5 Bankruptcy Papers

Introduction to Bankruptcy Papers

When an individual or a business is facing financial difficulties and is unable to pay their debts, they may consider filing for bankruptcy. The process of filing for bankruptcy involves submitting various legal documents, known as bankruptcy papers, to the court. These papers provide detailed information about the debtor’s financial situation, debts, assets, and other relevant details. In this article, we will discuss the 5 main bankruptcy papers that are typically required in a bankruptcy filing.
1. Voluntary Petition

The voluntary petition is the first and most important bankruptcy paper. It is a formal request to the court to declare the debtor bankrupt and provide relief from their debts. The petition includes basic information about the debtor, such as their name, address, and social security number. It also requires the debtor to specify the type of bankruptcy they are filing for, such as Chapter 7 or Chapter 13.
2. Schedules
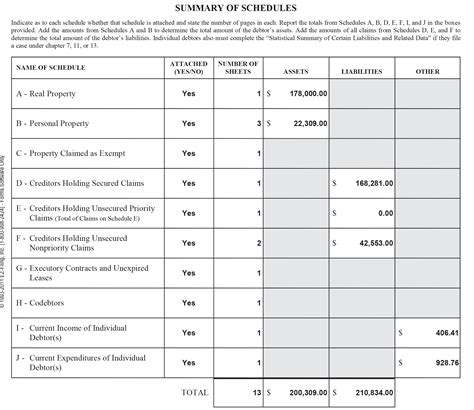
The schedules are a series of forms that provide detailed information about the debtor’s financial situation. They include:
- Schedule A/B: Property - This schedule lists all of the debtor’s assets, including real estate, personal property, and financial assets.
- Schedule C: Exemptions - This schedule lists the assets that the debtor is claiming as exempt from creditors, such as their primary residence or retirement accounts.
- Schedule D: Creditors Who Hold Claims Secured by Property - This schedule lists all of the debtor’s secured creditors, such as mortgage lenders or car loan lenders.
- Schedule E/F: Creditors Who Hold Unsecured Claims - This schedule lists all of the debtor’s unsecured creditors, such as credit card companies or medical providers.
- Schedule G: Executory Contracts and Unexpired Leases - This schedule lists all of the debtor’s executory contracts and unexpired leases, such as apartment leases or business contracts.
- Schedule H: Codebtors - This schedule lists all of the debtor’s codebtors, such as co-signers on loans or credit cards.
3. Statement of Financial Affairs

The statement of financial affairs is a detailed questionnaire that requires the debtor to provide information about their financial transactions and activities over the past few years. It includes questions about:
- Income and expenses
- Assets and liabilities
- Creditors and debtors
- Business dealings and transactions
- Legal proceedings and disputes
4. Means Test

The means test is a calculation that determines whether the debtor is eligible to file for Chapter 7 bankruptcy. It takes into account the debtor’s income, expenses, and debt obligations to determine whether they have enough disposable income to repay their creditors. If the debtor’s income is above the state median, they may be required to file for Chapter 13 bankruptcy instead.
5. Plan (for Chapter 13 Bankruptcy)
If the debtor is filing for Chapter 13 bankruptcy, they must submit a plan that outlines how they intend to repay their creditors over time. The plan must include:
- A list of all creditors and the amount of debt owed to each
- A proposal for how the debtor will repay their debts, including the amount and frequency of payments
- A description of how the debtor will treat each creditor, including whether they will be paid in full or partially
📝 Note: The specific bankruptcy papers required may vary depending on the type of bankruptcy and the debtor's individual circumstances. It is recommended that debtors consult with a qualified bankruptcy attorney to ensure they are completing the correct forms and providing all necessary information.
In summary, the 5 main bankruptcy papers are the voluntary petition, schedules, statement of financial affairs, means test, and plan (for Chapter 13 bankruptcy). These papers provide the court with a comprehensive understanding of the debtor’s financial situation and are used to determine the best course of action for resolving their debts.
What is the purpose of the voluntary petition?
+
The voluntary petition is a formal request to the court to declare the debtor bankrupt and provide relief from their debts.
What is the difference between a secured creditor and an unsecured creditor?

+
A secured creditor has a lien on a specific asset, such as a mortgage on a house, while an unsecured creditor does not have a lien on any asset, such as a credit card company.
What is the means test and how is it used in bankruptcy?

+
The means test is a calculation that determines whether the debtor is eligible to file for Chapter 7 bankruptcy. It takes into account the debtor’s income, expenses, and debt obligations to determine whether they have enough disposable income to repay their creditors.