DOT Out of Service Violation Paperwork

Understanding DOT Out of Service Violation Paperwork

The Department of Transportation (DOT) plays a crucial role in ensuring the safety of the nation’s transportation systems. One of the ways it achieves this is by enforcing strict regulations and guidelines for commercial vehicles and their operators. When a vehicle or driver is found to be in violation of these regulations, they may be issued an out-of-service (OOS) order, which prohibits them from operating until the violations are corrected. The paperwork involved in this process can be complex and overwhelming, especially for those who are unfamiliar with the regulations and procedures.
What is an Out of Service Order?

An out-of-service order is issued by a DOT inspector or law enforcement officer when a vehicle or driver is found to be in violation of federal safety regulations. This order prohibits the vehicle or driver from operating until the violations are corrected and the vehicle or driver is deemed safe to return to service. The order will specify the violations that must be corrected and provide instructions on how to appeal the order.
Types of Out of Service Violations

There are several types of out-of-service violations that can result in an OOS order. Some of the most common include: * Vehicle Maintenance Violations: These include violations related to the maintenance of the vehicle, such as faulty brakes, defective tires, or inadequate lighting. * Driver Qualification Violations: These include violations related to the driver’s qualifications, such as failing to meet the requirements for a commercial driver’s license (CDL) or having a disqualified CDL. * Hours of Service Violations: These include violations related to the driver’s hours of service, such as exceeding the maximum allowed driving time or failing to take required breaks. * Weight and Size Violations: These include violations related to the weight and size of the vehicle, such as exceeding the maximum allowed weight or size limits.
Correcting Out of Service Violations

To correct an out-of-service violation, the vehicle or driver must address the specific violations listed in the OOS order. This may involve: * Repairing or replacing faulty equipment * Providing documentation to prove compliance with regulations * Completing a required training program * Paying a fine or penalty
📝 Note: It is essential to carefully review the OOS order and follow the instructions provided to ensure that all violations are corrected and the vehicle or driver is deemed safe to return to service.
The Paperwork Involved

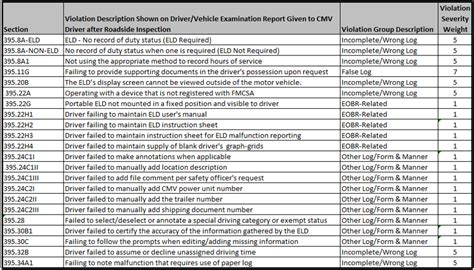
The paperwork involved in an out-of-service violation can be extensive and may include: * The OOS order itself, which will specify the violations and provide instructions on how to correct them * A Vehicle Inspection Report, which will detail the results of the inspection and identify any violations * A Driver Inspection Report, which will detail the results of the driver’s inspection and identify any violations * Correction Certificates, which must be completed and submitted to prove that the violations have been corrected
Appealing an Out of Service Order

If a vehicle or driver receives an OOS order, they may appeal the decision. The appeal process typically involves: * Submitting a written appeal to the DOT or the issuing authority * Providing evidence to support the appeal, such as documentation or witness statements * Participating in a hearing or conference to present the case
Penalties for Non-Compliance

Failure to comply with an OOS order can result in significant penalties, including: * Fines and Penalties: The vehicle or driver may be subject to fines and penalties for non-compliance * Loss of Operating Authority: The vehicle or driver may lose their operating authority, which can result in significant financial losses * Damage to Reputation: Non-compliance can damage the reputation of the vehicle or driver, making it more difficult to attract customers or secure contracts
| Violation | Penalty |
|---|---|
| First-time offense | $1,000 - $5,000 fine |
| Second-time offense | $5,000 - $10,000 fine |
| Third-time offense | $10,000 - $20,000 fine and loss of operating authority |

In summary, DOT out-of-service violation paperwork is a critical aspect of ensuring the safety of commercial vehicles and their operators. By understanding the types of violations, the correction process, and the penalties for non-compliance, vehicle and driver owners can take steps to avoid OOS orders and maintain compliance with federal safety regulations.
To recap, the key points to remember are: * Out-of-service orders are issued when a vehicle or driver is found to be in violation of federal safety regulations * The correction process involves addressing the specific violations listed in the OOS order * Failure to comply with an OOS order can result in significant penalties, including fines, loss of operating authority, and damage to reputation * It is essential to carefully review the OOS order and follow the instructions provided to ensure that all violations are corrected and the vehicle or driver is deemed safe to return to service.
What is an out-of-service order?
+
An out-of-service order is issued by a DOT inspector or law enforcement officer when a vehicle or driver is found to be in violation of federal safety regulations.
How do I correct an out-of-service violation?

+
To correct an out-of-service violation, the vehicle or driver must address the specific violations listed in the OOS order, which may involve repairing or replacing faulty equipment, providing documentation to prove compliance with regulations, or completing a required training program.
What are the penalties for non-compliance with an OOS order?

+
Failure to comply with an OOS order can result in significant penalties, including fines, loss of operating authority, and damage to reputation.