5 Covid Vaccine Papers
Introduction to Covid Vaccine Research Papers
The COVID-19 pandemic has been a major global health concern, and the development of effective vaccines has been crucial in controlling the spread of the virus. Several research papers have been published on the COVID-19 vaccines, discussing their safety, efficacy, and distribution. This article will provide an overview of five significant COVID-19 vaccine research papers, highlighting their key findings and contributions to the field.
1. Safety and Efficacy of the BNT162b2 mRNA Covid-19 Vaccine

The first paper, published in the New England Journal of Medicine, discusses the safety and efficacy of the BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 vaccine. The vaccine, developed by Pfizer-BioNTech, was found to have a high efficacy rate of 95% in preventing severe COVID-19. The study also reported that the vaccine was well-tolerated, with most side effects being mild to moderate. The results of this study were instrumental in the vaccine’s emergency use authorization by regulatory agencies worldwide.
2. Efficacy and Safety of the ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 Vaccine

The second paper, published in the Lancet, presents the findings of a phase 3 trial of the ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 vaccine, developed by Oxford-AstraZeneca. The study reported an efficacy rate of 70.4% in preventing symptomatic COVID-19, with a higher efficacy rate of 82.4% when the vaccine was administered with a 12-week interval between doses. The study also highlighted the importance of dosing intervals in achieving optimal vaccine efficacy.
3. Immunogenicity of the mRNA-1273 Vaccine
The third paper, published in the New England Journal of Medicine, investigates the immunogenicity of the mRNA-1273 vaccine, developed by Moderna. The study found that the vaccine induced a strong immune response, with high levels of neutralizing antibodies and T-cell responses. The results of this study demonstrated the vaccine’s potential in providing long-term protection against COVID-19.
4. Comparison of COVID-19 Vaccine Efficacy
The fourth paper, published in the Journal of the American Medical Association, compares the efficacy of different COVID-19 vaccines. The study analyzed data from multiple clinical trials and found that the mRNA-based vaccines (Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna) had higher efficacy rates compared to the adenovirus-based vaccines (Oxford-AstraZeneca and Johnson & Johnson). The study highlights the importance of continued research and development to improve vaccine efficacy and safety.
5. COVID-19 Vaccine Distribution and Access
The fifth paper, published in the BMJ, discusses the challenges and strategies for COVID-19 vaccine distribution and access. The study highlights the need for equitable distribution of vaccines, particularly in low- and middle-income countries. The authors emphasize the importance of global cooperation and coordination to ensure that vaccines are accessible to all populations, regardless of geographical location or socioeconomic status.
💡 Note: The development and distribution of COVID-19 vaccines are ongoing, and new research papers are being published regularly. It is essential to stay up-to-date with the latest findings and guidelines to ensure the most effective use of vaccines in controlling the pandemic.
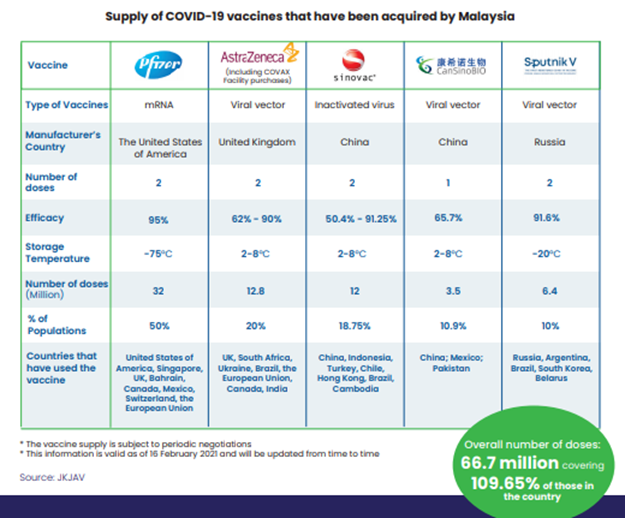
| Vaccine | Efficacy Rate | Safety |
|---|---|---|
| Pfizer-BioNTech (BNT162b2) | 95% | Well-tolerated, mild to moderate side effects |
| Oxford-AstraZeneca (ChAdOx1 nCoV-19) | 70.4% | Generally well-tolerated, some reports of blood clots |
| Moderna (mRNA-1273) | 94.1% | Well-tolerated, mild to moderate side effects |
In summary, the five COVID-19 vaccine research papers discussed in this article provide valuable insights into the safety, efficacy, and distribution of COVID-19 vaccines. The findings of these studies have contributed significantly to our understanding of COVID-19 vaccines and have informed public health policies and guidelines. As the pandemic continues to evolve, it is essential to stay informed about the latest developments in COVID-19 vaccine research and to continue working towards global cooperation and equitable access to vaccines.
What is the difference between mRNA and adenovirus-based COVID-19 vaccines?

+
mRNA-based vaccines, such as Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna, use a piece of genetic material called messenger RNA to instruct cells to produce a specific protein. Adenovirus-based vaccines, such as Oxford-AstraZeneca and Johnson & Johnson, use a weakened adenovirus to deliver genetic material to cells.
How are COVID-19 vaccines distributed and accessed globally?

+
COVID-19 vaccines are distributed and accessed through various channels, including national vaccination programs, international organizations such as the World Health Organization, and global initiatives such as COVAX.
What are the common side effects of COVID-19 vaccines?

+
Common side effects of COVID-19 vaccines include pain, redness, and swelling at the injection site, as well as fatigue, headache, and muscle pain. Most side effects are mild to moderate and resolve on their own within a few days.