Paperwork
Bankruptcy Records After 10 Years

Introduction to Bankruptcy Records

When an individual or business files for bankruptcy, a public record is created, detailing the bankruptcy proceedings. These records can have a significant impact on a person’s or company’s financial reputation and creditworthiness. One of the most common questions people ask is how long these records remain on their credit report and other public databases. In this article, we will delve into the specifics of bankruptcy records, their duration, and the implications of having such a record.
Understanding Bankruptcy Types

Before discussing the duration of bankruptcy records, it’s essential to understand the different types of bankruptcy filings. The most common types for individuals are Chapter 7 and Chapter 13 bankruptcies. Chapter 7 involves the liquidation of assets to pay off creditors, while Chapter 13 involves a repayment plan. For businesses, Chapter 11 is often used, which allows for the reorganization of the company. Each type of bankruptcy has its own set of rules and implications for the filer.
Duration of Bankruptcy Records

The duration that a bankruptcy record remains on an individual’s credit report is typically 10 years for Chapter 7 bankruptcies and 7 years for Chapter 13 bankruptcies, starting from the date of filing. However, the actual time it takes for the record to be completely removed from all public databases can vary. After the specified period, the credit bureaus are required to remove the bankruptcy from the credit report. Despite this, the record of the bankruptcy filing remains a public record and can still be found through other means, such as court records.
Impact of Bankruptcy Records
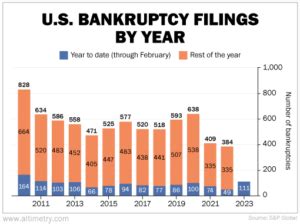
Having a bankruptcy record can significantly impact an individual’s or business’s ability to secure credit, loans, or even apartment rentals. Credit scores can be drastically lowered by a bankruptcy filing, making it harder to get approved for financial services at favorable rates. Employers and landlords may also consider bankruptcy records when making decisions about potential employees or tenants. However, it’s worth noting that rebuilding credit is possible after bankruptcy, and many people successfully recover and improve their financial health over time.
Rebuilding Credit After Bankruptcy
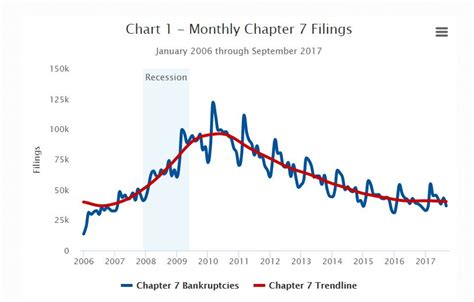
Rebuilding credit after a bankruptcy involves several steps, including: - Securing new credit: This can be through a secured credit card or becoming an authorized user on someone else’s credit account. - Making timely payments: Payment history accounts for a significant portion of credit scores, so making all payments on time is crucial. - Monitoring credit reports: Ensuring that credit reports are accurate and up-to-date can help in quickly identifying and resolving any errors or disputes. - Keeping credit utilization low: High credit utilization can negatively affect credit scores, so it’s essential to keep balances low compared to credit limits.
| Bankruptcy Type | Duration on Credit Report |
|---|---|
| Chapter 7 | 10 years |
| Chapter 13 | 7 years |

📝 Note: The duration of bankruptcy records on credit reports is governed by the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA), which mandates the removal of these records after a specified period.
Conclusion and Future Outlook

In summary, bankruptcy records can have a long-lasting impact on an individual’s or business’s financial standing, remaining on credit reports for 7 to 10 years. However, with careful planning, timely payments, and responsible credit behavior, it’s possible to recover and rebuild credit even after such a significant event. Understanding the implications of bankruptcy and the steps to rebuild credit can empower individuals and businesses to make informed financial decisions and work towards a healthier financial future.
How long does a Chapter 7 bankruptcy stay on my credit report?

+
A Chapter 7 bankruptcy remains on your credit report for 10 years from the date of filing.
Can I rebuild my credit after a bankruptcy?

+
Yes, it’s possible to rebuild your credit after a bankruptcy by securing new credit, making timely payments, monitoring your credit reports, and keeping credit utilization low.
Are bankruptcy records publicly available after they are removed from my credit report?

+
Yes, bankruptcy records remain public and can be accessed through court records even after they are removed from your credit report.