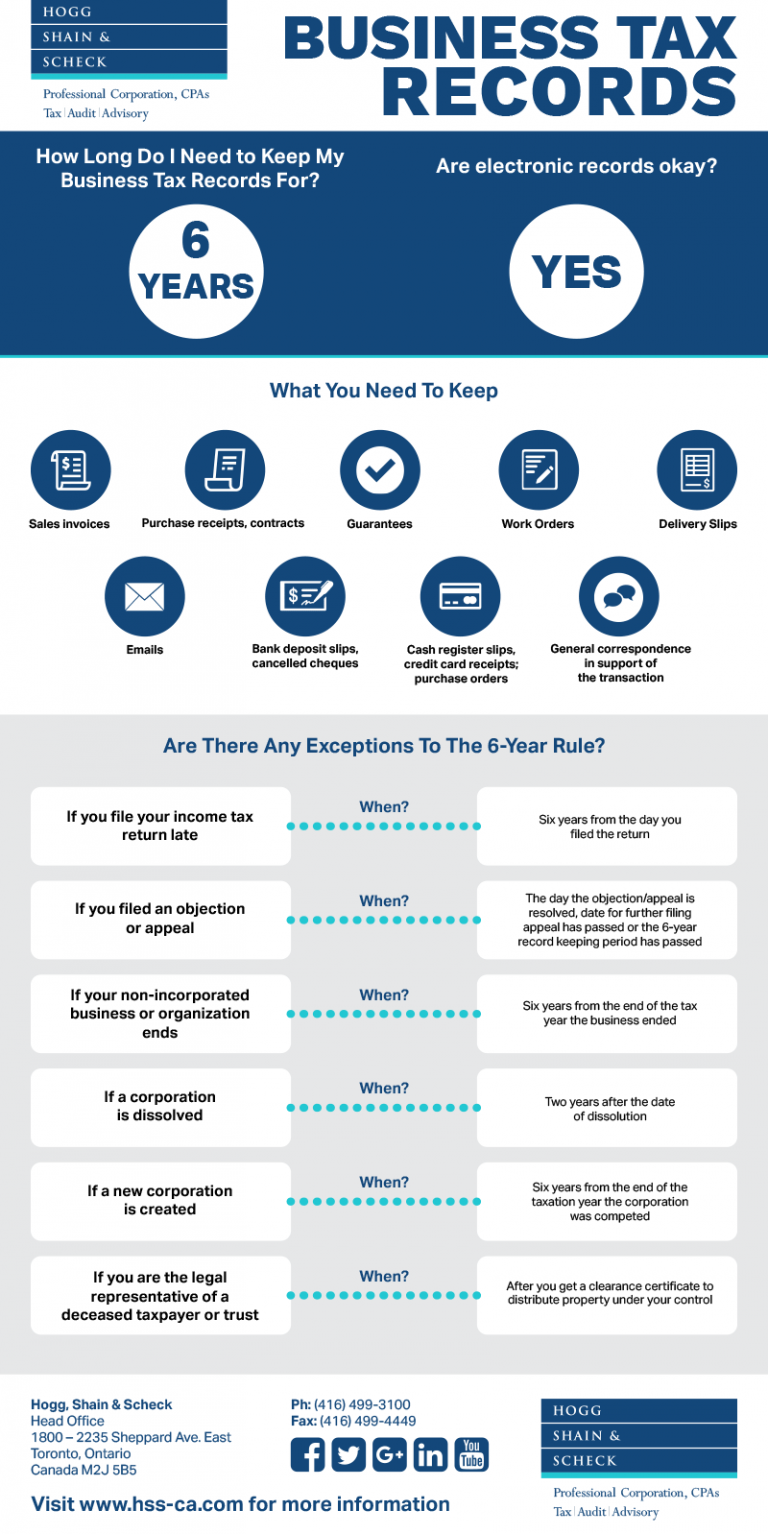
Keep Tax Paperwork For How Long
Introduction to Tax Paperwork

When it comes to tax paperwork, one of the most common questions individuals and businesses have is how long they should keep these documents. The answer can vary depending on the type of tax document and the potential need for it in future audits or financial situations. Proper record-keeping is essential for ensuring compliance with tax laws and for making the tax filing process smoother.
Understanding Tax Document Types

There are various types of tax documents, each with its own recommended retention period. These include: - Income tax returns: These are among the most critical tax documents. They summarize an individual’s or business’s income and the taxes paid on that income. - Supporting documents: These can include W-2 forms, 1099 forms, receipts for business expenses, charitable donations, and medical expenses. - Audit and correspondence records: Any communication with tax authorities, including audit notices and responses, should be kept.
Guidelines for Keeping Tax Records

The general rule of thumb is to keep tax records for as long as they might be needed for tax-related purposes. Here are some specific guidelines: - Income tax returns and supporting documents: Keep these for at least three years from the date the return was filed or due, whichever is later. This is because the IRS generally has three years to initiate an audit. - Employment tax records: For businesses, it’s recommended to keep employment tax records for four years from the date the tax was due or paid, whichever is later. - Records of assets: Keep records of purchases, sales, and improvements to assets (like real estate or investments) for as long as you own the asset plus three years after you dispose of it. - Business records: For self-employed individuals or businesses, keep records of business income and expenses for as long as they may be needed to support tax deductions or credits claimed.
Importance of Digital and Physical Storage

Given the lengthy retention periods, it’s crucial to have a reliable storage system, whether digital or physical. Digital storage solutions can offer convenience, security, and space savings, but it’s essential to ensure that digital files are backed up regularly and stored in a secure location, such as an external hard drive or cloud storage service. For physical documents, a fireproof safe or a secure offsite storage facility can provide protection against loss or damage.
Disposing of Tax Documents

When it’s time to dispose of tax documents, do so in a way that protects sensitive information. Shredding documents or using a secure document destruction service can help prevent identity theft.
| Document Type | Retention Period |
|---|---|
| Income Tax Returns and Supporting Documents | At least 3 years from the filing date or due date |
| Employment Tax Records | 4 years from the due date or payment date |
| Records of Assets | For as long as you own the asset plus 3 years |

📝 Note: Always consult with a tax professional or financial advisor to determine the specific retention requirements for your situation, as individual circumstances can affect how long documents should be kept.
In summary, keeping tax paperwork for the appropriate amount of time is crucial for compliance with tax laws, potential audits, and personal financial record-keeping. Understanding the types of tax documents and their respective retention periods can help individuals and businesses maintain organized and secure records, whether physically or digitally. This practice not only aids in the preparation of future tax returns but also provides a safeguard against potential disputes or inquiries from tax authorities. As tax laws and personal circumstances evolve, it’s essential to review and adjust record-keeping practices accordingly, ensuring that all necessary documents are retained for the required periods.
How long should I keep my income tax returns?

+
You should keep your income tax returns and supporting documents for at least three years from the date the return was filed or due, whichever is later.
What happens if I don’t keep my tax records?

+
Failing to keep tax records can lead to difficulties in audits, potential loss of deductions or credits, and even legal issues if you’re unable to support your tax filings.
Can I store my tax documents digitally?

+
Yes, storing tax documents digitally is a convenient and secure method, as long as you ensure they are backed up regularly and stored in a secure location, such as an external hard drive or a reputable cloud storage service.



