5 Steps

Introduction to a 5-Step Process
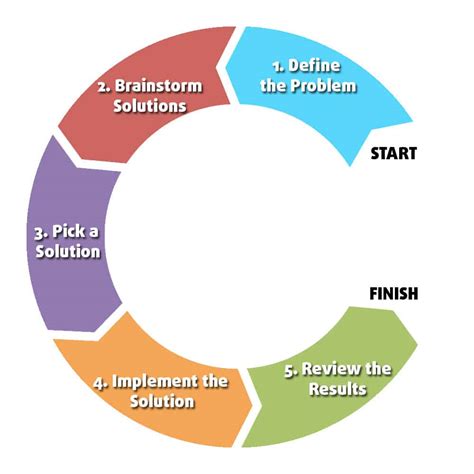
When approaching complex tasks or projects, breaking them down into manageable steps is crucial for success. This methodology applies across various fields, from business and technology to personal development and education. In this article, we will explore a generic 5-step process that can be adapted to numerous situations, highlighting its versatility and effectiveness.
Step 1: Planning and Preparation
The first step in any process is planning and preparation. This stage is critical because it sets the foundation for the entire project. It involves: - Defining objectives: Clearly outlining what needs to be achieved. - Conducting research: Gathering information necessary for the project. - Setting timelines: Creating a schedule to ensure the project is completed on time. - Allocating resources: Determining what resources (financial, human, material) are needed.
📝 Note: A well-planned project is more likely to succeed, as it considers potential challenges and opportunities from the outset.
Step 2: Execution and Implementation

After planning, the next step is execution and implementation. This is where the plan is put into action. Key aspects include: - Team management: Leading and coordinating the team to ensure tasks are completed efficiently. - Task allocation: Assigning specific tasks to team members based on their strengths and expertise. - Progress monitoring: Regularly checking the project’s progress to identify any issues early on.
Step 3: Monitoring and Adjustment
As the project progresses, continuous monitoring is essential to ensure it stays on track. This involves: - Tracking progress: Using metrics and benchmarks to measure how well the project is doing. - Analyzing feedback: Collecting and analyzing feedback from stakeholders to identify areas for improvement. - Making adjustments: Being flexible and making necessary changes to the project plan based on feedback and progress.
| Project Stage | Actions |
|---|---|
| Planning | Define objectives, conduct research, set timelines, allocate resources |
| Execution | Manage team, allocate tasks, monitor progress |
| Monitoring | Track progress, analyze feedback, make adjustments |

Step 4: Evaluation and Reflection
Once the project is nearing completion, it’s time for evaluation and reflection. This step involves: - Evaluating outcomes: Assessing whether the project has met its objectives. - Identifying lessons learned: Reflecting on what went well and what didn’t, to improve future projects. - Documenting the process: Keeping a record of the project from start to finish, including challenges and successes.
Step 5: Conclusion and Review
The final step is conclusion and review, where the project is officially completed, and a final review is conducted. This includes: - Finalizing the project: Ensuring all tasks are completed and deliverables are met. - Reviewing the project: Conducting a thorough review of the project’s success and areas for improvement. - Implementing changes for future projects: Using the lessons learned to improve processes and outcomes in future projects.
As we reflect on the 5-step process outlined, it’s clear that each stage builds upon the last, creating a cohesive and effective method for managing projects. Whether in professional or personal endeavors, this structured approach can enhance productivity, efficiency, and overall success.
What is the importance of planning in a project?
+
Planning is crucial as it sets the foundation for the project, helping to define objectives, allocate resources, and set realistic timelines, thereby increasing the project’s chances of success.
How does continuous monitoring help in project management?
+
Continuous monitoring allows for the early identification of issues, enabling prompt corrective actions. It also helps in tracking progress, ensuring the project stays on schedule and meets its objectives.
What are the benefits of documenting the project process?
+
Documenting the project process provides a valuable resource for future projects, offering insights into what worked well and what didn’t. It also aids in the evaluation and improvement of project management methodologies.



