File 2018 Taxes Paperwork

Understanding the Basics of Filing 2018 Taxes

Filing taxes can be a daunting task, especially when it comes to gathering all the necessary paperwork. For the 2018 tax year, it’s essential to have all the required documents to ensure a smooth and accurate filing process. The IRS requires taxpayers to report their income, deductions, and credits to determine their tax liability. In this article, we will guide you through the necessary paperwork and steps to file your 2018 taxes.
Gathering Necessary Paperwork
To start the filing process, you’ll need to collect various documents that showcase your income, deductions, and credits. Some of the essential paperwork includes: * W-2 forms: These forms display your income and taxes withheld from your employer. * 1099 forms: If you’re self-employed or have freelance work, you’ll receive 1099 forms that show your income from these sources. * Interest statements: You’ll need statements from your bank or financial institution that display the interest earned on your accounts. * Dividend statements: If you have investments, you’ll need statements that show the dividends earned. * Charitable donation receipts: Keep receipts for any charitable donations you made during the tax year. * Medical expense receipts: If you have significant medical expenses, keep receipts for these expenses. * Mortgage interest statements: If you’re a homeowner, you’ll need statements that show the mortgage interest paid.
Understanding Tax Forms
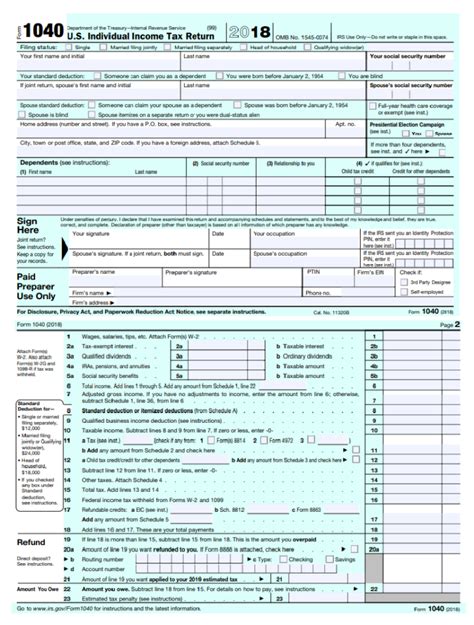
The IRS provides various tax forms to report different types of income and deductions. Some of the most common tax forms include: * Form 1040: This is the standard form for personal income tax returns. * Form 1040A: This form is for taxpayers who have simpler tax situations and don’t itemize deductions. * Form 1040EZ: This form is for single taxpayers with no dependents and only report income from one job. * Schedule A: This form is for itemizing deductions, such as charitable donations and medical expenses. * Schedule C: This form is for self-employed individuals to report their business income and expenses.
Filing Status

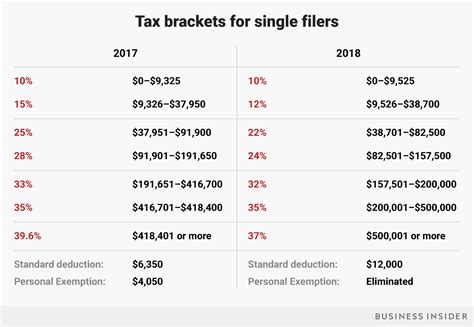
Your filing status plays a significant role in determining your tax liability. The most common filing statuses include: * Single: Unmarried individuals or those who are divorced or separated. * Married filing jointly: Married couples who file their taxes together. * Married filing separately: Married couples who file their taxes separately. * Head of household: Unmarried individuals who have dependents and meet specific requirements. * Qualifying widow(er): Individuals who have lost their spouse and meet specific requirements.
Tax Credits and Deductions
Tax credits and deductions can significantly reduce your tax liability. Some common tax credits include: * Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC): A credit for low-to-moderate income working individuals and families. * Child Tax Credit: A credit for families with qualifying children. * Education credits: Credits for education expenses, such as the American Opportunity Tax Credit and the Lifetime Learning Credit. Some common tax deductions include: * Mortgage interest deduction: A deduction for mortgage interest paid on your primary residence. * Charitable donation deduction: A deduction for charitable donations made during the tax year. * Medical expense deduction: A deduction for medical expenses that exceed a certain threshold.
📝 Note: It's essential to keep accurate records of your tax-related documents, as the IRS may request them during an audit or review.
Filing Options
You can file your 2018 taxes electronically or by mail. Electronic filing is faster and more accurate, and you’ll receive your refund sooner. You can also use tax software or hire a tax professional to help with the filing process.
| Filing Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Electronic Filing | Faster and more accurate, with a sooner refund |
| Mail Filing | Slower and more prone to errors, with a later refund |
| Tax Software | Guided filing process, with error checking and calculations |
| Tax Professional | Expert guidance and preparation, with a higher cost |
Deadlines and Extensions

The deadline for filing 2018 taxes was April 15, 2019. However, if you need more time, you can file for an extension, which will give you an additional six months to file your taxes. Keep in mind that an extension only extends the filing deadline, not the payment deadline. You’ll still need to pay any estimated taxes owed by the original deadline to avoid penalties and interest.
In summary, filing 2018 taxes requires gathering necessary paperwork, understanding tax forms, and choosing the right filing status and options. By following these steps and taking advantage of tax credits and deductions, you can minimize your tax liability and ensure a smooth filing process.
The key points to remember are to gather all necessary paperwork, choose the correct filing status, and take advantage of tax credits and deductions. It’s also essential to file electronically and meet the deadline to avoid penalties and interest. By following these guidelines, you’ll be able to navigate the tax filing process with confidence.
What is the deadline for filing 2018 taxes?

+
The deadline for filing 2018 taxes was April 15, 2019. However, if you need more time, you can file for an extension, which will give you an additional six months to file your taxes.
What are the most common tax forms?
+
The most common tax forms include Form 1040, Form 1040A, Form 1040EZ, Schedule A, and Schedule C. These forms are used to report different types of income and deductions.
What are tax credits and deductions?

+
Tax credits and deductions can reduce your tax liability. Tax credits, such as the Earned Income Tax Credit and the Child Tax Credit, can provide a direct reduction in your tax bill. Tax deductions, such as the mortgage interest deduction and the charitable donation deduction, can reduce your taxable income.



