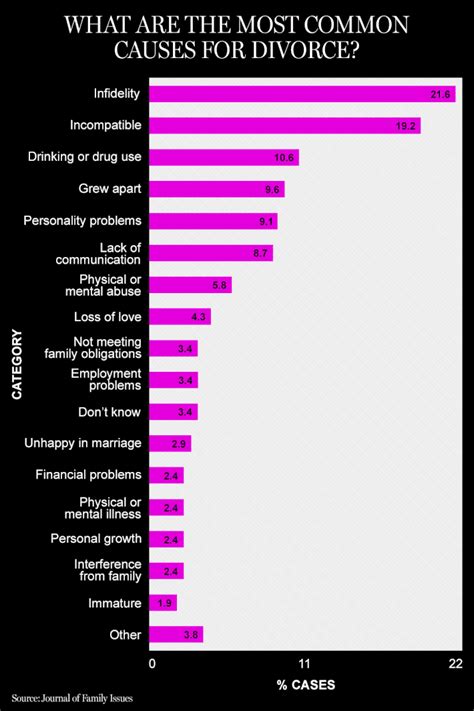
5 Ways File Divorce

Introduction to Divorce Proceedings

When a marriage reaches its end, the process of divorce can be complex and emotionally challenging. Understanding the steps and requirements for filing a divorce is essential for navigating this difficult time. This guide will walk you through the key aspects of divorce proceedings, highlighting the different ways to file for divorce and what to expect during the process.
Understanding Grounds for Divorce

Before diving into the ways to file for divorce, it’s crucial to understand the grounds for divorce. These grounds vary by jurisdiction but commonly include irreconcilable differences, adultery, abandonment, and cruelty. Some jurisdictions allow for no-fault divorce, where neither party is blamed for the end of the marriage. Understanding the specific grounds for divorce in your area is vital for determining the best approach to your divorce.
5 Ways to File for Divorce

There are several ways to initiate divorce proceedings, each with its own set of considerations and implications. Here are five common methods:
- Uncontested Divorce: This is the simplest and least expensive form of divorce. Both parties agree on all issues, including property division, child custody, and spousal support. An uncontested divorce can often be finalized without a court hearing.
- Mediated Divorce: In a mediated divorce, a neutral third-party mediator helps the couple reach an agreement on all issues. This approach can be less adversarial than traditional litigation and may reduce costs.
- Collaborative Divorce: Similar to mediation, collaborative divorce involves both parties working with their attorneys to reach a mutual agreement. However, if the collaborative process fails, both parties must hire new attorneys to proceed with litigation.
- Default Divorce: If one spouse files for divorce and the other fails to respond, the court may grant a default divorce. This method is typically faster but may not be suitable for all situations, especially those involving significant assets or child custody disputes.
- Litigated Divorce: This traditional approach involves each party hiring an attorney to represent their interests in court. A litigated divorce can be lengthy and expensive, especially if the case goes to trial.
Steps to File for Divorce

The process of filing for divorce generally involves the following steps: - Meet the Residency Requirement: Ensure you meet your state’s residency requirements to file for divorce. - Prepare and File the Petition: The petition for divorce, which includes the grounds for divorce and what you are asking the court to do, is prepared and filed with the court. - Serve the Other Party: The other spouse must be formally served with the divorce papers. - Wait for Response: The served spouse has a certain amount of time to respond to the divorce petition. - Negotiate a Settlement: Ideally, the couple will negotiate and agree on the terms of the divorce. - Finalize the Divorce: If an agreement is reached, or if the case goes to trial and a decision is made, the divorce is finalized by the court.
Financial Considerations
Divorce involves significant financial implications, including property division, spousal support, and child support. Understanding how these aspects will be handled is crucial for planning your financial future. It’s often beneficial to consult with a financial advisor in addition to your legal counsel to ensure you’re making informed decisions.
Emotional and Psychological Impact

The emotional and psychological impact of divorce should not be underestimated. It’s a significant life change that can affect not just the couple but also their children, friends, and family. Seeking support from therapists, support groups, or counselors can be invaluable in navigating this challenging time.
💡 Note: The divorce process and its implications can vary significantly depending on your location and individual circumstances. It's essential to consult with local legal professionals to understand the specific requirements and potential outcomes in your case.
In the end, navigating the divorce process requires careful consideration of legal, financial, and emotional factors. By understanding the different ways to file for divorce and the steps involved, individuals can better prepare themselves for this significant life change. Whether through uncontested, mediated, collaborative, default, or litigated means, the goal is to reach a resolution that respects the rights and well-being of all parties involved.
What is the difference between a contested and uncontested divorce?

+
An uncontested divorce occurs when both parties agree on all issues, while a contested divorce involves disputes that require court intervention to resolve.
How long does a divorce typically take?

+
The duration of a divorce can vary significantly depending on the complexity of the case, the jurisdiction, and whether the divorce is contested or uncontested. It can range from a few months for an uncontested divorce to several years for a highly contested case.
Do I need a lawyer to get a divorce?

+
While it’s possible to navigate a simple, uncontested divorce without a lawyer, it’s generally recommended to seek legal counsel. An attorney can protect your rights, ensure you understand the agreements you’re making, and represent you in court if necessary.