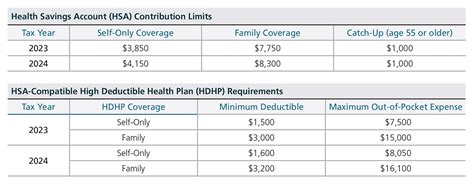
The IRS sets annual limits for HSA contributions, which can change from year to year. For example, in 2022, the annual limit for individual coverage was 3,650, and for family coverage, it was 7,300. Understanding these limits and ensuring contributions do not exceed them is crucial for avoiding penalties.
Employer Contributions
Employers may also contribute to an employee’s HSA, which can be a valuable benefit. However, employer contributions are subject to certain rules and limits, and they must be reported on the employee’s W-2 form.
Tax Benefits

One of the significant advantages of an HSA is its triple tax benefit: - Tax deductions for contributions - Tax-free growth of the account - Tax-free distributions for qualified medical expenses
Transitioning and Inheritance
When transitioning jobs or upon the death of the HSA holder, specific rules apply to the HSA. For instance, an HSA is portable, meaning it can be taken to a new employer. In the event of the account holder’s death, the HSA can be transferred to a spouse or become part of the estate.
| Event | Rule |
|---|---|
| Job Change | HSA is portable and can be taken to the new employer. |
| Death of Account Holder | HSA can be transferred to a spouse or becomes part of the estate. |

As we move forward in understanding the intricacies of HSA paperwork requirements, it becomes clear that maintaining compliance and maximizing the benefits of an HSA requires careful attention to detail and a thorough understanding of the rules and regulations governing these accounts.
In wrapping up our discussion on HSA paperwork requirements, it’s essential to summarize that compliance with IRS regulations, accurate record-keeping, and a clear understanding of contribution and distribution rules are key to successfully utilizing an HSA. By following these guidelines and staying informed about any changes to HSA regulations, individuals can effectively manage their health care costs and make the most of their Health Savings Account.
What are the eligibility criteria for opening an HSA?

+
To be eligible for an HSA, you must have a high-deductible health plan (HDHP) and not be covered under any other health plan that is not a high-deductible plan. You also cannot be enrolled in Medicare or be claimed as a dependent on someone else’s tax return.
Can I use HSA funds for non-medical expenses?

+
Using HSA funds for non-medical expenses before the age of 65 results in the amount being subject to income tax and a 20% penalty. After the age of 65, the penalty no longer applies, but the amount is still subject to income tax.
How do I report HSA contributions and distributions on my tax return?

+
You will receive a Form 1099-SA from your HSA custodian, detailing all distributions made from your HSA during the previous tax year. You must also file Form 8889 with your tax return to report HSA contributions and distributions.



