5 Steps NFA Compliance

Understanding NFA Compliance: A 5-Step Guide

The National Futures Association (NFA) is a self-regulatory organization that oversees the derivatives industry, including futures, options, and swaps. NFA compliance is crucial for firms and individuals involved in these markets to avoid penalties, fines, and reputational damage. In this article, we will outline the 5 steps to achieve NFA compliance.
Step 1: Registration and Membership
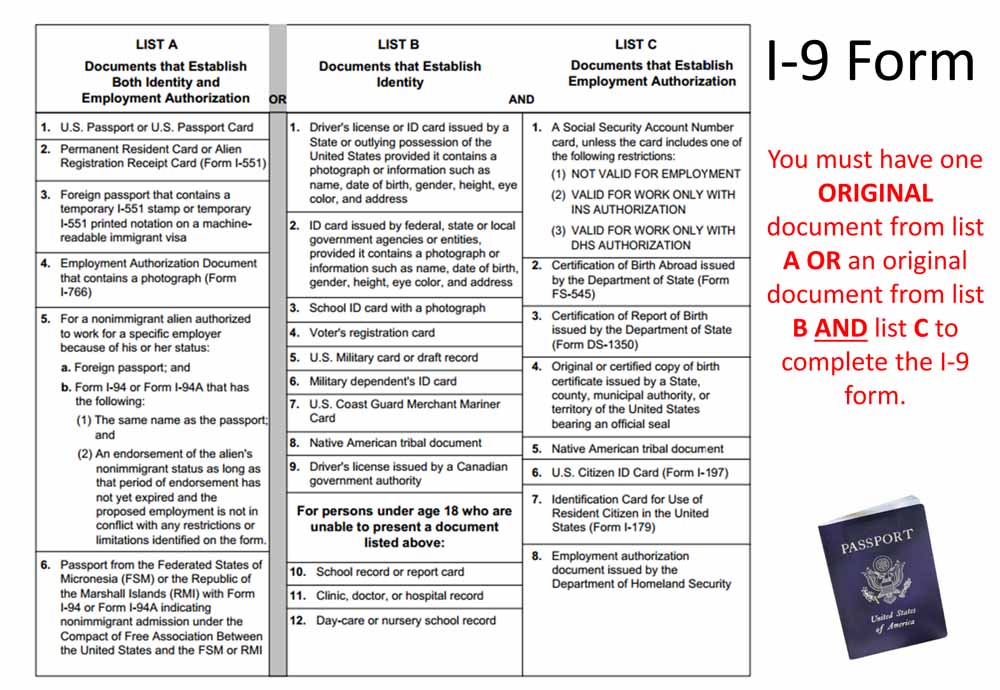
The first step towards NFA compliance is to register and become a member of the NFA. This applies to firms and individuals who intend to engage in futures, options, or swaps transactions. Registration categories include: * Futures Commission Merchant (FCM) * Introducing Broker (IB) * Commodity Trading Advisor (CTA) * Commodity Pool Operator (CPO) * Swap Dealer (SD) * Major Swap Participant (MSP) To register, applicants must submit the required forms and fees, and undergo a background check.
Step 2: Developing Compliance Policies and Procedures

NFA member firms must develop and implement compliance policies and procedures that address various aspects of their business, including: * Risk management * Trading practices * Customer protection * Record-keeping and reporting * Anti-money laundering (AML) and know-your-customer (KYC) These policies and procedures must be written, approved by senior management, and communicated to all employees.
Step 3: Implementing Risk Management and Supervision

Effective risk management and supervision are critical components of NFA compliance. Firms must implement risk management systems that identify, measure, and monitor risks associated with their business activities. This includes: * Market risk * Credit risk * Operational risk * Liquidity risk Firms must also establish a supervision framework that ensures compliance with NFA rules and regulations, including regular audits and reviews.
Step 4: Conducting Regular Audits and Reviews

Regular audits and reviews are essential to ensure ongoing NFA compliance. Firms must conduct: * Annual audits to review their financial statements and compliance with NFA rules * Regular reviews of their compliance policies and procedures, risk management systems, and supervision framework * Transaction monitoring to detect and prevent suspicious activity These audits and reviews must be conducted by independent third-party auditors or internal audit teams.
Step 5: Maintaining Accurate and Complete Records

NFA member firms must maintain accurate and complete records of their business activities, including: * Trading records * Customer account information * Financial statements * Compliance policies and procedures * Audit and review reports These records must be retained for a minimum of five years and be readily available for inspection by NFA staff.
📝 Note: Firms must also ensure that their records are securely stored and protected against unauthorized access or tampering.
| Category | Registration Requirements |
|---|---|
| FCM | Minimum net capital of $1 million |
| IB | Minimum net capital of $45,000 |
| CTA | No minimum net capital requirement |

In summary, achieving NFA compliance requires a thorough understanding of the regulatory requirements and a commitment to implementing effective compliance policies and procedures. By following these 5 steps, firms can ensure that they are meeting their regulatory obligations and minimizing the risk of non-compliance.
What is the purpose of NFA registration?

+
The purpose of NFA registration is to ensure that firms and individuals engaged in futures, options, and swaps transactions are qualified and competent to do so, and to protect customers from fraudulent or abusive practices.
What are the consequences of non-compliance with NFA regulations?

+
The consequences of non-compliance with NFA regulations can include fines, penalties, and reputational damage. In severe cases, non-compliance can result in suspension or revocation of NFA membership.
How often must NFA member firms conduct audits and reviews?

+
NFA member firms must conduct annual audits and regular reviews of their compliance policies and procedures, risk management systems, and supervision framework. The frequency of these audits and reviews may vary depending on the firm's size and complexity.
To recap, NFA compliance is a critical aspect of operating in the derivatives industry. By understanding the 5 steps outlined in this article, firms can ensure that they are meeting their regulatory obligations and minimizing the risk of non-compliance. Effective compliance policies and procedures, risk management, supervision, audits, and record-keeping are all essential components of a comprehensive NFA compliance program.