5 Ways Delay Social Security

Introduction to Delaying Social Security
Delaying Social Security benefits can be a strategic decision that enhances the financial security of individuals in their retirement years. Understanding the benefits and implications of this choice is crucial for maximizing one’s retirement income. In this article, we will explore the concept of delaying Social Security, its advantages, and provide guidance on how to make informed decisions regarding when to claim benefits.
Understanding Social Security Benefits
Social Security benefits are a vital component of retirement income for many Americans. The age at which one chooses to start receiving these benefits can significantly impact the monthly benefit amount. It’s essential to grasp how Social Security works and how delaying benefits can affect one’s financial situation in retirement.
Why Delay Social Security Benefits?

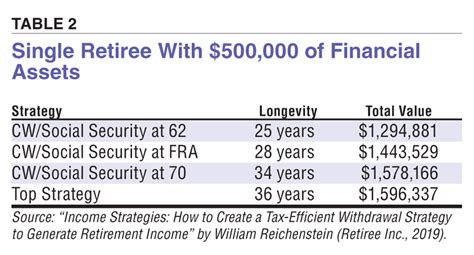
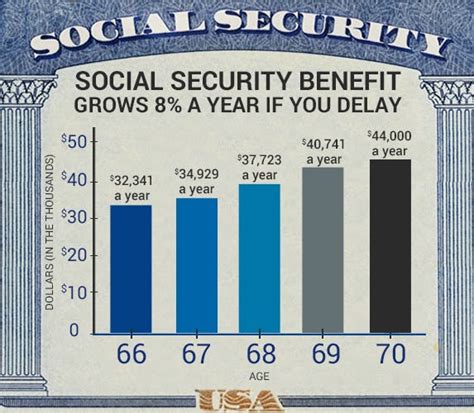
There are several reasons why individuals might consider delaying their Social Security benefits: - Increased Monthly Benefits: For every year one delays receiving Social Security benefits past full retirement age, the benefits increase by a certain percentage until age 70. - Longevity: If an individual expects to live into their 80s or 90s, delaying benefits can result in higher total lifetime benefits, despite the later start. - Survivor Benefits: A higher benefit amount can also mean higher survivor benefits for a spouse.
5 Ways to Delay Social Security
Here are strategies and considerations for delaying Social Security benefits:
- Work Longer: Continuing to work beyond the full retirement age can provide additional income and allow for the delay of Social Security benefits.
- Use Retirement Accounts Strategically: Individuals can use distributions from retirement accounts, such as 401(k)s or IRAs, to support living expenses while delaying Social Security.
- Employ Spousal Benefits Strategically: Married couples can employ strategies like the “restricted application” method (if born before January 2, 1954), which allows one spouse to receive spousal benefits while delaying their own benefits.
- Consider Health and Life Expectancy: Individuals with a family history of longevity or in good health may benefit more from delaying benefits.
- Seek Professional Advice: Financial advisors can help tailor a strategy that considers all sources of retirement income, expenses, and personal goals.
Strategic Planning for Delaying Benefits

Strategic planning is key when considering delaying Social Security benefits. This involves: - Evaluating current and projected income needs - Assessing health and longevity expectations - Understanding the impact on spousal benefits - Reviewing other retirement income sources
| Age | Percentage of Primary Insurance Amount |
|---|---|
| 62 | 70% |
| 65 | 86.7% |
| Full Retirement Age (varies by birth year) | 100% |
| 70 | 124% |

💡 Note: The decision to delay Social Security benefits should be made after careful consideration of personal financial circumstances and goals. It's also important to stay updated with any changes in Social Security rules and regulations.
In essence, delaying Social Security benefits can be a wise financial move for many individuals, offering increased monthly benefits and potentially higher total lifetime benefits. However, this decision should be part of a comprehensive retirement plan, considering all income sources, expenses, and personal expectations for the retirement years.
As individuals navigate the complexities of retirement planning, it’s crucial to weigh the pros and cons of delaying Social Security benefits against other financial priorities and goals. By doing so, retirees can make informed decisions that maximize their financial security and enjoyment in retirement.
What is the full retirement age for Social Security benefits?
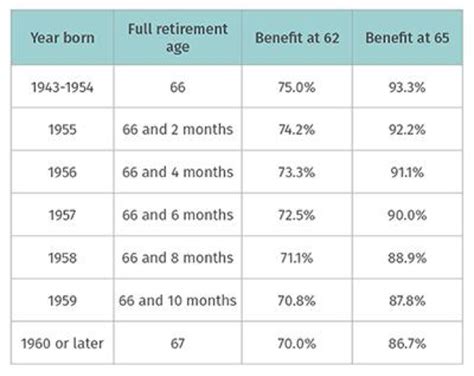
+
The full retirement age for Social Security benefits varies by birth year and ranges from 65 to 67 years old.
How much do Social Security benefits increase for each year delayed past full retirement age?

+
For every year one delays receiving Social Security benefits past full retirement age, the benefits increase by a certain percentage, typically around 8% per year, until age 70.
Can I still work while receiving Social Security benefits?

+
Yes, you can continue working while receiving Social Security benefits, but your benefits may be reduced if you are below full retirement age and your earnings exceed certain thresholds.