Sole Proprietorship Paperwork Requirements

Understanding the Basics of Sole Proprietorship

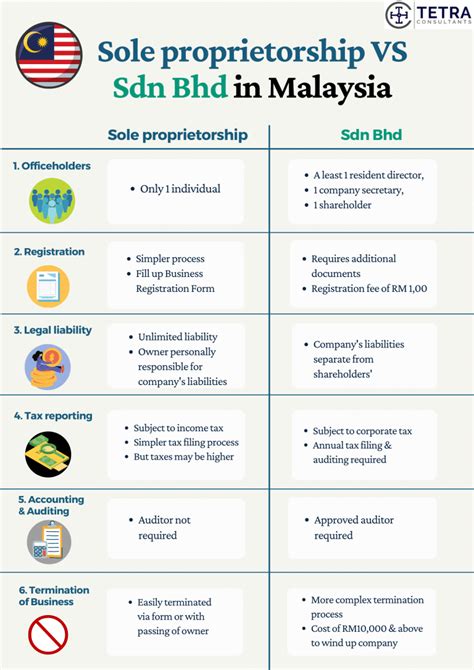
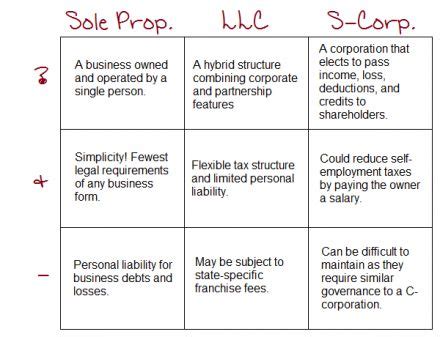
When starting a business, one of the most common and simplest forms of business structure is the sole proprietorship. This type of business is owned and operated by one individual, who is responsible for all aspects of the business, including its debts and liabilities. Given its simplicity, the paperwork requirements for a sole proprietorship are relatively minimal compared to other business structures like partnerships, LLCs, or corporations. However, there are still several key documents and registrations that sole proprietors must complete to operate their businesses legally and efficiently.
Business Name Registration
One of the first steps in establishing a sole proprietorship is choosing a business name. If the business is to be operated under a name that is different from the owner’s legal name, it is necessary to register the business name, also known as a fictitious business name or DBA (Doing Business As). This registration is typically done through the county clerk’s office or the state government, depending on the jurisdiction. The purpose of registering a DBA is to provide public notice of the business’s name and ownership, which can help protect the business’s identity and prevent confusion with other businesses.
Obtaining Licenses and Permits
Sole proprietors must obtain any necessary licenses and permits to operate their businesses. These requirements can vary significantly depending on the type of business, its location, and the products or services it offers. Local business licenses are usually required and can be obtained from the city or county government. Additionally, special permits may be needed for specific activities, such as selling food, providing healthcare services, or operating a home-based business. It is crucial for sole proprietors to research and comply with all licensing and permitting requirements to avoid fines or business closure.
Tax Registrations

Sole proprietors are required to report their business income on their personal tax returns, using Schedule C (Form 1040) to calculate the business’s profit or loss. However, they may also need to register for other tax purposes, such as obtaining an Employer Identification Number (EIN) from the IRS if they have employees or meet certain other criteria. An EIN is used to identify the business for tax purposes and is required for opening a business bank account, hiring employees, and filing certain tax returns.
Employment-Related Paperwork

If a sole proprietorship plans to hire employees, there are additional paperwork requirements. These include: - Obtaining an EIN, as mentioned earlier, for tax withholding and reporting purposes. - Completing Form I-9 to verify the employment eligibility of each employee. - Registering with the state’s unemployment insurance program and potentially with workers’ compensation insurance, depending on the state’s requirements. - Filing quarterly payroll tax returns (Form 941) with the IRS to report wages paid and taxes withheld.
Insurance and Benefits

While not strictly a paperwork requirement, sole proprietors should consider obtaining appropriate insurance coverage for their businesses, such as liability insurance to protect against business-related risks and health insurance for themselves and their employees, if applicable. Additionally, sole proprietors may want to establish retirement plans, such as a SEP-IRA (Simplified Employee Pension Individual Retirement Account), for themselves and their employees.
Record Keeping

Maintaining accurate and detailed business records is essential for sole proprietors. This includes keeping track of income, expenses, receipts, invoices, bank statements, and tax-related documents. Good record keeping helps in preparing tax returns, making business decisions, and demonstrating the business’s financial position if needed for loans or investments. Digital accounting tools and cloud storage services can be useful in organizing and securing business records.
📝 Note: It's crucial for sole proprietors to understand their specific paperwork requirements, as these can vary by location and type of business. Consulting with a legal or financial advisor can provide clarity and ensure compliance with all necessary regulations.
Conclusion and Future Steps
In summary, while the paperwork requirements for a sole proprietorship are less complex than those for other business structures, they are still critical for establishing and operating a business legally and effectively. By understanding and fulfilling these requirements, sole proprietors can focus on growing their businesses, knowing they have a solid foundation. Whether it’s registering a business name, obtaining necessary licenses, or maintaining thorough records, each step is vital in the journey to business success.
What is the primary difference between a sole proprietorship and other business structures?

+
The primary difference is that a sole proprietorship is owned and operated by one individual, who is personally responsible for all aspects of the business, including debts and liabilities.
Do all sole proprietors need to register their business?
+
No, not all sole proprietors need to register their business, especially if they operate under their legal name. However, registering a fictitious business name (DBA) is necessary if the business name differs from the owner’s legal name.
What tax forms do sole proprietors need to file?

+
Sole proprietors report their business income on their personal tax returns using Schedule C (Form 1040) and may need to file additional tax forms, such as quarterly payroll tax returns if they have employees.