Paperwork
5 Forms For Schedule D

Introduction to Schedule D
When it comes to filing taxes, individuals and businesses often encounter various forms that are crucial for reporting income, deductions, and other financial information. One such form is Schedule D, which is used to report capital gains and losses. In this article, we will delve into the world of Schedule D, exploring its significance, the types of forms associated with it, and providing guidance on how to navigate these forms effectively.
Understanding Schedule D
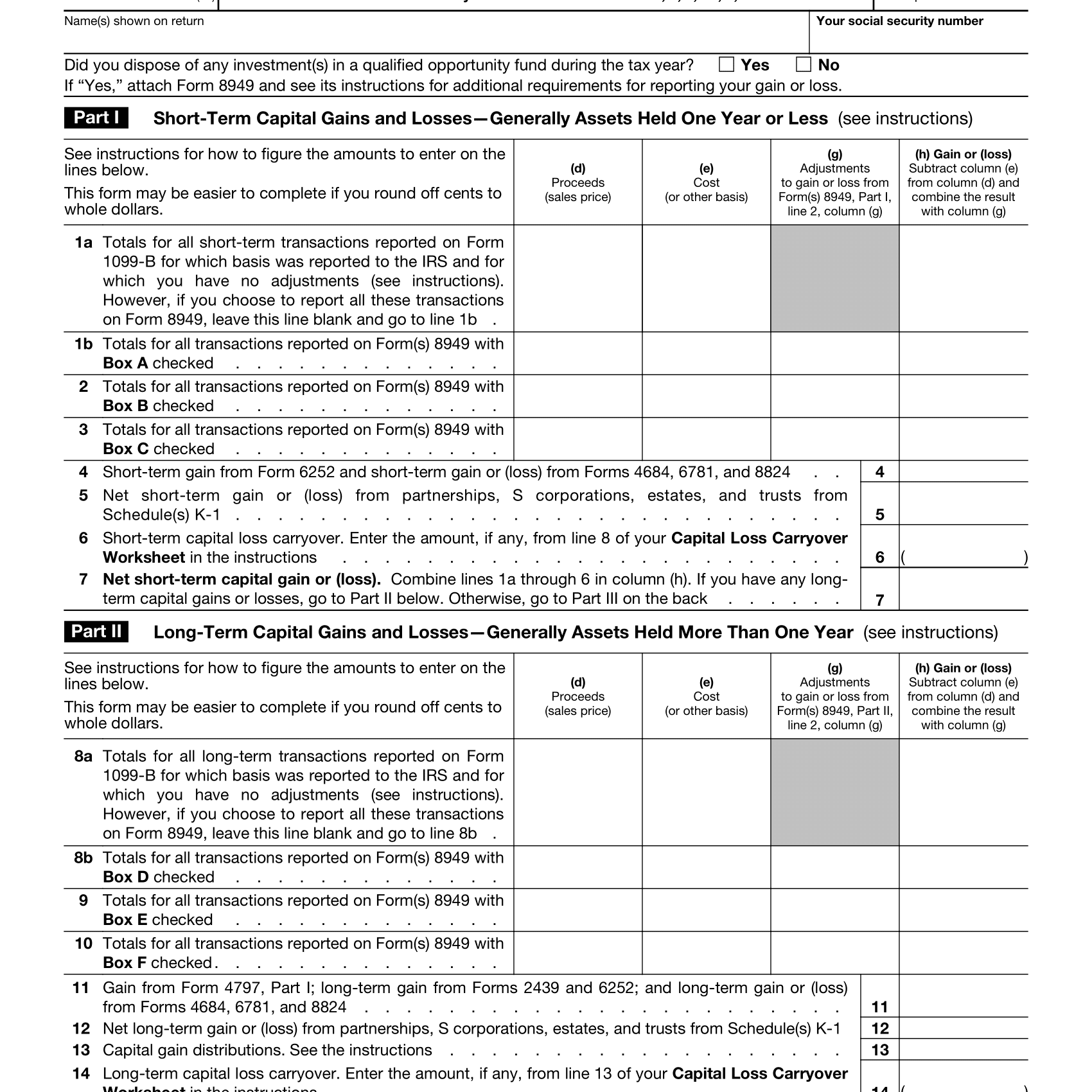
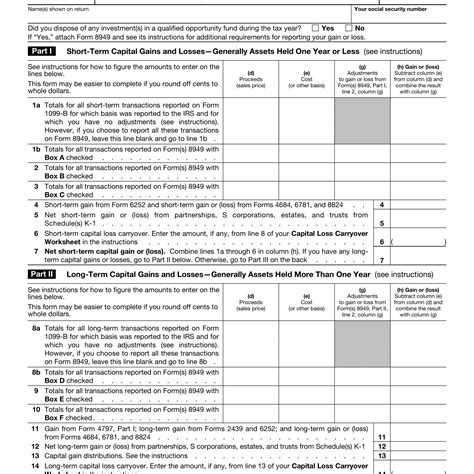
Schedule D is a part of the Form 1040, which is the standard form used for personal income tax returns. It is specifically designed for reporting capital gains and losses from the sale of assets such as stocks, bonds, real estate, and other investment properties. The form is essential for calculating the tax liability arising from these transactions.
5 Forms Associated with Schedule D

There are several forms and schedules that are directly related to Schedule D, each serving a unique purpose in the tax filing process. Here are five key forms:
- Form 1040: As mentioned, this is the standard form for personal income tax returns and includes Schedule D for reporting capital gains and losses.
- Form 8949: This form is used to list all the sales and other dispositions of capital assets. It provides detailed information about each transaction, including the date of sale, gross proceeds, and cost or other basis.
- Form 4797: Although primarily used for reporting sales, exchanges, and other dispositions of business property, it can also be relevant for Schedule D when dealing with the sale of business assets that have capital gain implications.
- Form 8594: The Asset Acquisition Statement is used in conjunction with Form 8593 when assets are being acquired. While not directly a part of the Schedule D filing process, it can be relevant in certain business acquisition scenarios where capital gains are a consideration.
- Form 8283: Noncash Charitable Contributions form is used for reporting charitable donations of property. While not exclusively related to capital gains, donations of appreciated property can result in capital gain issues that need to be addressed on Schedule D.
How to Fill Out These Forms
Filling out the forms associated with Schedule D requires careful attention to detail and an understanding of the tax implications of capital gains and losses. Here are some general steps and considerations:
- Gather all relevant documents: This includes receipts for the purchase and sale of assets, any records of improvements or expenses related to the assets, and information on any charitable donations.
- Determine the basis of the assets: The basis is crucial for calculating capital gains and losses. It generally includes the purchase price plus any costs associated with acquiring the asset.
- Calculate gains and losses: Using the information from Form 8949, calculate the gain or loss from each transaction. This involves subtracting the basis from the gross proceeds.
- Apply the correct tax rates: Capital gains tax rates vary based on the taxpayer’s income tax bracket and the length of time the asset was held. Assets held for more than one year are considered long-term and may qualify for lower tax rates.
📝 Note: It is essential to keep accurate records and to consult with a tax professional if there are any uncertainties about how to report capital gains and losses on Schedule D.
Importance of Accuracy

Accuracy is paramount when filling out Schedule D and associated forms. Errors can lead to delays in processing the tax return, potential audits, and even penalties. Here are a few tips for ensuring accuracy:
- Double-check calculations: Verify that all calculations, especially those related to basis and gains/losses, are correct.
- Match Form 8949 to Schedule D: Ensure that all transactions listed on Form 8949 are accurately reflected on Schedule D.
- Keep detailed records: Maintain comprehensive records of all transactions, including receipts, bank statements, and any other relevant documents.
Conclusion

Navigating the world of Schedule D and its associated forms can be complex, but understanding the purpose and requirements of each form is crucial for accurate tax reporting. By carefully following the instructions, keeping detailed records, and seeking professional advice when needed, individuals and businesses can ensure compliance with tax laws and avoid potential issues. Remember, the key to successful tax filing is attention to detail and a thorough understanding of the tax implications of capital gains and losses.
What is the primary purpose of Schedule D?
+
The primary purpose of Schedule D is to report capital gains and losses from the sale or exchange of capital assets.
Which form is used to list all sales and other dispositions of capital assets?

+
Form 8949 is used to list all sales and other dispositions of capital assets, providing detailed information about each transaction.
Why is accuracy important when filling out Schedule D and associated forms?
+
Accuracy is important because errors can lead to delays, audits, and penalties. It ensures compliance with tax laws and avoids potential issues.



