5 Bankruptcy Forms

Introduction to Bankruptcy Forms

When individuals or businesses are unable to pay their debts, they may consider filing for bankruptcy. The process of filing for bankruptcy involves submitting various forms to the court, which provide detailed information about the debtor’s financial situation. In the United States, the bankruptcy code requires debtors to complete and file several forms with the court. These forms are designed to ensure that debtors provide accurate and complete information about their financial affairs. In this article, we will discuss five key bankruptcy forms that debtors must file when seeking bankruptcy protection.
Form 101: Voluntary Petition for Individuals Filing for Bankruptcy
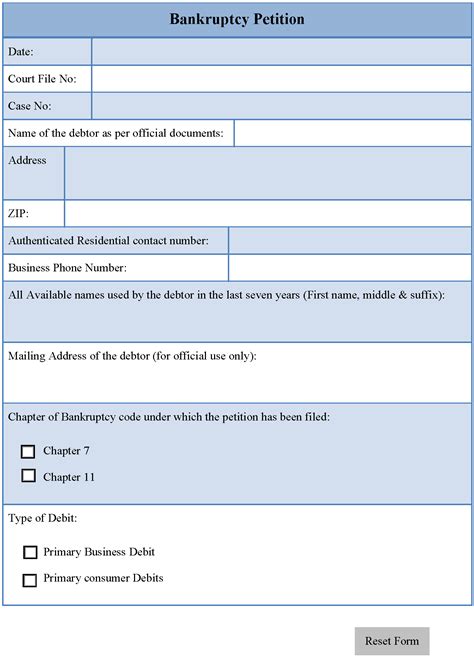
The Voluntary Petition for Individuals Filing for Bankruptcy (Form 101) is the initial form that debtors must file to commence a bankruptcy case. This form provides basic information about the debtor, including their name, address, and social security number. The form also requires debtors to indicate the type of bankruptcy they are seeking, such as Chapter 7 or Chapter 13. Additionally, debtors must provide information about their employer, income, and any prior bankruptcy filings.
Form 106A/B: Schedules A/B: Property

The Schedules A/B: Property (Form 106A/B) requires debtors to provide a detailed list of their assets, including real property, personal property, and any other property of value. This form helps the court and creditors understand the debtor’s financial situation and determine which assets may be exempt from the bankruptcy estate. Debtors must disclose all property, including:
- Real estate
- Vehicles
- Bank accounts
- Investments
- Personal property, such as jewelry and household goods
Form 106C: Schedules C: The Property You Claim as Exempt

The Schedules C: The Property You Claim as Exempt (Form 106C) allows debtors to claim certain property as exempt from the bankruptcy estate. Exempt property is protected from creditors and cannot be used to satisfy debts. Debtors must identify the property they claim as exempt and provide a brief description of each item. Common examples of exempt property include:
- Primary residence
- Retirement accounts
- Personal injury awards
- Household goods and furnishings
Form 106D: Schedules D: Creditors Who Have Claims Secured by Property
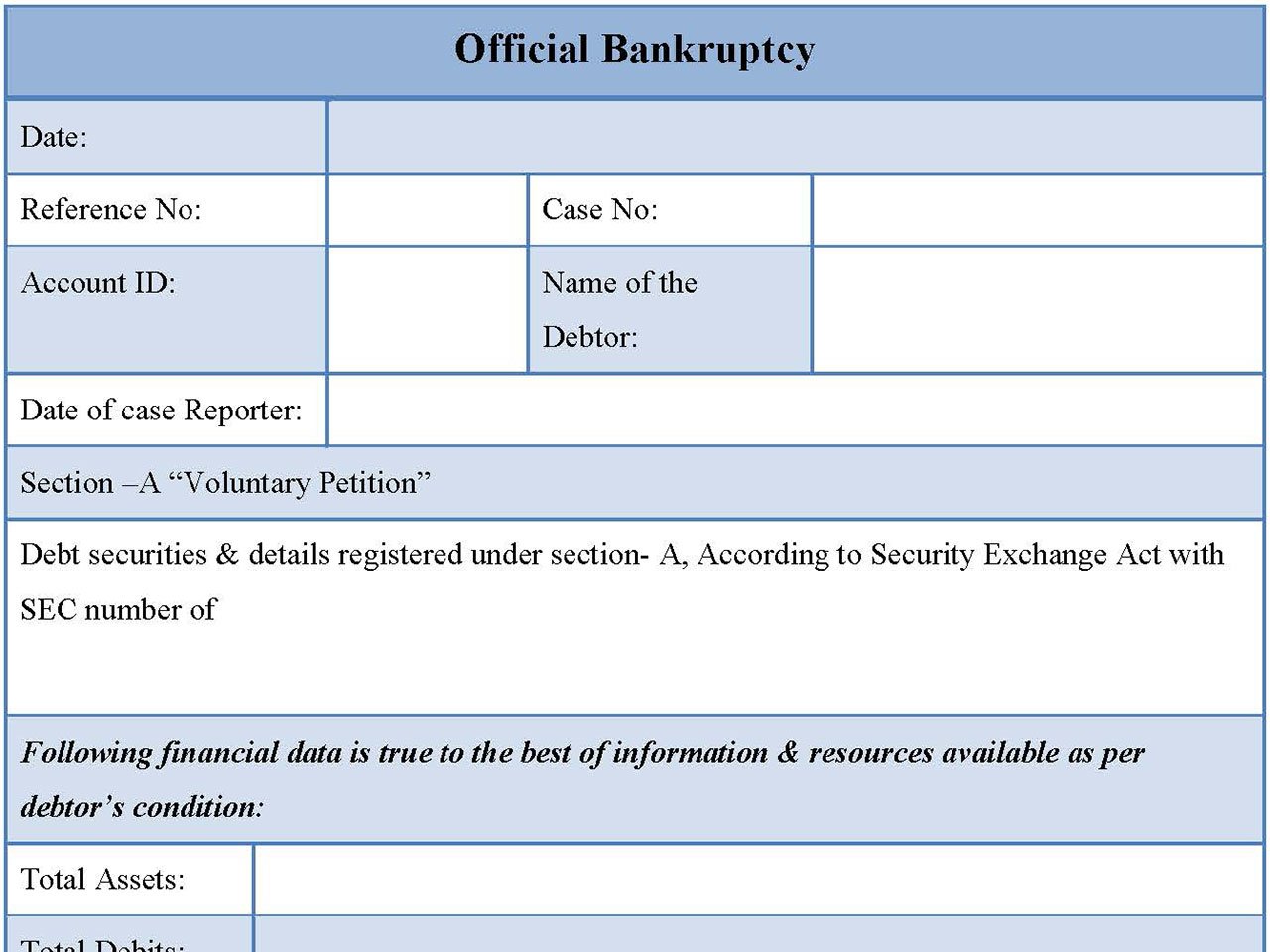
The Schedules D: Creditors Who Have Claims Secured by Property (Form 106D) requires debtors to list all creditors who have a security interest in their property. This form helps the court and creditors understand which debts are secured by collateral and which creditors may have a priority claim on the debtor’s property. Debtors must provide information about each secured creditor, including:
- Creditor name and address
- Type of property securing the debt
- Amount of the debt
- Current status of the debt
Form 106E/F: Schedules E/F: Creditors Who Have Unsecured Claims

The Schedules E/F: Creditors Who Have Unsecured Claims (Form 106E/F) requires debtors to list all creditors who do not have a security interest in their property. This form helps the court and creditors understand which debts are unsecured and which creditors may be eligible to receive a distribution from the bankruptcy estate. Debtors must provide information about each unsecured creditor, including:
- Creditor name and address
- Type of debt
- Amount of the debt
- Current status of the debt
💡 Note: Debtors must carefully review and complete all bankruptcy forms to ensure accuracy and completeness. Inaccurate or incomplete forms may result in delays or dismissal of the bankruptcy case.
Conclusion and Next Steps

Filing for bankruptcy requires debtors to complete and submit various forms to the court. The five bankruptcy forms discussed in this article provide a foundation for understanding the types of information debtors must disclose to the court and creditors. By carefully reviewing and completing these forms, debtors can ensure a smooth and successful bankruptcy process. It is essential for debtors to seek the advice of a qualified bankruptcy attorney to guide them through the process and ensure compliance with all applicable laws and regulations.
What is the purpose of the Voluntary Petition for Individuals Filing for Bankruptcy (Form 101)?
+
The Voluntary Petition for Individuals Filing for Bankruptcy (Form 101) is the initial form that debtors must file to commence a bankruptcy case. It provides basic information about the debtor, including their name, address, and social security number.
What types of property must debtors disclose on the Schedules A/B: Property (Form 106A/B)?
+
Debtors must disclose all property, including real estate, vehicles, bank accounts, investments, and personal property, such as jewelry and household goods.
What is the purpose of the Schedules C: The Property You Claim as Exempt (Form 106C)?
+
The Schedules C: The Property You Claim as Exempt (Form 106C) allows debtors to claim certain property as exempt from the bankruptcy estate. Exempt property is protected from creditors and cannot be used to satisfy debts.