Freight Forwarder Paperwork Requirements

Introduction to Freight Forwarder Paperwork

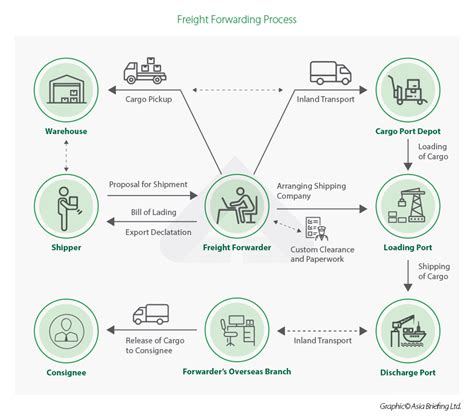
When it comes to international trade, the role of a freight forwarder is crucial. They act as intermediaries between the shipper and the carrier, ensuring that goods are transported efficiently and safely from one point to another. However, to facilitate this process, a significant amount of paperwork is involved. Understanding the various documents required and their purposes can help streamline the shipping process, reduce delays, and avoid potential legal issues.
Key Documents in Freight Forwarding
Several key documents are essential in the freight forwarding process. These include: - Commercial Invoice: This document is prepared by the seller and is used for customs clearance. It includes details such as the type, quantity, and value of the goods being shipped. - Bill of Lading (B/L): The B/L serves as a contract between the shipper and the carrier, detailing the type, quantity, and destination of the goods. It also acts as a receipt for the goods shipped. - Packing List: A detailed list of the goods being shipped, including their weight and dimensions. This document helps in the customs clearance process and in verifying the contents of shipments. - Certificate of Origin: This document certifies the country of origin of the goods being shipped. It is often required for customs clearance and can affect the duty rates applied to the shipment. - Shipper’s Export Declaration (SED): For shipments from the U.S., this form is required for all shipments valued over $2,500 or requiring an export license.
Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) in Freight Forwarding

The advancement in technology has led to the increased use of Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) in freight forwarding. EDI allows for the electronic exchange of business documents between companies, reducing paperwork and increasing efficiency. Key EDI documents in freight forwarding include: - ANSI X12: A set of standards for EDI used in the U.S. and Canada. - EDIFACT: Used internationally, it stands for Electronic Data Interchange for Administration, Commerce, and Transport.
Customs Clearance Documents
For international shipments, customs clearance is a critical step. The freight forwarder must ensure that all necessary documents are in order to avoid delays or fines. Key documents for customs clearance include: - Harmonized System (HS) Codes: These codes are used to classify goods for customs purposes, determining the applicable duty rates. - Customs Declaration Form: This form is used to declare the goods being imported or exported and is submitted to the customs authority.
Compliance with Regulations

Freight forwarders must comply with a myriad of regulations, including those related to security, safety, and environmental protection. For example, the U.S. Transportation Security Administration (TSA) requires freight forwarders to implement certain security measures to prevent the misuse of the transportation system for illegal activities.
Best Practices for Managing Freight Forwarder Paperwork

To efficiently manage the paperwork involved in freight forwarding, several best practices can be adopted: - Digitalization: Leveraging digital platforms to manage and exchange documents can significantly reduce paperwork and increase efficiency. - Training: Ensuring that staff is well-trained in the preparation and handling of freight documents can reduce errors and compliance issues. - Audit and Compliance: Regular audits can help identify and rectify any compliance issues before they become major problems.
📝 Note: Keeping up-to-date with the latest regulations and requirements is crucial for freight forwarders to avoid legal and financial repercussions.
Conclusion and Future Directions

In conclusion, the paperwork requirements in freight forwarding are complex and multifaceted. As the industry continues to evolve with technological advancements and changing regulatory landscapes, freight forwarders must adapt to maintain efficiency and compliance. Embracing digital solutions, ensuring staff training, and staying abreast of regulatory changes will be key to navigating the future of freight forwarding successfully.
To summarize, understanding and efficiently managing the paperwork involved in freight forwarding is essential for smooth international trade operations. By leveraging technology, ensuring compliance, and adopting best practices, freight forwarders can play their part in facilitating global trade while minimizing delays and legal issues.
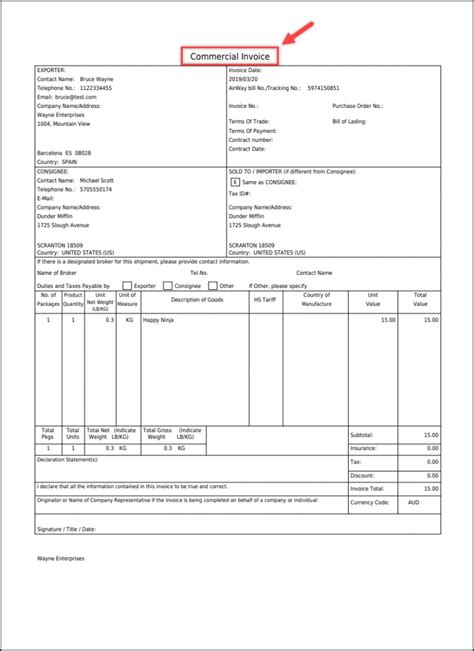
What is the primary purpose of a Commercial Invoice in freight forwarding?
+
The primary purpose of a Commercial Invoice is to provide detailed information about the goods being shipped, including their type, quantity, and value, for customs clearance purposes.
How does Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) benefit freight forwarding operations?

+
EDI benefits freight forwarding operations by reducing paperwork, increasing efficiency, and enhancing accuracy through the electronic exchange of business documents.
What is the significance of Harmonized System (HS) Codes in international shipping?

+
HS Codes are significant because they are used universally to classify goods for customs purposes, determining the applicable duty rates and facilitating international trade.



