Exporting Weapons Overseas Paperwork

Introduction to Exporting Weapons Overseas
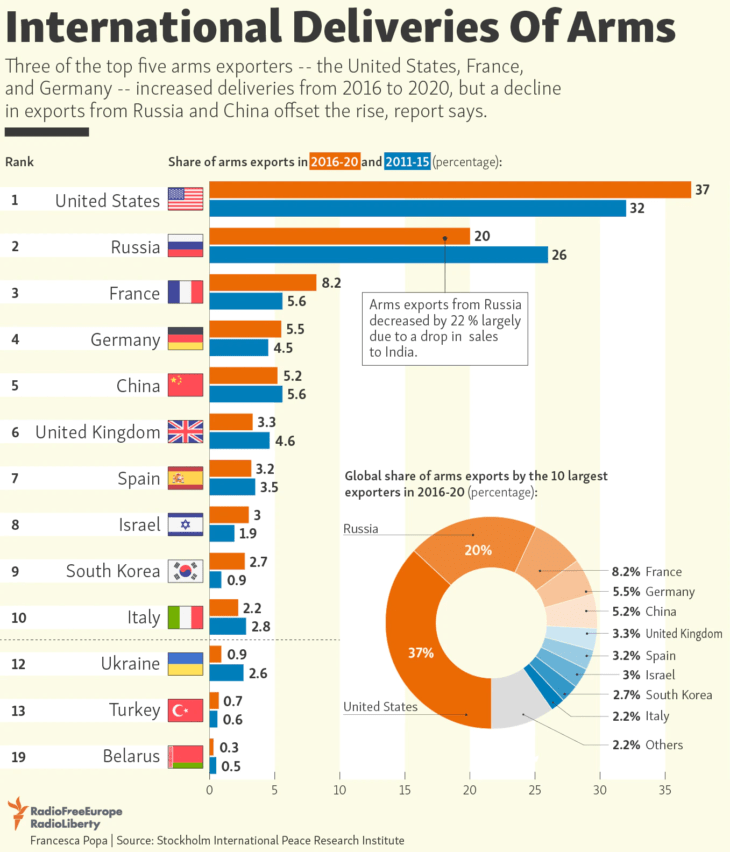
Exporting weapons overseas involves a complex process that requires careful attention to detail, adherence to regulations, and comprehensive paperwork. The international trade of weapons is heavily regulated due to the potential risks and consequences associated with their use. Countries have established stringent laws and regulations to control the export of weapons, ensuring they do not fall into the wrong hands. In this context, understanding the paperwork involved in exporting weapons overseas is crucial for individuals and organizations engaged in this trade.
Understanding Export Regulations

Before delving into the paperwork, it’s essential to understand the regulatory framework governing the export of weapons. The regulations vary by country, but most nations adhere to international agreements such as the Arms Trade Treaty (ATT), which aims to regulate the international trade in conventional arms. In the United States, for example, the export of weapons is regulated by the Department of State, the Department of Commerce, and the Department of Defense, among others. Compliance with these regulations is mandatory to avoid legal repercussions.
Types of Export Licenses

There are several types of export licenses required for exporting weapons overseas, depending on the nature of the transaction. These include: - Commercial Licenses: For the export of weapons for commercial purposes. - Government Licenses: For the export of weapons to foreign governments or for use by the U.S. government. - Temporary Licenses: For the temporary export of weapons, such as for demonstration or testing purposes.
Documentation Required

The documentation required for exporting weapons overseas includes: - Export License Application: Submitted to the relevant authority, detailing the type of weapon, quantity, and end-user. - Technical Data Package: Providing detailed technical information about the weapon system. - End-User Certificate: A document from the buyer guaranteeing the weapons will not be transferred to another party without authorization. - Export Compliance Documents: Such as commercial invoices and packing lists, which must be accurately completed to reflect the true nature and value of the exported goods.
Process of Obtaining an Export License
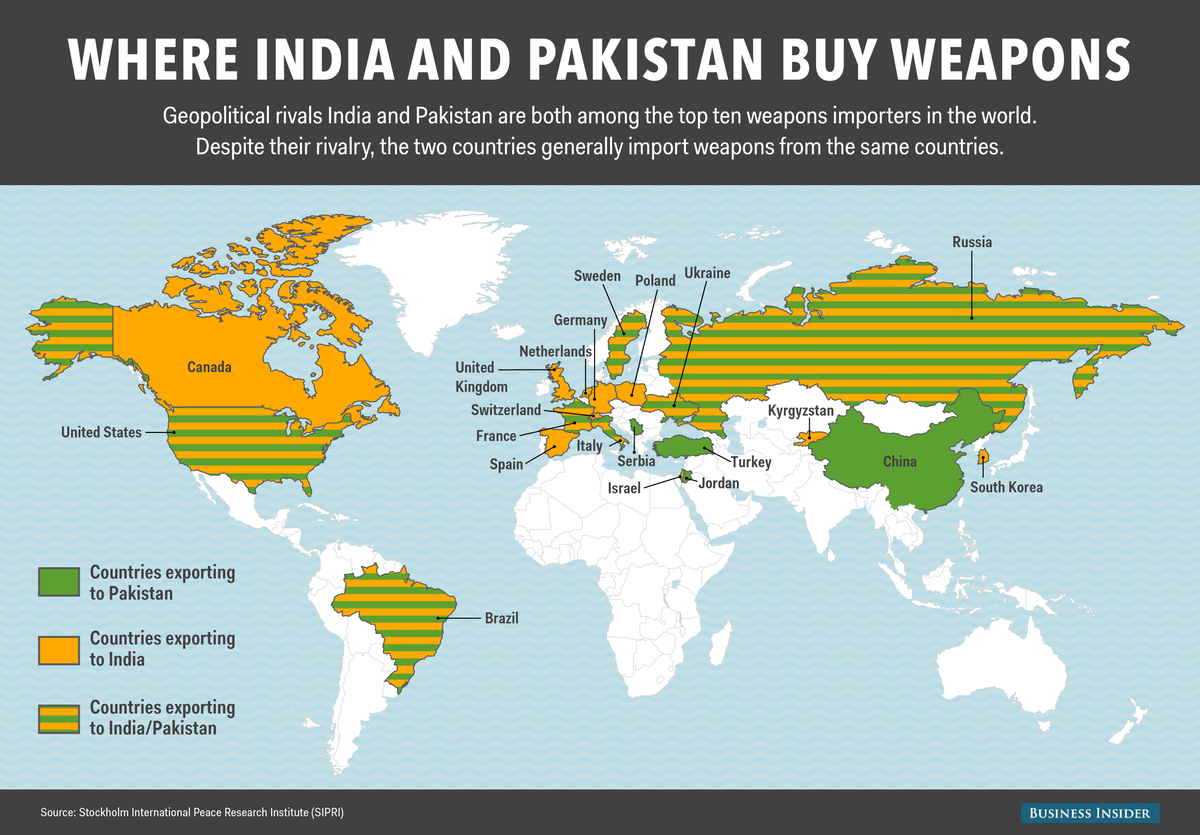
Obtaining an export license involves several steps: - Preparation of Documents: Gathering all necessary documents as per the regulatory requirements. - Submission of Application: Submitting the application to the relevant authority. - Review and Approval: The application is reviewed to ensure compliance with regulations and national security interests. - License Issuance: If approved, the export license is issued, allowing the export of the weapons.
📝 Note: The process can be lengthy and requires meticulous attention to detail to avoid delays or rejection of the application.
Challenges and Considerations
Exporting weapons overseas poses several challenges and considerations, including: - Political Sensitivities: Exporting weapons can be politically sensitive, affecting diplomatic relations between countries. - Human Rights Concerns: Ensuring that weapons are not used to commit human rights abuses. - Technical Challenges: Ensuring the compatibility and integration of weapon systems with the buyer’s existing infrastructure.
Conclusion and Final Thoughts

In conclusion, exporting weapons overseas is a complex and highly regulated process. It requires a deep understanding of the regulatory environment, meticulous preparation of documentation, and adherence to international agreements and national laws. The importance of compliance cannot be overstated, given the potential consequences of non-compliance. As the global landscape continues to evolve, the regulations and processes surrounding the export of weapons will likely become even more stringent, emphasizing the need for professionalism and diligence in this field.
What is the primary purpose of the Arms Trade Treaty?

+
The primary purpose of the Arms Trade Treaty is to establish common international standards for the import, export, and transfer of conventional arms, aiming to prevent the irresponsible and poorly regulated trade in these weapons.
Which U.S. department is primarily responsible for regulating the export of weapons?
+
The U.S. Department of State is primarily responsible for regulating the export of weapons, particularly through its Directorate of Defense Trade Controls (DDTC), which administers the export of defense articles, including weapons.
What is an End-User Certificate, and why is it required for exporting weapons?
+
An End-User Certificate is a document provided by the buyer (end-user) that guarantees the weapons will be used for the stated purpose and will not be transferred to another party without the authorization of the exporting country. It is required to ensure that exported weapons do not end up in the hands of unauthorized entities or for unauthorized uses.