7 Years UK
Introduction to the 7 Years UK Rule

The 7 years UK rule, also known as the 7-year rule, is a guideline used by the UK’s Information Commissioner’s Office (ICO) to determine how long personal data should be kept. This rule is not a law, but rather a best practice for organizations to follow when deciding on data retention periods. The rule suggests that personal data should be kept for no longer than 7 years, unless there is a valid reason to keep it for longer.
Understanding the 7 Years UK Rule

The 7 years UK rule is based on the idea that personal data should only be kept for as long as it is necessary to fulfill the purpose for which it was collected. After 7 years, the data is likely to be out of date and no longer relevant, and keeping it for longer could pose a risk to the individual’s privacy. There are some exceptions to this rule, such as when the data is required for historical research or for statistical purposes.
Exceptions to the 7 Years UK Rule

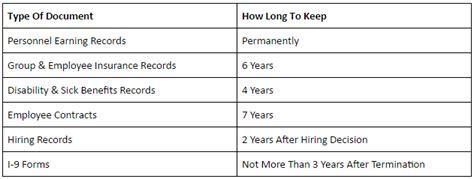
There are some exceptions to the 7 years UK rule, including: * Financial data: Financial data, such as bank statements and tax returns, can be kept for longer than 7 years if it is required for auditing or accounting purposes. * Health data: Health data, such as medical records, can be kept for longer than 7 years if it is required for the provision of medical care or for research purposes. * Employment data: Employment data, such as personnel records, can be kept for longer than 7 years if it is required for the management of employee relationships or for pension purposes.
Benefits of the 7 Years UK Rule

The 7 years UK rule has several benefits, including: * Reduced data storage costs: By limiting the amount of time that personal data is kept, organizations can reduce their data storage costs. * Improved data security: By keeping personal data for a shorter period, organizations can reduce the risk of data breaches and cyber attacks. * Enhanced privacy: By keeping personal data for a shorter period, organizations can enhance the privacy of individuals and reduce the risk of their data being misused.
Implementing the 7 Years UK Rule

To implement the 7 years UK rule, organizations should: * Conduct a data audit: Conduct a data audit to identify what personal data is being collected and stored. * Develop a data retention policy: Develop a data retention policy that outlines how long personal data will be kept and when it will be deleted. * Train staff: Train staff on the importance of data retention and the procedures for deleting personal data.
Challenges of the 7 Years UK Rule

There are some challenges associated with implementing the 7 years UK rule, including: * Legacy data: Legacy data, such as data that was collected before the 7 years UK rule was introduced, can be difficult to manage and delete. * Third-party data: Third-party data, such as data that is collected by third-party providers, can be difficult to manage and delete. * Compliance with other regulations: Compliance with other regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), can be challenging when implementing the 7 years UK rule.
📝 Note: The 7 years UK rule is not a law, but rather a best practice for organizations to follow when deciding on data retention periods.
Best Practices for Data Retention

To ensure that personal data is handled and stored correctly, organizations should follow best practices for data retention, including: * Clearly defining data retention periods: Clearly defining data retention periods and communicating them to staff and customers. * Implementing data deletion procedures: Implementing data deletion procedures to ensure that personal data is deleted when it is no longer required. * Providing training and awareness: Providing training and awareness to staff on the importance of data retention and the procedures for deleting personal data.
| Data Type | Data Retention Period |
|---|---|
| Financial data | Up to 10 years |
| Health data | Up to 20 years |
| Employment data | Up to 10 years |

In summary, the 7 years UK rule is a guideline that suggests personal data should be kept for no longer than 7 years, unless there is a valid reason to keep it for longer. By following this rule and implementing best practices for data retention, organizations can reduce the risk of data breaches and cyber attacks, and enhance the privacy of individuals.
What is the 7 years UK rule?

+
The 7 years UK rule is a guideline that suggests personal data should be kept for no longer than 7 years, unless there is a valid reason to keep it for longer.
What are the benefits of the 7 years UK rule?

+
The benefits of the 7 years UK rule include reduced data storage costs, improved data security, and enhanced privacy.
How can organizations implement the 7 years UK rule?
+
Organizations can implement the 7 years UK rule by conducting a data audit, developing a data retention policy, and training staff on the importance of data retention and the procedures for deleting personal data.