Beneficiary Paperwork Requirements

Introduction to Beneficiary Paperwork Requirements

When dealing with beneficiary paperwork, it is essential to understand the various requirements and documents needed to ensure a smooth process. Beneficiary paperwork typically involves designating an individual or entity to receive benefits, such as insurance payouts, retirement funds, or inheritances, in the event of a specific occurrence. The requirements for beneficiary paperwork can vary depending on the type of benefit, the provider, and the jurisdiction. In this blog post, we will delve into the details of beneficiary paperwork requirements, exploring the necessary documents, procedures, and considerations.
Types of Beneficiary Designations

There are several types of beneficiary designations, each with its unique requirements and implications. Some common types include: * Primary beneficiary: The primary beneficiary is the first in line to receive the benefits. * Contingent beneficiary: The contingent beneficiary receives the benefits if the primary beneficiary is unable or unwilling to accept them. * Revocable beneficiary: The revocable beneficiary designation can be changed or revoked by the account owner at any time. * Irrevocable beneficiary: The irrevocable beneficiary designation cannot be changed or revoked without the consent of the beneficiary.
Necessary Documents for Beneficiary Paperwork
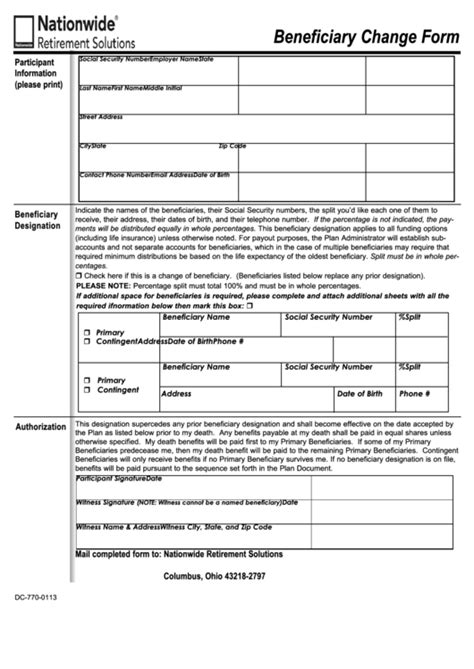
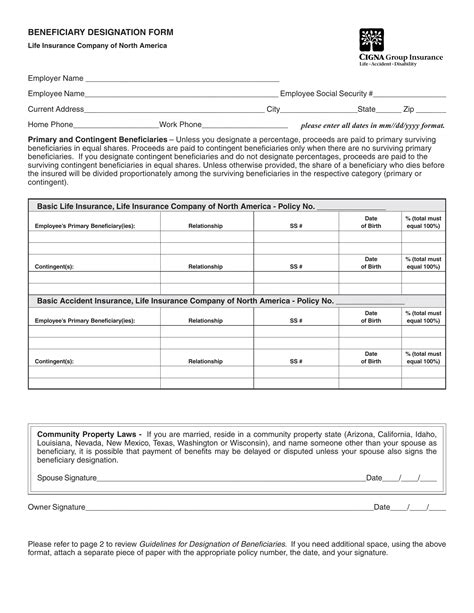
The necessary documents for beneficiary paperwork may vary depending on the type of benefit and the provider. However, some common documents required include: * Beneficiary designation form: This form is used to designate the beneficiary and specify the percentage of benefits they will receive. * Identification documents: The beneficiary may need to provide identification documents, such as a driver’s license or passport, to verify their identity. * Social Security number or tax identification number: The beneficiary’s Social Security number or tax identification number may be required for tax purposes. * Address and contact information: The beneficiary’s address and contact information are necessary to ensure they can be reached in the event of a benefit payout.
Procedures for Beneficiary Paperwork
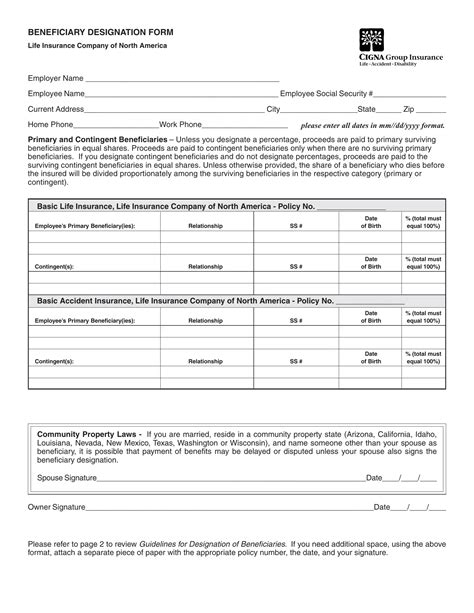
The procedures for beneficiary paperwork can vary depending on the provider and the type of benefit. However, some general steps include: * Obtaining the necessary forms: The account owner or beneficiary can obtain the necessary forms from the provider or download them from their website. * Completing the forms: The forms must be completed accurately and thoroughly, including all required information and signatures. * Submitting the forms: The completed forms must be submitted to the provider, either in person, by mail, or online. * Verifying the beneficiary designation: The provider will verify the beneficiary designation and update their records accordingly.
Considerations for Beneficiary Paperwork

There are several considerations to keep in mind when dealing with beneficiary paperwork, including: * Tax implications: Beneficiary designations can have tax implications, such as income tax or estate tax. * Probate avoidance: Beneficiary designations can help avoid probate, which can be a lengthy and costly process. * Minor or incapacitated beneficiaries: Special considerations must be taken into account when designating a minor or incapacitated individual as a beneficiary. * Updating beneficiary designations: Beneficiary designations should be reviewed and updated regularly to ensure they remain accurate and reflect any changes in circumstances.
💡 Note: It is essential to consult with a qualified professional, such as an attorney or financial advisor, to ensure compliance with all applicable laws and regulations.
Common Mistakes to Avoid

When dealing with beneficiary paperwork, there are several common mistakes to avoid, including: * Incomplete or inaccurate forms: Incomplete or inaccurate forms can delay or even invalidate the beneficiary designation. * Outdated beneficiary designations: Failing to update beneficiary designations can result in benefits being paid to the wrong individual or entity. * Insufficient documentation: Insufficient documentation can lead to delays or disputes in the event of a benefit payout. * Lack of communication: Failing to communicate with the beneficiary and other relevant parties can lead to misunderstandings and conflicts.
| Type of Beneficiary Designation | Description |
|---|---|
| Primary Beneficiary | The primary beneficiary is the first in line to receive the benefits. |
| Contingent Beneficiary | The contingent beneficiary receives the benefits if the primary beneficiary is unable or unwilling to accept them. |
| Revocable Beneficiary | The revocable beneficiary designation can be changed or revoked by the account owner at any time. |
| Irrevocable Beneficiary | The irrevocable beneficiary designation cannot be changed or revoked without the consent of the beneficiary. |

In the end, understanding the requirements and procedures for beneficiary paperwork is crucial to ensuring a smooth and efficient process. By being aware of the necessary documents, procedures, and considerations, individuals can avoid common mistakes and ensure that their beneficiary designations are accurate and up-to-date. This, in turn, can provide peace of mind and help to avoid potential conflicts or disputes in the event of a benefit payout.
What is a beneficiary designation?
+
A beneficiary designation is a formal declaration of who will receive benefits, such as insurance payouts or retirement funds, in the event of a specific occurrence.
What are the different types of beneficiary designations?
+
There are several types of beneficiary designations, including primary beneficiary, contingent beneficiary, revocable beneficiary, and irrevocable beneficiary.
What documents are required for beneficiary paperwork?

+
The necessary documents for beneficiary paperwork may vary depending on the type of benefit and the provider, but common documents include beneficiary designation forms, identification documents, and Social Security numbers or tax identification numbers.