Rubeola Vaccine Information

Introduction to Rubeola Vaccine
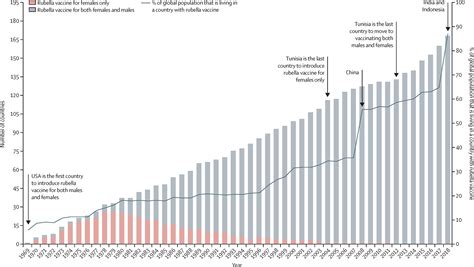
The Rubeola vaccine, also known as the measles vaccine, is a vital component of public health efforts to prevent the spread of measles, a highly contagious and potentially life-threatening disease. Measles, caused by the rubeola virus, can lead to severe complications, especially in young children, and has been responsible for significant morbidity and mortality worldwide. The introduction of the measles vaccine has dramatically reduced the incidence of measles globally, making it a cornerstone of vaccination programs.
How the Rubeola Vaccine Works

The Rubeola vaccine works by introducing a weakened or killed form of the measles virus to the body, which then triggers an immune response. This immune response prepares the body to recognize and fight the measles virus if exposed in the future. The vaccine is typically administered in two doses, with the first dose given to children around 12 to 15 months of age and the second dose around 4 to 6 years of age. The vaccine can also be given to individuals who have not been vaccinated or have not had measles, providing them with protection against the disease.
Types of Rubeola Vaccines
There are two main types of measles vaccines: the monovalent measles vaccine, which protects only against measles, and the combination vaccines, such as MMR (measles, mumps, and rubella) and MMRV (measles, mumps, rubella, and varicella), which protect against multiple diseases. The choice of vaccine depends on the individual’s health status, age, and the prevalence of the diseases in the area.
Benefits of the Rubeola Vaccine
The benefits of the Rubeola vaccine are numerous and well-documented. Some of the key advantages include: * High efficacy: The measles vaccine is highly effective in preventing measles, with two doses providing about 97% protection against the disease. * Herd immunity: Widespread vaccination against measles helps to protect those who are unable to receive the vaccine, such as individuals with weakened immune systems, by reducing the spread of the disease in the community. * Prevention of complications: By preventing measles, the vaccine also reduces the risk of complications associated with the disease, such as encephalitis (inflammation of the brain), pneumonia, and death. * Cost-effectiveness: Vaccination against measles is a cost-effective way to prevent the disease and its associated costs, including medical care and lost productivity.
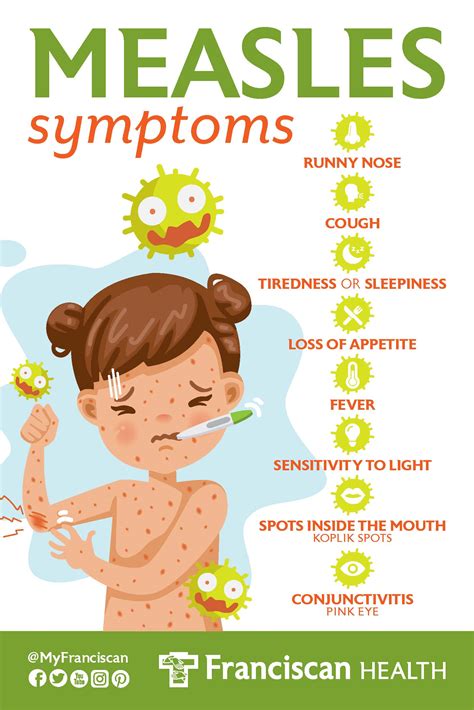
Risks and Side Effects of the Rubeola Vaccine
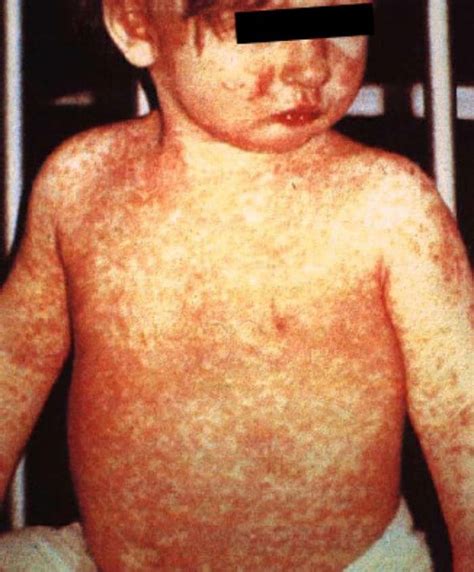
While the Rubeola vaccine is highly effective and safe, there are potential risks and side effects to be aware of. Common side effects include: * Mild fever * Redness and swelling at the injection site * Headache * Fatigue More serious side effects, such as allergic reactions and febrile seizures, are rare but can occur. It is essential to discuss any concerns or questions about the vaccine with a healthcare provider.
Special Considerations for the Rubeola Vaccine
There are certain individuals who may require special consideration when it comes to the Rubeola vaccine, including: * Pregnant women: The vaccine is not recommended for pregnant women, as the risk of transmission of the live, attenuated virus to the fetus is unknown. * Immunocompromised individuals: Those with weakened immune systems, such as individuals with HIV/AIDS or taking immunosuppressive therapy, may not be able to receive the live, attenuated vaccine. * Individuals with allergies: Those with a history of severe allergic reactions to the vaccine or its components may need to take precautions or avoid the vaccine altogether.
💡 Note: It is crucial to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the best approach for individuals with special considerations.
Vaccine Effectiveness and Duration of Protection
The Rubeola vaccine provides long-term protection against measles, with two doses of the vaccine providing protection for at least 20 years. However, immunity can wane over time, and booster doses may be necessary to maintain protection. The effectiveness of the vaccine can also be influenced by factors such as the individual’s immune status and the presence of other health conditions.
Global Efforts to Eradicate Measles

The global effort to eradicate measles is a complex and ongoing process, involving the coordination of healthcare systems, governments, and international organizations. The goal of measles eradication is to eliminate the disease worldwide, and significant progress has been made in reducing the incidence of measles globally. However, challenges remain, including vaccine hesitancy, conflict, and poor healthcare infrastructure, which can hinder efforts to achieve and maintain high vaccination coverage.
| Year | Number of Measles Cases | Vaccination Coverage |
|---|---|---|
| 2000 | 852,937 | 72% |
| 2010 | 215,129 | 85% |
| 2020 | 120,111 | 90% |
Future Directions for Rubeola Vaccine Research
Research on the Rubeola vaccine is ongoing, with a focus on improving the vaccine’s effectiveness, safety, and convenience. Some areas of research include: * New vaccine formulations: Developing new vaccine formulations that can provide better protection and longer-lasting immunity. * Combination vaccines: Exploring the development of combination vaccines that can protect against multiple diseases, such as measles, mumps, rubella, and varicella. * Vaccine delivery systems: Investigating new vaccine delivery systems, such as needle-free injectors and microneedle patches, to improve the convenience and acceptability of vaccination.
In summary, the Rubeola vaccine is a highly effective and safe way to prevent measles, a potentially life-threatening disease. By understanding the benefits, risks, and special considerations of the vaccine, individuals can make informed decisions about their health and contribute to global efforts to eradicate measles. The future of Rubeola vaccine research holds promise for improved vaccine formulations, combination vaccines, and innovative delivery systems, which will help to protect individuals and communities from the threat of measles.
What is the Rubeola vaccine, and how does it work?
+
The Rubeola vaccine, also known as the measles vaccine, works by introducing a weakened or killed form of the measles virus to the body, which triggers an immune response, preparing the body to recognize and fight the measles virus if exposed in the future.
What are the benefits of the Rubeola vaccine?
+
The benefits of the Rubeola vaccine include high efficacy, herd immunity, prevention of complications, and cost-effectiveness. The vaccine provides long-term protection against measles and has been instrumental in reducing the incidence of the disease globally.
What are the risks and side effects of the Rubeola vaccine?
+
Common side effects of the Rubeola vaccine include mild fever, redness and swelling at the injection site, headache, and fatigue. More serious side effects, such as allergic reactions and febrile seizures, are rare but can occur. It is essential to discuss any concerns or questions about the vaccine with a healthcare provider.